Proof-of-principle demonstration of 3-D magnetic recording
Possibility of ultra-high density hard disk drives with areal densities exceeding 10 Tbit/in² using multi-level magnetic recording
2024-04-08
(Press-News.org) 1. Research groups from NIMS, Seagate Technology, and Tohoku University have made a breakthrough in the field of hard disk drives (HDD) by demonstrating the feasibility of multi-level recording using a three-dimensional magnetic recording medium to store digital information. The research groups have shown that this technology can be used to increase the storage capacity of HDDs, which could lead to more efficient and cost-effective data storage solutions in the future.
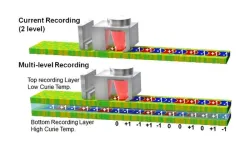
2. Data centers are increasingly storing vast amounts of data on hard disk drives (HDDs) that use perpendicular magnetic recording (PMR) to store information at areal densities of around 1.5 Tbit/in². However, to transition to higher areal densities, a high anisotropy magnetic recording medium consisting of FePt grains combined with heat-assisted laser writing is required. This method, known as heat-assisted magnetic recording (HAMR), is capable of sustaining areal recording densities of up to 10 Tbit/in². Furthermore, densities of larger than 10 Tbit/in² are possible based on a new principle demonstrated by storing multiple recording levels of 3 or 4 compared with the binary level used in HDD technology.
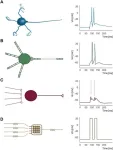
3. In this study, we succeeded in arranging the FePt recording layers three dimensionally, by fabricating lattice-matched, FePt/Ru/FePt multilayer films, with Ru as a spacer layer. Measurements of the magnetization show the two FePt layers have different Curie temperatures. This means that three-dimensional recording becomes possible by adjusting the laser power when writing. In addition, we have demonstrated the principle of 3D recording through recording simulations, using a media model that mimics the microstructure and magnetic properties of the fabricated media.
4. The three-dimensional magnetic recording method can increase recording capacity by stacking recording layers in three dimensions. This means that more digital information can be stored with fewer HDDs, leading to energy savings for data centers. In the future, we plan to develop processes to reduce the size of FePt grains, to improve the orientation and magnetic anisotropy, and to stack more FePt layers to realize a media structure suitable for practical use as a high-density HDD.
***
5. This research was conducted by Dr. P. Tozman, Distinguished Researcher, and Dr. Yukiko Takahashi, Group Leader of NIMS Center for Magnetic and Spintronics Materials Research, Dr. T.Y. Chang, Researcher at Seagate Technology, and Prof. S.J. Greaves of Tohoku University. This work was supported by Japan Science and Technology Agency (JST) Strategic Basic Research Programs (CREST) "Integrated Devices and Systems Utilizing Information Carriers" JPMJCR22C3.
6. This research was published in Acta Materialia on March 24, 2024.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-04-08
While 3D printing has exploded in popularity, many of the plastic materials these printers use to create objects cannot be easily recycled. While new sustainable materials are emerging for use in 3D printing, they remain difficult to adopt because 3D printer settings need to be adjusted for each material, a process generally done by hand.
To print a new material from scratch, one must typically set up to 100 parameters in software that controls how the printer will extrude the material as it fabricates an object. Commonly ...
2024-04-08
The biological brain, especially the human brain, is a desirable computing system that consumes little energy and runs at high efficiency. To build a computing system just as good, many neuromorphic scientists focus on designing hardware components intended to mimic the elusive learning mechanism of the brain. Recently, a research team has approached the goal from a different angle, focusing on measuring information transfer instead. Their method went through biological and simulation experiments and then proved effective in an electronic neuromorphic system. It was published ...
2024-04-08
Philadelphia, April 8, 2024 – Researchers from Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) found that teens and young adults with mood disorders, such as depression and bipolar disorder, were 30% less likely to obtain their driver’s license than peers without such disorders. Additionally, those youths with mood disorders experienced a slightly elevated risk of crashing. These findings suggest that these teens and young adults could benefit from guidance on obtaining licensure and accessing training to avoid crashes when they are newly licensed.
