(Press-News.org) About The Study: In this randomized clinical trial with 314 participants, self-administered acupressure with a brief knee health education program was efficacious and cost-effective in relieving knee pain and improving mobility in middle-aged and older adults with probable knee osteoarthritis.
Authors: Wing-Fai Yeung, Ph.D., of the Hong Kong Polytechnic University in Hong Kong, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.5830)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time http://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.5830?utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_term=041924
About JAMA Network Open: JAMA Network Open is an online-only open access general medical journal from the JAMA Network. On weekdays, the journal publishes peer-reviewed clinical research and commentary in more than 40 medical and health subject areas. Every article is free online from the day of publication.
END
Self-administered acupressure for probable knee osteoarthritis in middle-aged and older adults
JAMA Network Open
2024-04-19
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024 Communicator Award goes to “Cyber and the City” research team based in Tübingen
2024-04-19
This year’s Communicator Award presented by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG, German Research Foundation) and Stifterverband goes to an interdisciplinary research team consisting of one computer scientist and two cultural scholars, all of whom are based in Tübingen: Ulrike von Luxburg, Professor for the Theory of Machine Learning at the University of Tübingen, Tim Schaffarczik, doctoral researcher at the Institute of Historical and Cultural Anthropology, University of Tübingen, and Thomas Thiemeyer, Professor of Museum Studies, likewise at the Institute of ...
A new therapeutic target for traumatic brain injury
2024-04-19
SAN FRANCISCO—April 19, 2024—For the roughly 1.5 million Americans per year who survive a traumatic brain injury, health outcomes vary widely. Not only can these injuries lead to a loss of coordination, depression, impulsivity, and difficulty concentrating, but they come with an amplified risk for developing dementia in the future.
The glaring absence of treatments for such a widespread condition drove a team of scientists at Gladstone Institutes to uncover, on a molecular level, how traumatic brain injuries trigger neurodegeneration—and just as importantly, how to target that process to prevent long-term damage.
“We set out to ...
Cosmic rays streamed through Earth’s atmosphere 41,000 years ago
2024-04-19
Earth’s magnetic field cocoons our planet from the onslaught of cosmic radiation streaming through space while also shielding us from charged particles hurled outward by the sun. But the geomagnetic field is not stationary. Not only does magnetic north wobble, straying from true north (a geographically defined location), but occasionally, it flips. During these reversals, north becomes south, south becomes north, and in the process, the intensity of the magnetic field wanes.
But there’s also ...
ACP issues clinical recommendations for newer diabetes treatments
2024-04-19
Embargoed for release until 9:00 a.m. ET on Friday 19 April 2024
Embargoed Content from the Annals of Internal Medicine Breaking News Scientific Plenary at Internal Medicine 2024
Annals of Internal Medicine Tip Sheet
@Annalsofim
Below please find summaries of new articles that will be published in the next issue of Annals of Internal Medicine. The summaries are not intended to substitute for the full articles as a source of information. This information is under strict embargo and by taking it into possession, media representatives are committing ...
New insights into the connections between alcohol consumption and aggressive liver cancer
2024-04-19
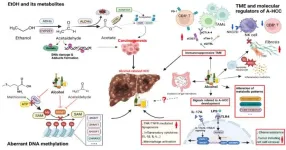
While heavy drinking is a well-established risk factor for liver cancer, the specific mechanisms by which alcohol contributes to A-HCC remain unclear.
This insightful review, published in Hepatology, provides a comprehensive summary of the pathogenesis, heterogeneity, preclinical approaches, epigenetic and genetic profiles of A-HCC. Compared to other types of liver cancer, A-HCC is often diagnosed at a later stage, when the disease is more advanced. This is partly due to a lack of readily available screening tools for individuals with alcohol-related liver disease (ALD).
"A-HCC is a serious public health concern," ...
Unraveling water mysteries beyond Earth
2024-04-19
The first clue for finding life on other planets is finding liquid water. The moons of Saturn and Jupiter like Enceladus, Ganymede, Europa, and Callisto are suspected of holding oceans of liquid water beneath icy crusts. Similarly, some exoplanets beyond our solar system likely host liquid water, crucial for habitability. But detecting water, when we can’t physically access these celestial bodies, poses challenges. Ice-penetrating radar, a geophysical tool, has proven capable of detecting liquid water ...
Signs of multiple sclerosis show up in blood years before symptoms
2024-04-19
In a discovery that could hasten treatment for patients with multiple sclerosis (MS), UC San Francisco scientists have discovered a harbinger in the blood of some people who later went on to develop the disease.
In about 1 in 10 cases of MS, the body begins producing a distinctive set of antibodies against its own proteins years before symptoms emerge. These autoantibodies appear to bind to both human cells and common pathogens, possibly explaining the immune attacks on the brain and spinal cord that are the hallmark of MS.
The findings were published in Nature Medicine on ...
Ghost particle on the scales
2024-04-19
In the 1930s, it turned out that neither the energy nor the momentum balance is correct in the radioactive beta decay of an atomic nucleus. This led to the postulate of "ghost particles" that "secretly" carry away energy and momentum. In 1956, experimental proof of such neutrinos was finally obtained. The challenge: neutrinos only interact with other particles of matter via the weak interaction that is also underlying the beta decay of an atomic nucleus. For this reason, hundreds of trillions of neutrinos from the cosmos, especially the sun, can pass through our bodies every second without causing any damage. Extremely ...
Light show in living cells
2024-04-19
Observing proteins precisely within cells is extremely important for many branches of research but has been a significant technical challenge - especially in living cells, as the required fluorescent labelling had to be individually attached to each protein. The research group led by Stefan Kubicek at CeMM has now overcome this hurdle: With a method called "vpCells," it is possible to label many proteins simultaneously, using five different fluorescent colours. This automated high-throughput approach, aided by AI-assisted image recognition, opens up entirely new applications in various disciplines, from fundamental cell biology to drug discovery. The study ...
Climate change will increase value of residential rooftop solar panels across US, study shows
2024-04-19
Graphic
Climate change will increase the future value of residential rooftop solar panels across the United States by up to 19% by the end of the century, according to a new University of Michigan-led study.
The study defines the value of solar, or VOS, as household-level financial benefits from electricity bill savings plus revenues from selling excess electricity to the grid—minus the initial installation costs.
For many U.S. households, increased earnings from residential rooftop ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
[Press-News.org] Self-administered acupressure for probable knee osteoarthritis in middle-aged and older adultsJAMA Network Open