(Press-News.org) A University of Tennessee Extension specialist has been selected to assist land-grant university teams implementing grants through the Extension Collaboration on Immunization Teaching and Engagement (EXCITE), a national effort to encourage adult vaccinations in rural areas and among underserved communities.
Laura Clark, UT Extension state specialist in family and consumer sciences, will serve as a national EXCITE Bridge Grant coach and work with six land-grant universities that are grant recipients through the program. Clark has worked for UT Extension for six years, which includes four years as a county director and FCS agent and two years as project manager for a grant awarded to the Department of Family and Consumer Sciences through the Tennessee Department of Health.
EXCITE started in 2021 as a nationwide local response by U.S. Cooperative Extension. EXCITE is made possible through an interagency agreement between United States Department of Agriculture – National Institute of Food and Agriculture (USDA-NIFA) and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and a cooperative agreement with the Extension Foundation in partnership with the ECOP (Extension Committee on Organization and Policy) Health Program Action Team.
EXCITE focuses on education, engagement, partnerships and access to encourage adults to receive immunizations, including the COVID-19 vaccine. The initiative includes 96 projects through 73 land-grant institutions. Through the first two years of the project, there were 1,148 vaccination clinics and 26,023 immunizations provided. As a national coach, Clark will help support grant teams by providing resources, feedback and assistance and act as a liaison between the funders and the grantees.
“I am honored to have been chosen to be a part of the Extension Foundation’s EXCITE program and for the opportunity to support innovative teams who are working to better the lives of individuals and families in communities across the nation. I am looking forward to supporting the mission of the Extension Foundation to increase the visibility and impact of Cooperative Extension as a representative for the University of Tennessee Extension FCS program and working alongside such a talented group of people,” Clark said.
Janet Fox, assistant dean of UT Extension and head of the Department of Family and Consumer Sciences, noted the national recognition and Clark's leadership, saying, "Laura’s selection recognizes the exceptional work she is leading and the outstanding professional she is."
The University of Tennessee Institute of Agriculture is comprised of the Herbert College of Agriculture, UT College of Veterinary Medicine, UT AgResearch and UT Extension. Through its land-grant mission of teaching, research and outreach, the Institute touches lives and provides Real. Life. Solutions. to Tennesseans and beyond. utia.tennessee.edu.
END
UT Extension specialist chosen to help support national immunization program
Laura Clark to serve as a grant coach for land-grant universities
2024-04-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Economic wealth may be linked with happiness in China – if inequality is low
2024-04-10
A country’s economic prosperity is linked with improved well-being in its residents, according to a study published April 10, 2024 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Feng Huang from the Chinese Academy of Sciences, and colleagues.
Philosophers have long pondered the fraught relationship between money and happiness. Aristotle and Solon argued against the euphoric powers of wealth, while the Easterlin Paradox suggests that a nation’s economic fortitude can influence its residents’ health and happiness. Little evidence exists to support this claim in China, especially after the country’s recent economic expansion and rapid industrialization.
Huang and colleagues ...
Most cybercriminal threats are concentrated in just a few countries
2024-04-10
A newly developed World Cybercrime Index shows that most cybercriminal threats are concentrated in several countries, with different countries associated with distinct cybercrime types. Miranda Bruce (University of Oxford/University of New South Wales), Jonathan Lusthaus (University of Oxford), Ridhi Kashyap (University of Oxford), Nigel Phair (Monash University), and Federico Varese (Sciences Po) present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on April 10, 2024.
Worldwide, cybercrimes are estimated to cost hundreds ...
US building footprints could help identify neighborhood sociodemographic traits
2024-04-10
An analysis of building footprints in major US metropolitan areas identifies five different neighborhood types that vary in footprint size, shape, and placement, and which are statistically associated with varying neighborhood socioeconomic and demographic traits. Noah Durst of Michigan State University, US, and colleagues present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on April 10, 2024.
People have long studied the shape and placement of human settlements—“neighborhood morphology”—to help inform urban planning and management. Recent technological advancements, such as high-resolution satellite imagery and more powerful computational ...
Indigenous Australian message sticks, which feature markings to convey messages over long distances, analyzed for first time at scale through new database of 1,500 artifacts
2024-04-10
Indigenous Australian message sticks, which feature markings to convey messages over long distances, analyzed for first time at scale through new database of 1,500 artifacts
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0299712
Article Title: AMSD: The Australian Message Stick Database
Author Countries: Australia, Germany
Funding: The lead author (Piers Kelly) receives salary and project funding specifically for the research described in this paper. He is funded by an ARC Discovery Early Career Researcher ...
Mixed diets balance nutrition and carbon footprint
2024-04-10
What we eat can impact our health as well as the environment. Many studies have looked at the impacts of diets in very general terms focused at the level of food groups. A new study led by researchers at the University of Tokyo explores this issue following a more nuanced dish-level approach. One of the benefits of this kind of study is that people’s connections with their diets vary around the world and have strong cultural associations. Knowledge of the impacts of diets using dishes rather than broad food groups can help individuals make informed choices and those in the food industry improve ...
