UM Researcher writes about a key issue for the US 2024 elections: Air pollution exposures ought to be of significant interest for US voters
2024-04-05
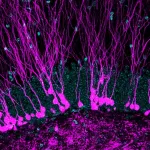
(Press-News.org) MISSOULA – An opinion paper published by University of Montana professor Lilian Calderón-Garcidueñas MD, PhD identifies air pollution risk exposures and the development of Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases, frontotemporal lobar degeneration (FTLD) and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) in exposed populations.
Calderón-Garcidueñas coauthors, Dr. Alberto Ayala and Dr. Partha Mukherjee discussed US citizens are not fully aware of the harmful brain impact of exposures to ubiquitous anthropogenic combustion emissions and friction-derived nanoparticles, industrial nanoplastics, wildfires and smoke plumes of soot. The researchers have significant experience with the development of pediatric and early adulthood hallmarks of Alzheimer, Parkinson, FTLD and ALS and associations with neuropsychiatric and neurodevelopmental disorders in populations exposed to concentrations of fine particulate matter PM 2.5 above the current 9μg/ m3 USEPA annual standard.
Although the USEPA has a new 9.0 μg/m3 PM2.5 annual standard, these measurements are still above the World Health Organization (WHO)guidelines of 5 μg/m3 and strikingly, significant air pollution exposures disparities will persist and increase, affecting mostly people in lower income brackets, with reduced access to health care, and high occupational exposure risks.
Dr. Calderón-Garcidueñas comments that with the new PM 2.5 standard de facto, millions of US residents will be living in PM2.5 non-attainment regions and in addition, society must deal with the tinniest particles, so called ultrafine particulate matter UFPM and industrial nanoparticles NPs exposures because their ability to cross all biological barriers, reaching the brain and other critical organs (i.e., the heart). This fraction of PM2.5 has strong neurodegenerative/neurobehavioral/brain structural associations. The early development and progression of Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases and FTLD and ALS already killing thousands of Americans - should raise red flags about the need to understand this serious potential UFPM and NPs risk to urban and rural US populations.
Dr. Calderón-Garcidueñas who trained at the EPA in Chapel Hill, North Carolina while a Toxicology doctoral UNC student stated, “We all should be aware that under lifetime exposures to PM2.5 above safe thresholds, the relentless development of Alzheimer, Parkinson and TDP-43 pathology could be in place and emphasized that wildfires are particularly worrisome in terms of exposure of PM2.5 to thousands of citizens. From 2013 to 2022, an average of 7.2 million acres have burned annually and fires burned 2,633,636 acres in 2023. Unfortunately, humans were responsible for 89% of wildfires in the period 2018-2022.”
The authors concluded that control of UFPM/NPs in ambient air, their atmospheric transformations, their industrial sources, wildfire prevention, education, and environmental management are critical.US voters would like to be assured that a significant part of the 13 million projected AD cases for 2050, the current 1 million PD, the 60,000 FTLD and the 18,000 ALS cases could be avoided, and future generations be protected if our pollution reduction efforts are strengthened and accelerated.
A full report of Calderon’s research is available through the Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-04-05
Diagnosing infectious conditions can be challenging. Diagnosis is especially challenging for uncommon and emerging infectious diseases for which there’s limited clinical experience. Nevertheless, successfully identifying patients with infectious diseases, especially communicable ones, is critical, so patients can be isolated to reduce disease spread.
To address this challenge, investigators from Massachusetts General Hospital, a founding member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare system, recently developed and validated a computer program that can be incorporated into electronic medical record systems to help clinicians diagnose mpox (formerly known as monkeypox).
The research ...
2024-04-05
WMG at the University of Warwick has boosted the West Midlands economy by £450 million – with every £1 invested into WMG’s small and medium enterprise (SME) programmes, around £22 has returned to the local economy.
Celebrating 20 years of tailored business support, WMG has delivered manufacturing expertise to 15,000 SMEs in the Midlands. It has supported the creation of more than 13,000 jobs, 350 new businesses and 355 internships over the last two decades.
