(Press-News.org)
Research today doesn't only occur in a lab; indeed, many university researchers extend their work into the community with the goal of inspiring the next generation of scientists and engineers. And some government agencies, like the National Science Foundation, provide the funding to do so. Most recently, Xiayun Zhao, assistant professor of mechanical engineering & materials science at the University of Pittsburgh, completed such outreach at the Carnegie Science Center (CSC).
Zhao and her students hosted the AIM3DP Boot Camp the Carnegie Science Center BNY Mellon Mobile Fab Lab from March 16–17 as part of Zhao's NSF CAREER award for young investigators (Award #: 2238557).
Over the course of two engaging days, Carnegie Science Center’s “Mentors in the Making” students had the opportunity to delve into the world of advanced manufacturing, machine learning, and measurement science under the guidance of Zhao and her dedicated ZIP-AM team (ZXY Intelligent Precision Advanced Manufacturing Laboratory) members: Heyang Zhang, Haolin Zhang, Yousra Bensouda, Yue Zhang, Yiquan Wang, and MD Jahangir Alam at the Swanson School of Engineering. Through a series of interactive sessions and hands-on experiments, the high school students gained invaluable insights into the fundamental principles and applications of these cutting-edge technologies.
“Thanks to the generous support from both the NSF CAREER Program and the CSC, our ZIP-AM research lab has been able to dedicate resources to developing and delivering seminars, demonstrations, and hands-on workshops for the Mentors-in-the-Making," Zhao explained. "Since the onset of our CAREER project, in collaboration with six PhD students, ten undergraduate students from the school’s senior design projects, and four MS students who participated in our ME 2088 class, we have worked tirelessly to create materials and prepare for the 2-day camps.
“Leveraging these combined resources and talents, our team is committed to introducing advanced manufacturing technologies and igniting children's interest in STEM through the AIM3DP (AI & Metrology aided 3D Printing) Camp at the CSC Fab Lab. We are excited about the opportunities ahead and grateful for all the support that has made this initiative possible.”
Supported in part by Zhao’s CAREER award, the event exemplified the collaborative efforts between academia and industry to foster STEM education and workforce development.
“The AIM3DP Boot Camp exemplifies our commitment to inspiring the next generation of engineers and innovators,” said Sanjeev Shroff, Interim U.S. Steel Dean at the Swanson School of Engineering. “Our faculty are proud to partner with organizations like Carnegie Science Center to make STEM education accessible and engaging for students of diverse backgrounds.”
“Through collaborative initiatives like the AIM3DP Boot Camp, we envision a future where our students are equipped with not just knowledge, but also the practical skills and passion needed to drive innovation in advanced manufacturing and beyond. This partnership between academia and industry paves the way for transformative collaborations that will shape the future of STEM education and workforce development,” said Jon Doctorick, Director of STEM Outreach Programs at Carnegie Science Center.
High school students who attended the boot camp are encouraged to explore additional opportunities for further learning and research with Professor Xiayun Zhao, reinforcing their interest and proficiency in advanced manufacturing and general STEM fields including materials, measurement and testing, process control, and data analytics/mining.
"We are thrilled with the positive response and enthusiastic participation we witnessed during the AIM3DP Boot Camp,” Zhao said. “It was inspiring to see young minds actively engaging with the material and expressing interest in pursuing further studies and careers in advanced manufacturing.”
Carnegie Science Center, soon to be the Daniel G. and Carole L. Kamin Science Center, is dedicated to inspiring learning and curiosity by connecting science and technology with everyday life. By making science both relevant and fun, the Science Center’s goal is to increase science literacy in the region and motivate young people to seek careers in science and technology. One of the four Carnegie Museums of Pittsburgh, the Science Center is Pittsburgh’s premier science exploration destination, reaching more than 500,000 people annually through its hands-on exhibits, camps, classes, and off-site education programs.
END
RIVERSIDE, Calif. -- NeuroHIV refers to the effects of HIV infection on the brain or central nervous system and, to some extent, the spinal cord and peripheral nervous system. A collection of diseases, including neuropathy and dementia, neuroHIV can cause problems with memory and thinking and compromise our ability to live a normal life.
Using a mouse model of neuroHIV, a research team led by biomedical scientists at the University of California, Riverside, studied the effects of interferon-β (IFNβ), a small protein involved in cell signaling and integral to the body’s natural defense mechanism against viral infections. The researchers found that higher or lower than ...
