(Press-News.org) A nitrogen-fixing bacterial endosymbiont of marine algae is evolving into a nitrogen-fixing organelle, or nitroplast, according to a new study, thereby expanding a function that was thought to be exclusively carried out by prokaryotic cells to eukaryotes. Eukaryotic cells are remarkably complex and contain various organelles, which are specialized structures within a living cell that have specific biological functions. Two organelles, mitochondria and chloroplasts, play a key role in energy metabolism and photosynthesis, respectively, and likely evolved from the integration of endosymbiotic bacteria to the eukaryotic cell. Biological nitrogen (N2) fixation, the conversion of atmospheric N2gas to biologically available ammonia, is a key metabolic process that maintains the fertility of aquatic and terrestrial systems. N2 fixation in eukaryotes is only known to exist through diverse symbiotic partnerships with prokaryotic microbes capable of N2 fixation. However, the nature of these symbiotic relationships is poorly understood, and, to date, a N2-fixing organelle in eukaryotic cells has yet to be described. Tyler Coale and colleagues investigated the interactions between Candidatus Atelocyanobacterium thalassa, or UCYN-A, a metabolically streamlined N2-fixing cyanobacterium. which is a known endosymbiont of the unicellular marine algae Braarudosphaera bigelowii. Through subcellular images taken with soft X-ray tomography to visualize the algae’s cell morphology and division, Coale et al. observed a coordinated cell cycle in which endosymbiotic UCYN-A divided and is split evenly between daughter B. bigelowii cells, which is similar to the way chloroplast and mitochondria organelles are transmitted during cell division. Moreover, further proteomic and genomic analyses show that UCYN-A contains many proteins that are imported from the eukaryotic host cell’s nucleus, including those essential for cellular metabolism and control of the cell cycle. According to Coale et al., the findings suggest that UCYN-A has evolved beyond endosymbiosis and functions as an early evolutionary stage N2-fixing organelle. “The nitroplast represents a textbook case of a eukaryotic organelle that complements the energy, carbon, and nitrogen needs of the algal host and is another example of how ecology is the theater where evolution takes place,” writes Ramon Massana in a related Perspective.
END
The nitroplast revealed: a nitrogen-fixing organelle in a marine alga
2024-04-11
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
First step to untangle DNA: supercoiled DNA captures gyrase like a lasso ropes cattle
2024-04-11
Picture in your mind a traditional “landline” telephone with a coiled cord connecting the handset to the phone. The coiled telephone cord and the DNA double helix that stores the genetic material in every cell in the body have one thing in common; they both supercoil, or coil about themselves, and tangle in ways that can be difficult to undo. In the case of DNA, if this overwinding is not dealt with, essential processes such as copying DNA and cell division grind to a halt. Fortunately, cells have an ingenious solution to carefully regulate DNA supercoiling.
In this study published in the journal Science, researchers ...
Brainless memory makes the spinal cord smarter than previously thought
2024-04-11
Aya Takeoka at the RIKEN Center for Brain Science (CBS) in Japan and colleagues have discovered the neural circuitry in the spinal cord that allows brain-independent motor learning. Published in Science on April 11, the study found two critical groups of spinal cord neurons, one necessary for new adaptive learning, and another for recalling adaptations once they have been learned. The findings could help scientists develop ways to assist motor recovery after spinal cord injury.
Scientists have known for some time that motor output from the spinal cord can be adjusted through practice ...
Study reveals giant store of global soil carbon
2024-04-11
Soil carbon usually refers only to the organic matter component of soils, known as soil organic carbon (SOC). However, soil carbon also has an inorganic component, known as soil inorganic carbon (SIC). Solid SIC, often calcium carbonate, tends to accumulate more in arid regions with infertile soils, which has led many to believe it is not important.
In a study published in Science, researchers led by Prof. HUANG Yuanyuan from the Institute of Geographic Sciences and Natural Resources Research of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) and Prof. ZHANG Ganlin from the Institute of Soil Science of CAS, together ...