WMG has delivered critical projects to SMEs to help them succeed in digitalisation, business change and product design. A key ongoing project is helping SMEs mange the energy crisis with a specialised ...
2024-04-05
The Department of Defense awarded a little more than $1.9 million to a multidisciplinary team of researchers at the University of Arkansas and University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences to develop a wearable device that will assist with the early detection and monitoring of internal and external bleeding. The grant comes as part of the Department of Defense’s prestigious Congressionally Directed Medical Research Programs.
Hemorrhagic shock is currently the leading cause of preventable death in casualty care settings. Existing methods often fail to detect blood loss until the onset of shock, which can be too late for some patients. This makes early detection and management ...
2024-04-05
Scientists at St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital are preparing to demonstrate their expertise and foster collaborations at the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) annual meeting. It will be held April 5-10, 2024 in San Diego, California.
Each year, members of the cancer research community including scientists, clinicians, healthcare professionals, cancer survivors, patients and advocates attend AACR’s annual meeting. It provides an opportunity for St. Jude researchers to share their research findings ...
2024-04-05
Nerve cells (neurons) are amongst the most complex cell types in our body. They achieve this complexity during development by extending ramified branches called dendrites and axons and establishing thousands of synapses to form intricate networks. The production of most neurons is confined to embryonic development, yet few brain regions are exceptionally endowed with neurogenesis throughout adulthood. It is unclear how neurons born in these regions successfully mature and remain competitive to exert their functions within a fully formed organ. However, understanding these processes holds great potential for brain repair approaches during disease.
A team ...
2024-04-05
The results of a pioneering study support the safety of the bioimplants called PeriCord, made from stem cells of the umbilical cord and pericardium from a tissue donor, which aid in the regeneration and revascularisation of the affected area.
The study has monitored 7 interventions of this pioneering tissue engineering surgery over three years, noting excellent biocompatibility and no rejection in patients.
The therapy has been developed by the research group ICREC (Heart Failure and Cardiac Regeneration) at Germans Trias i Pujol Research ...
2024-04-05
About The Study: Supply chain issues associated with drug shortages increased at the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic according to the results of this national cross-sectional study. Ongoing policy work is needed to protect U.S. drug supplies from future shocks and to prioritize clinically valuable drugs at greatest shortage risk.
Authors: Katie J. Suda, Pharm.D., M.S., of the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For ...
2024-04-05
Researchers at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center showed that altering the sequence of breast cancer treatment to administer radiation before mastectomy allowed for concurrent breast reconstruction surgery, which reduced the number of operations required, minimized treatment delays and improved patient satisfaction.
The Phase II trial results, published today in JAMA Network Open, evaluated 49 patients who received radiation therapy followed by mastectomy with immediate breast reconstruction. There were no complete flap ...
2024-04-05
A research group centered at the University of California San Diego School of Medicine has drilled deep into a dataset of over 3 million individuals compiled by the direct-to-consumer genetics company 23andMe, Inc., and found intriguing connections between genetic factors influencing alcohol consumption and their relationship with other disorders.
The study was recently published in the Lancet eBioMedicine.
Sandra Sanchez-Roige, Ph.D., corresponding author and associate professor at UC San Diego School of Medicine Department of Psychiatry, explained that the study used genetic data to broadly classify individuals as being European, Latin American ...
2024-04-05
The CHEOPS space telescope, whose scientific operations centre is based at the University of Geneva (UNIGE), is providing new information on the mysterious exoplanet WASP-76b. This ultra-hot giant is characterised by an asymmetry between the amount of light observed on its eastern terminator - the fictitious line that separates its night side from its day side - and that observed on its western terminator. This peculiarity is thought to be due to a ‘‘glory’’, a luminous phenomenon similar to a rainbow, which occurs if the light from the star - the ‘‘sun’’ around which the ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] UM Researcher writes about a key issue for the US 2024 elections: Air pollution exposures ought to be of significant interest for US voters