(Press-News.org) WINSTON-SALEM, N.C. – April 10, 2024 – Racial discrimination experienced during midlife is associated with Alzheimer’s disease pathology, according to a new study from researchers at Wake Forest University School of Medicine and the University of Georgia.
The findings appear online today in Alzheimer’s & Dementia: The Journal of the Alzheimer’s Association.
“We know that Black Americans are at an elevated risk of Alzheimer’s disease and other dementias compared to non-Hispanic white Americans, but we don’t fully understand all the factors that contribute to this disproportionate risk,” said Michelle Mielke, Ph.D., professor of epidemiology and prevention at Wake Forest University School of Medicine.
Mielke, who is a co-corresponding author of the study, said that these racial disparities cannot be attributed to only genetic differences and that research suggests that exposure to racism and its associated stress may increase the risk of dementia.
For the present study, the research team used 17 years of data, which included interviews and blood draws, from a sample of 255 Black Americans who participated in the Family and Community Health Study, a multi-site and longitudinal investigation, which was initiated in 1996 and included more than 800 families in the U.S.
Since the beginning of the Family and Community Health Study, data has been collected every two to three years to study the health and well-being of Black Americans.
In the current study, researchers analyzed serum biomarkers, which are associated with Alzheimer’s disease and related dementias, including serum phosphorylated tau181 (p-Tau181), a marker of Alzheimer’s pathology; neurofilament light (NfL), a non-specific marker of neurodegeneration; and glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP), a marker of brain inflammation.
To measure racial discrimination, the study team surveyed individuals about discriminatory events they experienced such as encountering disrespectful treatment by store owners, salespeople or police officers, being called racial slurs, being excluded from social activities, and not being expected to do well because of being a Black American.
“We found no correlations between racial discrimination and increased levels of the serum biomarkers in 2008 at Wave 5 when participants were a mean age of 46 years,” said Ronald L. Simons, Ph.D., professor of sociology at the University of Georgia and co-corresponding author of the study. “However, 11 years later when the study participants were roughly 57 years old, we found that increased discrimination during middle age significantly correlated with higher levels of both p-Tau181 and NfL.”
While additional research is needed to better understand the complexity of these processes, Mielke said it’s clear that future studies should also focus on the challenges and racism experienced by Black Americans to further understand their risk of dementia.
“These findings provide evidence that the chronic stress of racial discrimination often encountered by Black Americans in midlife become biologically embedded and contribute to Alzheimer’s disease pathology and neurodegeneration later in life,” Mielke said. “This research can help inform policies and interventions to reduce racial disparities and reduce dementia risk.”
This work was supported by the National Institute on Aging (RF1 AG077386 and R01 AG055393), and the National Heart, Lung, Blood Institute (R01 HL118045).
END
Study suggests racial discrimination during midlife associated with Alzheimer’s disease pathology later in life
2024-04-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
The future of xenotransplantation is nearly here
2024-04-10
Embargoed until 10:30 a.m. Wednesday, 10 April, 2024 Central European Summer Time (GMT +2)
10 April, 2024, Prague, Czech Republic—Speaking today at the Annual Meeting and Scientific Sessions of the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation (ISHLT) in Prague, Muhammad Mohiuddin, MBBS, said xenotransplantation, hailed as the future of organ transplantation, is poised to become a clinical reality within the next several years.
In January 2022, the University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM) became the first institution in the world to implant a genetically modified pig heart ...
Treating gum disease after heart rhythm ablation reduced risk of AFib recurrence
2024-04-10
Research Highlights:
Treating gum disease within three months after a heart procedure to correct an irregular heart rhythm, known as atrial fibrillation (AFib), may lower the chances of it reoccurring.
Inflamed gums may predict AFib recurrence after heart ablation, a procedure to fix the irregular heartbeat.
AFib patients should be examined for gum disease and encouraged to seek dental treatment, researchers said.
Embargoed until 4 a.m. CT/5 a.m. ET Wednesday, April 10, 2024
DALLAS, April 10, 2024 — Treating gum disease in the 3-months after a procedure to correct an irregular heartbeat known as atrial fibrillation ...
AI makes retinal imaging 100 times faster, compared to manual method
2024-04-10
Researchers at the National Institutes of Health applied artificial intelligence (AI) to a technique that produces high-resolution images of cells in the eye. They report that with AI, imaging is 100 times faster and improves image contrast 3.5-fold. The advance, they say, will provide researchers with a better tool to evaluate age-related macular degeneration (AMD) and other retinal diseases.
