(Press-News.org) When we catch a cold, the immune system steps in to defend us. This is a well-known biological fact, but is difficult to observe directly. Processes at a molecular level are not only miniscule, they are often extremely fast, and therefore difficult to capture in action. Scientists at Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin für Materialien und Energie (HZB) and the Technische Uni-versität Berlin (TUB) now present a method that takes us a good step towards producing a "molecular movie". They can record two pictures at such a short time interval that it will soon be possible to observe molecules and nanostructures in real time.
A "molecular movie" that shows how a molecule behaves at the crucial moment of a chemical reaction would help us better understand fundamental processes in the natural sciences. Such processes are often only a few femtoseconds long. A femtosecond is a millionth of a billionth of a second.
While it is possible to record a single femtosecond picture using an ultra-short flash of light, it has never been possible to take a sequence of pictures in such rapid succession. On a detector that captures the image, the pictures would overlap and "wash out". An attempt to swap or refresh the detector between two images would simply take too long, even if it could be done at speed of light.
In spite of these difficulties, members of the joint research group "Functional Nanomaterials" of HZB and the Technische Universität Berlin have now managed to take ultrafast image sequences of objects mere micrometres in size using pulses from the X-ray laser FLASH in Hamburg, Germany. Furthermore, they chart out a path how their approach can be scaled to nanometer resolution in the future. Together with colleagues from DESY and the University of Münster, they have published their results in the journal Nature Photonics (DOI: 10.1038/NPHOTON.2010.287).
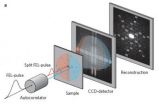
The researchers came up with an elegant way to descramble the information superimposed by the two subsequent X-ray pulses. They encoded both images simultaneously in a single X-ray hologram. It takes several steps to obtain the final image sequence: First, the scientists split the X-ray laser beam into two separate beams. Using multiple mirrors, they force one beam to take a short detour, which causes the two pulses to reach the object under study at ever so slightly different times – the two pulses arrive only 0.00000000000005 seconds apart. Due to a specific geometric arrangement of the sample, the pulses gen-erate a "double-hologram". This hologram encodes the structure of the object at the two times at which the X-ray pulses hit., Using a mathematical reconstruction procedure, the researchers can then simply associate the images with the respective X-ray puses and thus determine the image sequence in correct temporal order.
Using their method, the scientists recorded two pictures of a micro-model of the Brandenburg Gate, separated by only 50 femtoseconds. "In this short time interval, even a ray of light travels no further than the width of a human hair," says PhD student Christian Günther, the first author of the publication. The short-wavelength X-rays used allow to reveal extremely small detail, since the shorter the wavelength of light you use, the smaller the objects you can resolve.
"The long-term goal is to be able to follow the movements of molecules and nanostructures in real time," says project head Prof. Dr. Stefan Eisebitt. The extremely high temporal resolution in conjunction with the possibility to see the tiniest objects was the motivation to develop the new technique. A picture may be worth a thousand words, but a movie made up of several pictures can tell you about an object's dynamics.
INFORMATION:
Contact Press Office:
Dr. Ina Helms, Tel.: +49 30 8062 42034
ina.helms@helmholtz-berlin.de
Fastest movie in the world recorded
Scientists develop a method to film nanostructures
2011-01-13
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Sleep-disordered breathing comes at a heavy cost
2011-01-13
"Snoring, sleep apnoea, and obesity-related respiratory difficulties are fairly common disorders that affect a large proportion of the population," according to Poul Jennum, Professor of Clinical Neurophysiology at the Center for Healthy Ageing at the University of Copenhagen Faculty of Health Sciences. He is head of the Danish Centre for Sleep Medicine, Glostrup Hospital, which treats patients from all over the country.
"Previous studies show that these disorders seriously affect quality of life, and our new studies show that people who snore violently, and particularly ...
'Yo-yo' effect of slimming diets explained
2011-01-13
If you want to lose the kilos you've put on over Christmas, you may be interested in knowing that the hormones related to appetite play an important role in your likelihood of regaining weight after dieting. A new study confirms that people with the highest levels of leptin and lowest levels of ghrelin are more likely to put the centimetres they lost back on again.
Doctors often have to deal with patients who, after sticking to a slimming diet, have regained the kilos lost in just a short time – or weigh even more than they did before they started the diet. This is called ...
Drug reduces the increase in fear caused by previous traumatic experiences in mice
2011-01-13
Mice previously exposed to traumatic situations demonstrate a more persistent memory of fear conditioning - acquired by associating an acoustic stimulus with an aversive stimulus - and lack the ability to inhibit this fear. This phenomenon is similar to that of people who suffer from Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD), an anxiety disorder which appears after being exposed to highly traumatic situations, such as a violent attack, a natural disaster or physical abuse.
In the study researchers verified that the 7,8-Dihydroxyflavone injected into mice previously subjected ...
Cosmic magnifying lenses distort view of distant galaxies
2011-01-13
Looking deep into space, and literally peering back in time, is like experiencing the universe in a house of mirrors where everything is distorted through a phenomenon called gravitational lensing. Gravitational lensing occurs when light from a distant object is distorted by a massive object that is in the foreground. Astronomers have started to apply this concept in a new way to determine the number of very distant galaxies and to measure dark matter in the universe. Though recent progress has been made in extending the use of gravitational lensing, a letter published ...
Researchers show how 1 gene becomes 2 (with different functions)
2011-01-13
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — Researchers report that they are the first to show in molecular detail how one gene evolved two competing functions that eventually split up – via gene duplication – to pursue their separate destinies.