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — Public policies blocked many families of Mexican descent living in the U.S. from accessing vital services such as food and mental health care during the COVID-19 pandemic, even though these communities experienced some of the highest infection and mortality rates.
Thirty-eight perinatal women and mothers of young children were interviewed about the challenges they faced during the pandemic and proposed solutions to better meet the needs of their communities during future large-scale crises in a study led by University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign kinesiology and community health ...
The lab of Yongchao C. Ma, PhD, at Stanley Manne Children’s Research Institute at Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago discovered a fundamental biological mechanism that could lead to new treatments for neurological diseases, such as spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) and autism, as well as different cancers. The study was published in the journal Human Molecular Genetics.
Dr. Ma’s team found that chemical modification of RNA (called RNA methylation) regulates mitochondrial ...
Despite their ancient ages, some stars orbiting the Milky Way’s central supermassive black hole appear deceptively youthful. But unlike humans, who might appear rejuvenated from a fresh round of collagen injections, these stars look young for a much darker reason.
They ate their neighbors.
This is just one of the more peculiar findings from new Northwestern University research. Using a new model, astrophysicists traced the violent journeys of 1,000 simulated stars orbiting our galaxy’s central supermassive black hole, Sagittarius A* (Sgr A*).
So densely packed with stars, the region commonly experiences brutal stellar collisions. ...
A team of researchers has uncovered alarming trends in the first range-wide genetic study of an endangered bee species. The study, led by Colorado State University and published in the Journal of Insect Science, will inform conservation and recovery efforts for the rusty-patched bumblebee – a species that was once common in the United States but has declined from about 90% of its historic range.
The rusty-patched bumblebee was the first bee species to be federally listed as endangered in 2017 through the U.S. Endangered Species Act. Its numbers dropped rapidly starting in the late 1990s, likely due to a combination of pesticides, ...
ST. LOUIS, MO., April 4, 2024 — Acidic soil caused by changing climate patterns threatens agriculture sustainability across the globe. But the problem goes far beyond rising temperatures. One major cause for concern is more acidic soil, a product of increasing rainfall. Acidic soils with low pH are widespread globally and common in tropical and sub-tropical regions, where food security is a serious challenge. Climate change has exacerbated the problem. Acidic soil can result in aluminum toxicity, putting further stress on global agriculture. A new collaborative research team from the US and Brazil received a $2 ...
NEW YORK – April 4, 2024 – The Cardiovascular Research Foundation® (CRF®) is excited to introduce New York Valves: The Structural Heart Summit, the expanded next iteration of our renowned annual Transcatheter Valve Therapy (TVT®) conference. Taking place June 5-7, 2024, at the Jacob K. Javits Convention Center, North in New York City, the new summit will be a world-class educational experience in the field of structural heart interventions.
“New York Valves 2024 signifies an important milestone for our organization,” said Juan F. Granada, MD, President and Chief Executive Officer of CRF® and New York ...
Mixing livestock and crops, integrating flower strips and trees, water and soil conservation and much more: Massive new global study led by the University of Copenhagen and University of Hohenheim, has examined the effects of diversified agriculture. The conclusion is abundantly clear – positive effects increase with every measure, while negative effects are hard to find.
Laura Vang Rasmussen of the University of Copenhagen can finally wipe the sweat from her brow. For the last four years, she has served as the link between 58 researchers on five continents and as lead author of a major agricultural study which gathered ...
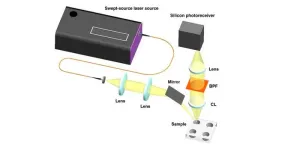
In 1928, Indian physicist Sir C. V. Raman and his colleague K. S. Krishnan discovered that when light interacts with matter, parts of the scattered light undergo changes in energy due to interaction with molecular vibrations, resulting in what is known as Raman scattering. The discovery laid the foundation for Raman spectroscopy, a technique that takes advantage of these energy changes to create a unique fingerprint of the molecular structure of the material.
Currently, dispersive Raman spectroscopy ...
Argininosuccinate lyase deficiency (ASLD), also known as argininosuccinic aciduria, is a disease that has been enriched in the Finnish genetic heritage. In this severe metabolic disease, the body does not process proteins normally, instead resulting in a very dangerous accumulation of argininosuccinic acid and ammonia. Excess ammonia causes disturbances of consciousness, coma and even death.
In Finland, infants are screened for ASLD to determine the disease risk before symptoms develop. The treatment is an extremely ...