“Artificial intelligence helps overcome a key limitation of imaging cells in the retina, which is time,” said Johnny Tam, Ph.D., who leads the Clinical and Translational Imaging Section at NIH's National Eye Institute.
Tam ...
Impact of aldehydes on DNA damage and aging
2024-04-10
A team of researchers at Nagoya University in Japan has discovered that aldehydes are metabolic byproducts associated with premature aging. Published in Nature Cell Biology, their findings reveal insights into premature aging diseases and potential strategies to combat aging in healthy individuals such as controlling exposure to aldehyde-inducing substances including alcohol, pollution, and smoke.
A person's health can be harmed by aldehydes. However, the group’s findings suggest these detrimental effects also include aging. The team who made this discovery included Yasuyoshi Oka, Yuka Nakazawa, Mayuko Shimada, and Tomoo Ogi of Nagoya University.
“DNA ...
New method of measuring qubits promises ease of scalability in a microscopic package
2024-04-10
Chasing ever-higher qubit counts in near-term quantum computers constantly demands new feats of engineering.
Among the troublesome hurdles of this scaling-up race is refining how qubits are measured. Devices called parametric amplifiers are traditionally used to do these measurements. But as the name suggests, the device amplifies weak signals picked up from the qubits to conduct the readout, which causes unwanted noise and can lead to decoherence of the qubits if not protected by additional large components. More importantly, the bulky size of the amplification chain becomes technically challenging to work around as qubit counts increase ...
Study shedding new light on Earth’s global carbon cycle could help assess liveability of other planets
2024-04-10
Research has uncovered important new insights into the evolution of oxygen, carbon, and other vital elements over the entire history of Earth – and it could help assess which other planets can develop life, ranging from plants to animals and humans.
The study, published today in Nature Geoscience and led by a researcher at the University of Bristol, reveals for the first time how the build up of carbon-rich rocks has accelerated oxygen production and its release into the atmosphere. Until now the exact nature of how the atmosphere became oxygen-rich has long eluded scientists and generated conflicting explanations.
As carbon dioxide is steadily ...
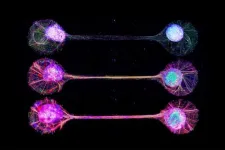
Connecting lab-grown brain cells provides insight into how our own brains work
2024-04-10
Tokyo, Japan – The idea of growing a functioning human brain-like tissues in a dish has always sounded pretty far-fetched, even to researchers in the field. Towards the future goal, a Japanese and French research team has developed a technique for connecting lab-grown brain-mimicking tissue in a way that resembles circuits in our brain.
It is challenging to study exact mechanisms of the brain development and functions. Animal studies are limited by differences between species in brain structure and function, and brain cells grown in the lab tend to lack the characteristic ...
Breakthrough for next-generation digital displays
2024-04-10
Researchers at Linköping University, Sweden, have developed a digital display screen where the LEDs themselves react to touch, light, fingerprints and the user’s pulse, among other things. Their results, published in Nature Electronics, could be the start of a whole new generation of displays for phones, computers and tablets.
“We’ve now shown that our design principle works. Our results show that there is great potential for a new generation of digital displays where new advanced ...
Wistar scientists identify pro-aging ‘sugar signature’ in the blood of people living with HIV
2024-04-10
PHILADELPHIA — (April 10, 2024) — The Wistar Institute’s associate professor Mohamed Abdel-Mohsen, Ph.D., along with his team and collaborators, has identified sugar abnormalities in the blood that may promote biological aging and inflammation in people living with HIV (PLWH). The findings, taken from a large data study comprising more than 1200 participants, are detailed in the new paper, “Immunoglobulin G N-glycan Markers of Accelerated Biological Aging During Chronic HIV Infection,” published in the journal Nature Communications.
Despite advances ...
CAMH develops first ever clinically validated natural supplement to prevent postpartum blues
2024-04-10
A new study published in the Lancet discovery science journal eClinicalMedicine has confirmed that a novel natural supplement—invented, researched, developed and commercialized at the Centre for Addiction and Mental Health (CAMH)—prevents postpartum blues, and reduces symptoms of postpartum depression over the following six months after giving birth.
Up to 8 out of ten new mothers experience postpartum, or ‘baby,’ blues, characterized by mood swings, crying spells, anxiety and difficulty sleeping. The condition usually begins within the first few days after delivery and may last for up to two weeks. Postpartum ...