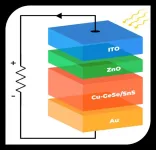
New quantum material promises over 190% quantum efficiency in solar cells
2024-04-10
Researchers from Lehigh University have developed a material that demonstrates the potential for drastically increasing the efficiency of solar panels.
A prototype using the material as the active layer in a solar cell exhibits an average photovoltaic absorption of 80%, a high generation rate of photoexcited carriers, and an external quantum efficiency (EQE) up to an unprecedented 190%—a measure that far exceeds the theoretical Shockley-Queisser efficiency limit for silicon-based materials and pushes the field of quantum materials for photovoltaics to ...
AI powered “digital twin” models the infant microbiome
2024-04-10
The gut microbiome has a profound impact on the health and development of infants. Research shows that dysbiosis—or imbalances in the microbial community—is associated with gastrointestinal diseases and neurodevelopmental deficits. Understanding how gut bacteria interact, and how these interactions may lead to some of these problems, however, is difficult and time consuming through traditional laboratory experiments.
Researchers at the University of Chicago have developed a new generative artificial intelligence (AI) tool that models the infant microbiome. This “digital ...
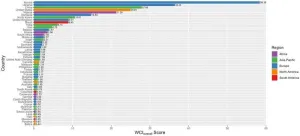
World-first “Cybercrime Index” ranks countries by cybercrime threat level
2024-04-10
Following three years of intensive research, an international team of researchers have compiled the first ever ‘World Cybercrime Index’, which identifies the globe’s key cybercrime hotspots by ranking the most significant sources of cybercrime at a national level.
The Index, published today in the journal PLOS ONE, shows that a relatively small number of countries house the greatest cybercriminal threat. Russia tops the list, followed by Ukraine, China, the USA, Nigeria, and Romania. The UK comes in at number eight.
Co-author of the study, Dr Miranda Bruce from the ...
A study in Science Advances suggests liquid biopsy could detect and monitor aggressive small cell lung cancer
2024-04-10
A new lab assay developed by researchers at Fred Hutch Cancer Center could make diagnosis and treatment of small-cell lung cancer and non-small cell lung cancer easier.
The blood-based test, also called a “liquid biopsy,” can detect differences between types of lung cancer by examining patterns in cell-free tumor DNA in blood samples. It’s a desirable option for detecting small-cell lung cancer (SCLC) as standard needle biopsies fail due the number of smaller tumors typically present and the variety of tumor subtypes that indicate different treatment pathways.
“There ...
New drug prevents flu-related inflammation and lung damage
2024-04-10
(MEMPHIS, Tenn. – April 10, 2024) Infection with the influenza virus leads to lung injury through inflammation over-activation that causes collateral damage to cells required for breathing. Such damage can be life-threatening, but scientists have a new preventative treatment. A team from St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital, University of Houston, Tufts University School of Medicine and Fox Chase Cancer Center created a drug that can prevent flu-induced lung injury. In a mouse model, the ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Here's why seafarers have little confidence in autonomous ships
MYC amplification in metastatic prostate cancer associated with reduced tumor immunogenicity
The gut can drive age-associated memory loss
Enhancing gut-brain communication reversed cognitive decline, improved memory formation in aging mice
Mothers exposure to microbes protect their newborn babies against infection
How one flu virus can hamper the immune response to another
Researchers uncover distinct tumor “neighborhoods”, with each cell subtype playing a specific role, in aggressive childhood brain cancer
Researchers develop new way to safely insert gene-sized DNA into the genome
Astronomers capture birth of a magnetar, confirming link to some of universe’s brightest exploding stars
New photonic device, developed by MIT researchers, efficiently beams light into free space
UCSB researcher bridges the worlds of general relativity and supernova astrophysics
Global exchange of knowledge and technology to significantly advance reef restoration efforts
Vision sensing for intelligent driving: technical challenges and innovative solutions
To attempt world record, researchers will use their finding that prep phase is most vital to accurate three-point shooting
AI is homogenizing human expression and thought, computer scientists and psychologists say
Severe COVID-19, flu facilitate lung cancer months or years later, new research shows
Housing displacement, employment disruption, and mental health after the 2023 Maui wildfires
GLP-1 receptor agonist use and survival among patients with type 2 diabetes and brain metastases
Solid but fluid: New materials reconfigure their entire crystal structure in response to humidity
New research reveals how development and sex shape the brain
New discovery may improve kidney disease diagnosis in black patients
What changes happen in the aging brain?
Pew awards fellowships to seven scientists advancing marine conservation
Turning cancer’s protein machinery against itself to boost immunity
Current Pharmaceutical Analysis releases Volume 22, Issue 2 with open access research
Researchers capture thermal fluctuations in polymer segments for the first time
16-year study finds major health burden in single‑ventricle heart
Disposable vapes ban could lead young adults to switch to cigarettes, study finds
Adults with concurrent hearing and vision loss report barriers and challenges in navigating complex, everyday environments
Breast cancer stage at diagnosis differs sharply across rural US regions
[Press-News.org] UT Extension specialist chosen to help support national immunization programLaura Clark to serve as a grant coach for land-grant universities