(Press-News.org)
Embargoed until 8:30 a.m. Wednesday, 10 April, 2024, Central European Summer Time
10 April, 2024, Prague, Czech Republic—Amid the persistent threat of missiles from the air and an array of hazardous terrestrial obstacles, the Heart Institute of the Ministry of Health in Kyiv has continued to provide heart transplants to Ukraine’s citizens, performing 40 of the life-saving procedures since Russia’s full-scale invasion of the country in 2022. The Heart Institute’s Director Borys Todurov, MD, PhD, reported on his team’s extraordinary efforts today at the Annual Meeting and Scientific Sessions of the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation (ISHLT) in Prague.
The Heart Institute, which served as a bomb shelter early in the war, purchased its own generators and autonomous water supply to continue operating during blackouts. When it became impossible to use helicopters to transport donor organs, Dr. Todurov and his eight-person heart transplantation team had to pivot.
“Without the use of a helicopter, our organ travel time was too long. So we removed some seats from the back of a Mercedes bus and began taking our entire team and all of our equipment to the donor heart recipient,” Dr. Todurov said. “We usually drive at night, but that’s when the drones and rockets are flying everywhere as well. We need to do our work, even if it’s dangerous.”
A driver, the surgeon and two assistant surgeons, two anesthesiologists, a perfusionist, and a nurse travel for each operation. Because the clinics and hospitals throughout the country don’t have the specialized equipment for a heart transplant operation, the team must also bring its own equipment and supplies. The bus accommodates four boxes per service in addition to a bypass machine, heart-lung machine, warming and cooling devices, perfusion systems, monitors, and surgical equipment.
“We have to take everything with us because there’s no chance to fail,” he said. “The first time we packed the van, it took us four or five hours, especially trying to fit in the heart-lung machine. Now we’ve got it down to a matter of minutes.”
Dr. Todurov recalled a recent transplant operation at a regional clinic where the heart donor was in one operating room (OR) and the heart recipient lay in the adjoining OR.
“The nurses in the clinics want to help us, but they lack the expertise,” he said. “We must send the patient by ambulance back to the Heart Institute for care in the ICU following the operation.”
Finding decent roads is another obstacle for the team as it travels up to 500 kilometers to reach patients in need.
“For each trip, I must arrange special permission to drive across Ukraine’s various regions beyond curfew,” he said. “Sometimes that means traveling on heavily damaged roads or through control points with snake-like roads.”
Dr. Todurov said there’s great enthusiasm for the Heart Institute’s heart transplantation program, which is just 20 years old.
“There’s greater awareness in our country for heart donation after circulatory death (DCD), especially after we transplanted a DCD donor heart from a six-year-old boy into a four-year-old girl earlier this year.”
Despite the perils of the invasion and disruption to their daily lives, almost all of the Heart Institute’s employees have remained in place.
“Eleven million people need our help,” said Dr. Todurov. “If not us, who will help? Continuing our work every day is important. Our country is full of people, children, and life. We’re grateful for all the support we’ve been given.”
END
About ISHLT
The International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation (ISHLT) is a not-for-profit, multidisciplinary, professional organization dedicated to improving the care of patients with advanced heart or lung disease through transplantation, mechanical support, and innovative therapies via research, education, and advocacy. ISHLT members focus on transplantation and a range of interventions and therapies related to advanced heart and lung disease.
The ISHLT Annual Meeting and Scientific Sessions will be held 10-13 April at the Prague Congress Centre in Prague, Czech Republic.
CONTACT:
Jess Burke, CAE
ISHLT Director of Marketing and Communications
+1.312.224.0015
END
Investigators have applied artificial intelligence techniques to gait analyses and medical records data to provide insights about individuals with leg fractures and aspects of their recovery.
The study, which is published in the Journal of Orthopaedic Research, uncovered a significant association between the rates of hospital readmission after fracture surgery and the presence of underlying medical conditions. Correlations were also found between underlying medical conditions and orthopedic complications, although these links were not significant.
It was also ...
Previous studies have questioned whether gut microbe imbalances and vitamin D deficiency may be linked to schizophrenia. New research published in Neuropsychopharmacology Reports now indicates that taking probiotics plus vitamin D supplements may improve cognitive function in individuals with the disease.
