(Press-News.org) This report presents gained knowledge identified at two events during the Greenland Science Week on the 7th of November 2023 in Nuuk, Greenland:
The 1st Biennial Greenland Marine Research Seminar and
The workshop on Status and Development for East Greenland Waters
Both events had a forward-looking focus, to gain insight and knowledge from stakeholders and other parties, to be implemented in future research. The marine research seminar also served as a follow-up on earlier ECOTIP and Face-It stakeholder involvement in Greenland and was an opportunity to share project results and recommendations for decision-makers.
This report is divided into three parts, representing firstly the Greenland Marine Research Seminar, secondly insights from a survey distributed at the seminar, and thirdly the workshop on Status and Development of East Greenland Waters. The aim of this report is to present gained knowledge from the three parts as it has been discussed and presented by participants, stakeholders, and other parties.
END
Challenges in Greenland marine research and insights and priorities for development of East Greenland marine and coastal environments
A report on the first Greenland Marine Research Seminar and Workshop on Status and Development of East Greenland waters
2024-04-17
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Copper beads in pig feed reshape swine gut microbiome
2024-04-17
Highlights:
In lab experiments, copper shows antimicrobial properties, including against pathogens like Salmonella.
Copper beads in animal feeds may improve gut health in pigs.
A new bead design effectively delivers copper to the lower intestine.
New findings show copper beads influence the microbial makeup in a pig’s gut, but more work is needed to optimize the benefits.
Washington, D.C. — April 17, 2024 — Copper is a natural antimicrobial material that, when added to pig feed, may promote the growth and ...
FAU Engineering selected by NASA for University Nanosatellite Program
2024-04-17
Florida Atlantic University’s College of Engineering and Computer Science is among eight university teams in the United States selected to work with NASA and the U.S. military to foster innovation and expertise in the small satellite sector.
NASA’s CubeSat Launch Initiative (CSLI) is partnering with the U.S. Air Force and U.S. Space Force for the 2024 Mission Concept Program. A CubeSat is among a class of research spacecraft called nanosatellites about the size of a 4-inch cube and typically weighing less than 5 pounds.
Running from May through August, the University Nanosatellite ...
Nursing resources affect hospital patient experience ratings
2024-04-17
Waltham — April 10, 2024 — The nursing work environment, nurse education, and staffing levels are independent factors affecting hospital scores on a key measure of patient-centered care – with significant implications for reimbursements, reports a study in Medical Care. The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
"Our results provide evidence-based guidance about which modifiable aspects of hospital nursing are likely to improve patient experience ratings," said Kathleen E. Fitzpatrick Rosenbaum, PhD, RN, CCRN, of Yale University.
How do nursing factors affect HCAHPS ...
Tracking a protein’s fleeting shape changes
2024-04-17
Researchers at Weill Cornell Medicine have developed a powerful, new technique to generate “movies” of changing protein structures and speeds of up to 50 frames per second.
Senior author, Dr. Simon Scheuring, the Distinguished Professor of Anesthesiology Research at Weill Cornell Medicine and colleagues developed the new approach to gain a better understanding of how biological molecules change structurally over time. Although investigators in this field routinely image static proteins and other molecules finely ...
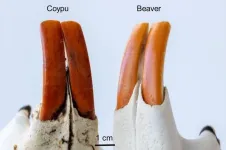
Study finds iron-rich enamel protects, but doesn’t color, rodents’ orange-brown incisors
2024-04-17
Chattering squirrels, charming coypus, and tail-slapping beavers — along with some other rodents — have orange-brown front teeth. Researchers have published high-resolution images of rodent incisors in ACS Nano, providing an atomic-level view of the teeth’s ingenious enamel and its coating. They discovered tiny pockets of iron-rich materials in the enamel that form a protective shield for the teeth but, importantly, don’t contribute to the orange-brown hue — new insights that could improve human dentistry.
Human and animal teeth are coated in a ...
Continuing efforts are addressing health disparities among Hispanic Latino people in U.S.
2024-04-17
DALLAS, April 17, 2024 — Language barriers, longstanding structural racism barriers, underrepresentation within the ranks of health care professionals and higher than average rates of poor health risk factors are among the alarming trends that continue to impede quality health care outcomes for Hispanic Latino people living in the United States. The American Heart Association, celebrating 100 years of lifesaving service as the world’s leading nonprofit organization focused on heart and brain health for all, is making strides ...
CHEST and APCCMPD announce recipient of collaborative fellow scholarship
2024-04-17
Glenview, Illinois – Esha Kapania, MD, will be the mentee for the inaugural year of the 2024 APCCMPD and CHEST Medical Educator Scholar Diversity Fellowship.
Designed to pair a fellow-in-training with an established medical educator, the unique scholarship was launched in August by the American College of Chest Physicians (CHEST) and the Association of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine Program Directors (APCCMPD) to improve diversity in pulmonary and critical care medical education.
The program focuses ...
E-tongue can detect white wine spoilage before humans can
2024-04-17
PULLMAN, Wash. – While the electronic tongue bears little physical resemblance to its namesake, the strand-like sensory probes of the “e-tongue” still outperformed human senses when detecting contaminated wine in a recent study.
In an experiment at Washington State University, the e-tongue identified signs of microorganisms in white wine within a week after contamination—four weeks before a human panel noticed the change in aroma. This was also before those microbes could be grown from the wine in a petri-dish. Winemakers traditionally rely on these two methods, sniffing the wine and petri-dish testing, to ...
Adults with congenital heart disease faced higher risk of abnormal heart rhythms
2024-04-17
Research Highlights:
Almost 1 in 5 adults with congenital heart disease living in Israel had or developed an abnormal heart rhythm over five years.
Adults with congenital heart disease who developed an irregular heart rhythm in the heart’s upper chambers faced a 65% increased risk of premature death.
The adults who developed an irregular heart rhythm in the heart’s lower chambers had double the risk of premature death.
Embargoed until 4 a.m. CT/5 a.m. ET Wednesday, April 17, 2024
DALLAS, April 17, 2024 — Almost 1 in 5 adults with congenital heart disease living in Israel had or developed an abnormal ...
A better view with new mid-infrared nanoscopy
2024-04-17
A team at the University of Tokyo have constructed an improved mid-infrared microscope, enabling them to see the structures inside living bacteria at the nanometer scale. Mid-infrared microscopy is typically limited by its low resolution, especially when compared to other microscopy techniques. This latest development produced images at 120 nanometers, which the researchers say is a thirtyfold improvement on the resolution of typical mid-infrared microscopes. Being able to view samples more clearly at this smaller scale can aid multiple fields of research, including into infectious diseases, and opens the way for developing ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
[Press-News.org] Challenges in Greenland marine research and insights and priorities for development of East Greenland marine and coastal environmentsA report on the first Greenland Marine Research Seminar and Workshop on Status and Development of East Greenland waters