The findings were published online today ...
2024-04-08
NEW YORK, NY (April 8, 2024)--A new type of investigational therapeutic in development for pancreatic cancer has shown unprecedented tumor-fighting abilities in preclinical models of the disease, suggesting it has the potential to offer novel treatment options for nearly all pancreatic tumors, a comprehensive study has found.
The inhibitors in this new class of oral medications, being developed by Revolution Medicines Inc., target the oncogenic or active cancer-causing form of RAS proteins (such as KRAS, NRAS, and HRAS). These RAS “oncoproteins” drive up to a third of all human cancers. The research ...
2024-04-08
The introduction of a policy protecting parental leave benefits in Sweden in 1980 had unintended consequences on child health. The policy led to an increase in premature birth rates. This is shown by a study from researchers at Stockholm University, published in JAMA Pediatrics.
The Swedish so-called speed premium policy was introduced in 1980 in order to protect couples’ level of income-based parental leave benefits when they had children in quick succession. The new study from Stockholm University evaluates the health consequences of the policy. The researchers conclude that by ...
2024-04-08
IMMUNE KEY TO CHRONIC VIRAL INFECTIONS DISCOVERED
Australian researchers have discovered a previously unknown rogue immune cell that can cause poor antibody responses in chronic viral infections. The finding, published today (9 April) in the journal, Immunity, may lead to earlier intervention and possibly prevention of some types of viral infections such as HIV or hepatitis.
One of the remaining mysteries of the human immune system is why a certain cell, called a B cell, which retains a memory for past infections – ensuring we fight off diseases we have experienced before – often only has a weak capacity to protect us from persistent infections.
Researchers ...
2024-04-08
Per-and poly-fluoroalkyl substances – commonly known as PFAS – are a group of over 14,000 human-made chemicals that have been popular since the 1950s for their diverse skills in resisting heat, water, grease and stains.
They’ve been commonly found in household products like non-stick frypans, clothing, cosmetics, insecticides, and food packaging, as well as specialty industry products, like firefighting foam.
But despite their broad skillset, the chemicals have a dark side: they’re known as ‘forever chemicals’ as once they’re in the environment – ...
2024-04-08
About 4.5 billion years ago, a small planet smashed into the young Earth, flinging molten rock into space. Slowly, the debris coalesced, cooled and solidified, forming our moon. This scenario of how the Earth's moon came to be is the one largely agreed upon by most scientists. But the details of how exactly that happened are "more of a choose-your-own adventure novel," according to researchers in the University of Arizona Lunar and Planetary Laboratory who published a paper in Nature Geoscience. The findings offer important insights into the evolution ...
2024-04-08
Using artificial intelligence, satellite observations, and climate model projections, a team of researchers from Switzerland and Belgium calculate that for every tenth of a degree of increase in global air temperature, an average of nearly 9,000 meteorites disappear from the surface of the ice sheet. This loss has major implications, as meteorites are unique samples of extraterrestrial bodies that provide insights into the origin of life on Earth and the formation of the Moon.
Disappearing at an alarming rate
By 2050, about a quarter of the estimated of 300,000 - 800,000 meteorites in Antarctica will be lost ...
2024-04-08
Through a large-scale analysis, researchers at the Netherlands Institute for Neuroscience have uncovered the ways in which consensual touch can benefit a person’s physical and mental wellbeing.
You might recognize the comforting feeling when someone offers you a hug at the end of a stressful day or strokes your shoulder when you’re feeling down. But the question remains: can touch really help you feel better, and does it matter who it’s from or how they touch you? To explore these questions, researchers from the Social Brain Lab at the Netherlands Institute for Neuroscience and the University Hospital ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Proof-of-principle demonstration of 3-D magnetic recording
Possibility of ultra-high density hard disk drives with areal densities exceeding 10 Tbit/in² using multi-level magnetic recording