For the study, 70 adults with schizophrenia were randomized to take a placebo or probiotic supplements plus 400 IU vitamin D daily for 12 weeks. Severity of the disease and cognitive function were evaluated by tests called the Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS) and the 30-point Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA), respectively.
A total of 69 patients completed the study. The MoCA ...
Chronic infection with the hepatitis B virus (HBV) causes progressive liver problems, and eradication of the virus remains a formidable challenge. New research in FEBS Letters indicates that treatment that boosts the effects of immune cells called stem cell memory T cells (TSCMs) may be a promising strategy for combating HBV.
In the study, investigators identified TSCMs in patients with chronic HBV infection and analyzed their effects in a mouse model of HBV. After introducing TSCMs from patients ...
CLEVELAND, Ohio (April 10, 2024)—After the Women’s Health Initiative (WHI) in 2002, many women have resisted taking hormone therapy (HT), especially after age 65 years, because of fears of increased risks for various cancers and heart disease. A new study shows that those fears may be unfounded, depending on the type, route, and dose of HT. Results of the study are published online today in Menopause, the journal of The Menopause Society.
Despite the conflicting results of a follow-up WHI study in 2004 and dozens of other studies since that time, a percentage of healthcare professionals and their middle-aged female patients continue to believe that ...
Adolescence is an important period of life for healthy growth. Malnutrition during this seminal period may have long-term adverse effects on health and development. In sub-Saharan Africa, there is a lack of nutrition programming for adolescents. Adolescent malnutrition represents an urgent issue in sub-Saharan Africa, which has a long history of undernutrition and a rising issue of overweight and obesity.
Findings from a new study suggest that a four-component school-based nutritional intervention package improved ...
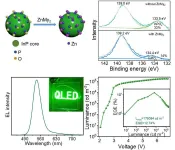
Compared with Cd-based QDs, InP-based QDs have lower photoluminescence quantum yields (PL QYs) and broader full-width at half-maximum (FWHM). In particular, bare InP core has extremely low PL QY (<1%) due to the ease of oxidation of their highly reactive surface even in insert reaction chambers. It has been reported that the defects from oxidative species are probably the reasons for the non-radiative recombination and poor PL QY of these materials. Over the last decade, extensive studies have been conducted to improve the optoelectronic properties of InP-based QDs for display and lighting applications, ...
Undertaking the majority of daily physical activity in the evening is linked to the greatest health benefits for people living with obesity, according to researchers from the University of Sydney, Australia who followed the trajectory of 30,000 people over almost 8 years.
Using wearable device data to categorise participant’s physical activity by morning, afternoon or evening, the researchers uncovered that those who did the majority of their aerobic moderate to vigorous physical activity– the kind that raises our heartrate and gets us out of breath– between 6pm and midnight had the lowest risk of premature ...
Against the backdrop of global challenges such as climate change, diminishing natural resources, and the need to feed a growing population, the imperative for fostering worldwide agricultural sustainability has reached unprecedented levels. China’s Agricultural Green Development (AGD) serves as an important model for global sustainable agricultural development. What advantages does this model offer in terms of concept and implementation path compared to other international sustainable agriculture initiatives? What ...
Parents and youth sport coaches need to have positive relationships to foster positive sporting experiences and enable young people to reach their sporting potential – but there’s currently no clear direction about the best way for them to come together.
Flinders University researchers examining youth sport say that developing better coach-parent relationships that create an environment conducive to positive youth sport experiences and outcomes will require a fresh approach and a more interactive perspective.
Improving interactions and communication between parents and coaches needs ...
Engineered bacteria can produce a plastic modifier that makes renewably sourced plastic more processable, more fracture resistant and highly biodegradable even in sea water. The Kobe University development provides a platform for the industrial-scale, tunable production of a material that holds great potential for turning the plastic industry green.
Plastic is a hallmark of our civilization. It is a family of highly formable (hence the name), versatile and durable materials, most of which are also persistent in nature and therefore a significant source of pollution. Moreover, many plastics are produced from crude oil, a non-renewable resource. Engineers and researchers ...