Wired to learn and remember
2024-04-11
Leuven (Belgium), 11 April 2024 — The role of the spinal cord is often simplified to that of a simple relay station, carrying messages between the brain and the body. However, the spinal cord can actually learn and remember movements on its own. A team of researchers at the Leuven-based Neuro-Electronics Research Flanders (NERF) details how two different neuronal populations enable the spinal cord to adapt and recall learned behavior in a way that is completely independent of the brain. These remarkable ...
Penn Engineers recreate Star Trek’s Holodeck using ChatGPT and video game assets
2024-04-11
In Star Trek: The Next Generation, Captain Picard and the crew of the U.S.S. Enterprise leverage the holodeck, an empty room capable of generating 3D environments, to prepare for missions and to entertain themselves, simulating everything from lush jungles to the London of Sherlock Holmes. Deeply immersive and fully interactive, holodeck-created environments are infinitely customizable, using nothing but language: the crew has only to ask the computer to generate an environment, and that space appears in the holodeck.
Today, virtual interactive environments are also used to train robots prior to real-world deployment in a ...
UC Santa Cruz researchers value salt marsh restoration as a crucial tool in flood risk reduction and climate resilience in the San Francisco Bay
2024-04-11
Salt marsh restoration can mitigate flood risk and bolster community resilience to climate change in our local waterways, according to a recent study published in Nature by a postdoctoral fellow with UC Santa Cruz’s Center for Coastal Climate Resilience (CCCR).
The study, titled “The value of marsh restoration for flood risk reduction in an urban estuary,” explores the social and economic advantages of marsh restoration amidst the growing threats of sea level rise and storm-driven flooding. Climate change will put many communities at risk. In California, some of the study co-authors from the U.S. Geological ...
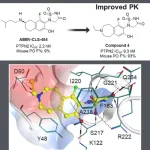
Insilico Medicine develops novel PTPN2/N1 inhibitor for cancer immunotherapy using generative AI
2024-04-11
In recent years, cancer immunotherapy, exemplified by PD-1 and its ligand PD-L1 blockade, has made remarkable advances. But while immunotherapy drugs offer new treatment possibilities, only about 20% to 40% of patients respond to these treatments. The majority either don't respond or develop drug resistance. Researchers are now looking for ways to enhance the scope of tumor immunotherapy in order to benefit a wider range of patients.
One such avenue is through the protein tyrosine phosphatase non-receptor type 2 (PTPN2) and its close superfamily member, PTPN1, identified in previous research as crucial modulators involved in the regulation ...
$318 million New York City community parks initiative is associated with increased use of urban parks in low-income neighborhoods
2024-04-11
A new study in JAMA Network Open led by researchers from the CUNY Graduate School of Public Health and Health Policy observed 28,322 park users across 54 neighborhood parks and found a clear association between park renovation and park use in low-income neighborhoods in New York City (NYC).
As the global trend toward urbanization continues, two thirds of the world’s population is predicted to live in cities by 2050. Amid the noise, stress, and crowding of city life, urban parks have the potential to provide opportunities for physical activity, mitigate heat and pollution, lower stress, and improve mental and social well-being, all of which can decrease the prevalence ...
Trapped in the middle: billiards with memory
2024-04-11
Adding one simple rule to an idealized game of billiards leads to a wealth of intriguing mathematical questions, as well as applications in the physics of living organisms. This week, researchers from the University of Amsterdam, including two master students as first authors – have published a paper in Physical Review Letters about the fascinating dynamics of billiards with memory.
Billiards: a mathematical mystery
An idealized version of the game of billiards has fascinated mathematicians for decades. The basic ...
A new spin on organic shampoo makes it sudsier, longer lasting
2024-04-11
While there’s no regulation in the U.S. for what’s in organic shampoos, they tend to contain ingredients perceived as safe or environmentally friendly. However, these “clean” shampoos separate and spoil faster than those made with synthetic stabilizers and preservatives. Now, researchers in ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering demonstrate that a simple process — spinning organic shampoo at high speeds — improved the final products’ shelf lives and ability to clean hair.
Natural emulsifiers, such as xanthan gum and cetyl alcohol, ...