The study, in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, validates a decades-old hypothesis about a key mechanism of evolution. The study also confirms the ancestry of a family of "antifreeze proteins" that helps the Antarctic eelpout survive in the frigid waters of the Southern Ocean.
"I'm always asking the question of where these antifreeze ...
MicroRNAs could increase the risk of amputation in diabetics
2011-01-13
New research has found one of the smallest entities in the human genome, micro-RNA, could increase the risk of limb amputation in diabetic patients who have poor blood flow.
The study by Dr Andrea Caporali and colleagues in Professor Costanza Emanueli's research group in the Regenerative Medicine Section of the School of Clinical Sciences at the University of Bristol was funded by the Medical Research Council and is published online in Circulation: Journal of the American Heart Association.
The research group have shown in an experimental cell study that conditions ...
Some school social workers don't feel prepared to manage cyberbullying, study finds
2011-01-13
ATHENS, Ohio (Jan. 12, 2011) – Some school social workers report that they don't feel equipped to handle incidents of cyberbullying among teens.
A new Ohio University-led survey of 399 members of the 11-state Midwest School Social Work Council found that while nearly all agreed that cyberbullying can cause psychological harm— including suicide—and deserved more attention from schools, just more than half felt empowered to deal with the issue. In contrast, other research on traditional bullying suggests that 86 percent of school staff members are confident in their ability ...
Hold the Red Bull: Energy drinks don't blunt effects of alcohol, study finds
2011-01-13
Marketing efforts that encourage mixing caffeinated "energy" drinks with alcohol often try to sway young people to believe that caffeine will offset the sedating effects of alcohol and increase alertness and stamina.
But a new study led by researchers from the Boston University School of Public Health [BUSPH] and the Center for Alcohol and Addiction Studies at Brown University has found that the addition of caffeine to alcohol -- mixing Red Bull with vodka, for example -- has no effect on enhancing performance on a driving test or improving sustained attention or reaction ...
Climate disasters: New Baylor study explores how people respond
2011-01-13
New results from a Baylor University study show that different behaviors and strategies lead some families to cope better and emerge stronger after a weather-related event.
Dr. Sara Alexander, an applied social anthropologist at Baylor who conducts much of her research in Central America, studied different households in several coastal communities in Belize. While climate change has been an emerging topic of interest to the world community, little scientific data exists on exactly how people respond to different climate-related "shocks" and events such as more intense ...
Toronto astronomers among those announcing first scientific results of Planck satellite mission
2011-01-13
University of Toronto astronomers are in Paris this week as part of an international conference announcing the first scientific results of the Plank space telescope mission.
Launched in May 2009, the telescope has nearly completed three of its four planned surveys of the entire sky, providing astronomers a glimpse of conditions near the beginning of the Universe and providing data that will help answer the big questions: How was the Universe formed? How has it evolved to its present form? And what shape will it take in future?
"Planck has worked flawlessly to give us ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Striking genomic architecture discovered in embryonic reproductive cells before they start developing into sperm and eggs
Screening improves early detection of colorectal cancer
New data on spontaneous coronary artery dissection (SCAD) – a common cause of heart attacks in younger women
How root growth is stimulated by nitrate: Researchers decipher signalling chain
Scientists reveal our best- and worst-case scenarios for a warming Antarctica
Cleaner fish show intelligence typical of mammals
AABNet and partners launch landmark guide on the conservation of African livestock genetic resources and sustainable breeding strategies
Produce hydrogen and oxygen simultaneously from a single atom! Achieve carbon neutrality with an 'All-in-one' single-atom water electrolysis catalyst
Sleep loss linked to higher atrial fibrillation risk in working-age adults
Visible light-driven deracemization of α-aryl ketones synergistically catalyzed by thiophenols and chiral phosphoric acid
Most AI bots lack basic safety disclosures, study finds
How competitive gaming on discord fosters social connections
CU Anschutz School of Medicine receives best ranking in NIH funding in 20 years
Mayo Clinic opens patient information office in Cayman Islands
Phonon lasers unlock ultrabroadband acoustic frequency combs
Babies with an increased likelihood of autism may struggle to settle into deep, restorative sleep, according to a new study from the University of East Anglia.
National Reactor Innovation Center opens Molten Salt Thermophysical Examination Capability at INL
International Progressive MS Alliance awards €6.9 million to three studies researching therapies to address common symptoms of progressive MS
Can your soil’s color predict its health?
Biochar nanomaterials could transform medicine, energy, and climate solutions
Turning waste into power: scientists convert discarded phone batteries and industrial lignin into high-performance sodium battery materials
PhD student maps mysterious upper atmosphere of Uranus for the first time
Idaho National Laboratory to accelerate nuclear energy deployment with NVIDIA AI through the Genesis Mission
Blood test could help guide treatment decisions in germ cell tumors
New ‘scimitar-crested’ Spinosaurus species discovered in the central Sahara
“Cyborg” pancreatic organoids can monitor the maturation of islet cells
Technique to extract concepts from AI models can help steer and monitor model outputs
Study clarifies the cancer genome in domestic cats
Crested Spinosaurus fossil was aquatic, but lived 1,000 kilometers from the Tethys Sea
MULTI-evolve: Rapid evolution of complex multi-mutant proteins
[Press-News.org] Fastest movie in the world recordedScientists develop a method to film nanostructures