Illuminating the path to hearing recovery
2024-04-16
(Press-News.org)
Professor Yunje Cho’s research team from the Department of Life Sciences at Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH, Republic of Korea) has collaborated with Professor Kwang Pyo Kim’s group from the Department of Applied Chemistry at Kyung Hee University (KHU, ROK), Professor Vsevolod Katritch’s team from the University of Southern California (USC, USA), and Professor Carol V. Robinson from the University of Oxford (UK) to uncover the mysteries surrounding a specific receptor protein associated with hearing. Their findings have recently been published in the online edition of Nature Structural & Molecular Biology.
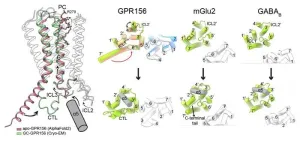
Deep within the inner ear lie the cochlea, responsible for sound detection, and the vestibular apparatus, which oversees balance. Cells within these regions harbor a class C orphan G-protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) called GPR156. When this receptor is activated, it binds with G-proteins inside the cell, facilitating signal transmission. Unlike its counterparts, GPR156 exhibits sustained activity even in the absence of external stimuli, playing a pivotal role in upholding auditory and balance functions. Unveiling the structural and functional intricacies of GPR156 holds promise for devising interventions for individuals with congenital hearing impairments.
The research team employed cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) analysis to delve into the GPR156 in the Go-free and Go-coupled states, achieving unprecedented resolution. Their investigation unearthed the mechanisms behind GPR156’s ability to maintain heightened activity sans activators.
Their analysis confirmed that GPR156 activation hinges on its interaction with abundant lipids in the cell membrane, triggering structural shifts upon engagement with G-proteins in the cytoplasm. Notably, unlike conventional GPCRs, GPR156 exhibits flexibility in altering the structure of the seventh helix as it traverses the cell membrane, thereby facilitating binding with G-proteins and orchestrating signal activation to detect sound. This study represents a crucial step forward in unraveling the structural dynamics and activation mechanisms of GPR156.
Professor Yunje Cho of POSTECH remarked, “Congenital hearing and balance impairments afflict numerous individuals. I am hopeful that our research will pave the way for groundbreaking treatments and drug discoveries to alleviate their suffering.”
This research received financial support from the National Research Foundation of Korea.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-04-16
A research team reviews the critical relationship between the accumulation of anthocyanins and organic acids in fruits, highlighting how these factors influence fruit color and consumer appeal through changes in vacuolar pH. The analysis focused on the transcription factors (TFs) responsible for the co-regulation of genes affecting these quality traits, aiming to enhance fruit marketability. By establishing a genetic link and identifying the regulatory mechanisms involved, the team provides a roadmap for breeders to target specific traits for modification. Although progress has been made, the review underlines the ...
2024-04-16
Ferroelectric binary oxides thin films are garnering attention for their superior compatibility over traditional perovskite-based ferroelectric materials. Its compatibility and scalability within the CMOS framework make it an ideal candidate for integrating ferroelectric devices into mainstream semiconductor components, including next-generation memory devices and various logic devices such as Ferroelectric Field-effect Transistor, and Negative Capacitance Field-effect Transistor. It has been reported that challenges ...
2024-04-16
Citrus is the world’s most economically significant fruit crop, but it faces various environmental adversities that restrict its distribution. Grafting is a crucial factor in enhancing citrus productivity. Current research focuses on selecting genetically uniform rootstocks, such as trifoliate orange for its disease resistance. However, issues such as sensitivity to alkalinity and incompatibility with certain cultivars persist.
Addressing these challenges, a study (DOI: 10.48130/frures-0023-0042) published in Fruit Research on 01 February 2024, introduces 'Shuzhen No.1', a novel rootstock ...
2024-04-16
People who as teenagers felt pressure to lose weight from family or from the media, females, people who are not heterosexual, and people experiencing socioeconomic disadvantage, are most at risk of ‘internalised’ weight stigma, new research led by the University of Bristol has found. The study is published in The Lancet Regional Health Europe today [15 April].
‘Internalised’ weight stigma, is when people apply negative obesity-related stereotypes to themselves, such as thinking they are less attractive, less competent, or less valuable as a person because of their weight. This is the first time a study has used a large UK sample to examine who is most at risk.
In ...
2024-04-16
A new study published in the Strategic Management Journal cautions startups against prioritizing early scaling, as it’s positively associated with a higher rate of firm failure — especially for platform companies. Although managers could see the potential benefits of scaling as a way to prevent competitor imitation, scaling early can also prematurely curtail learning through experimentation and committing to a business idea that lacks product-market fit.
Although a few high-growth startups such as Facebook and Uber made their fortunes by scaling early — also known as “blitzscaling” — study authors Saerom (Ronnie) Lee and ...
2024-04-16
**Embargo: 23.30 [UK time] / 19.30 [ET], Monday 15 April 2024**
Peer-reviewed/Literature review, Survey, and Opinion/People
Embargoed access to the papers and contact details for authors and patient advocates are available in Notes to Editors at the end of the release.
Breast cancer is now the world’s most common cancer; at the end of 2020, 7.8 million women were alive having been diagnosed in the previous five years. In the same year, 685,000 women died from the disease. Despite significant improvements in research, treatment, and survival, gross inequities persist, and many patients ...
2024-04-16
People with a nonfatal opioid overdose who have access to a peer support program while in the emergency department are more likely to initiate treatment and less likely to have repeated overdoses, according to a Rutgers Health study.
The study is the largest study on outcomes associated with emergency department-based peer support for opioid use disorders and was published in JAMA Network Open online ahead of print in the April 2024 issue.
According to the Centers for Disease ...
2024-04-16
DETROIT - The diagnosis of male fertility has not changed in decades and primarily relies on conventional semen parameter analyses such as sperm count, motility and morphology, which are poor predictors of couples’ reproductive success.
A new $3.4 million award to the Wayne State University School of Medicine from the National Institutes of Health aims to overcome the limitations of conventional semen analyses by examining mitochondrial DNA levels in sperm as a novel biomarker of sperm fitness.
The project will be led by School of Medicine Professor of Obstetrics and Gynecology J. Richard Pilsner, Ph.D., M.P.H. ...
2024-04-16
New research in the Global Strategy Journal has bad news for companies struggling with corruption, discrimination, or sweatshops in their supply chain: corporate misconduct demonstrably hurts international sales. Consumers and investors increasingly read about unethical business practices globally and demonstrate their displeasure locally.
“Socially irresponsible acts transcend geographic boundaries and negatively affect foreign subsidiary performance,” said Nuruzzaman Nuruzzaman of the University of Manchester, one of the study’s ...
2024-04-16
A new USC-led study on rats that feasted on a high-fat, sugary diet raises the possibility that a junk food-filled diet in teens may disrupt their brains’ memory ability for a long time.
“What we see not just in this paper, but in some of our other recent work, is that if these rats grew up on this junk food diet, then they have these memory impairments that don’t go away,” said Scott Kanoski, a professor of biological sciences at the USC Dornsife College of Letters, Arts and Sciences. “If you just simply put them on a healthy diet, these effects unfortunately last well into adulthood.”
The study appears in the May issue of the journal ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Illuminating the path to hearing recovery