(Press-News.org) Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the second most common cancer in the United States. This highlights the importance of early detection and treatment of precancerous lesions like large polyps. Endoscopy offers a minimally invasive approach to removing these polyps, reducing the need for traditional surgery.
This review, published in eGastroenterology, explores advancements in endoscopic resection techniques, specifically Endoscopic Mucosal Resection (EMR) and Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection (ESD).
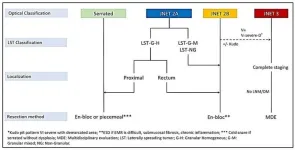
Complete removal of large polyps (>10 mm) is crucial to prevent progression to CRC. Piecemeal resection during endoscopic procedures can increase the risk of recurrence. EMR, the standard approach for large, non-pedunculated polyps, utilizes submucosal injection to create a cushion, allowing for safer and more complete resection with a snare. ESD, a more advanced technique, is employed for complex polyps with a higher risk of submucosal invasion. It involves creating a precise incision and dissecting the polyp layer by layer from the underlying tissue.
Both EMR and ESD offer advantages over surgery. They are less invasive, require shorter recovery times, and are associated with fewer complications. However, selecting the most suitable technique depends on various factors, including polyp size, morphology, location, and depth of submucosal invasion. EMR is generally preferred for simpler polyps, while ESD is indicated for those with features suggestive of deeper invasion.
ESD offers several benefits over EMR. It achieves higher rates of en-bloc resection (removing the entire polyp in one piece), leading to more accurate histological assessment and a lower risk of recurrence. However, ESD is a more complex and time-consuming procedure requiring hospitalization and carries a slightly higher risk of complications. Endoscopic expertise is paramount for successful ESD, with studies showing a significant improvement in success rates with increasing experience.
The choice between EMR and ESD should be individualized based on the patient's specific needs, polyp characteristics, and the available expertise at the treatment center. In some cases, particularly in facilities with limited ESD experience or when delays due to complex procedures could outweigh the benefits, EMR might be the preferred approach.
In conclusion, EMR and ESD are valuable endoscopic techniques for managing large colorectal polyps. Selecting the most appropriate procedure requires careful consideration of individual factors and the endoscopist's skillset. Ongoing research will refine these techniques and guide optimal treatment decisions for patients with precancerous colorectal lesions.
See the article:
Taghiakbari M, Kim DHD, Djinbachian R, et al. Endoscopic resection of large non-pedunculated colorectal polyps: current standards of treatment. eGastroenterology
2024;2:e100025. doi:10.1136/egastro-2023-100025
About eGastroenterology
eGastroenterology is a new, open-access, and open peer-reviewed BMJ Journal, which focuses on basic, clinical, translational, and evidence-based medicine research in all areas of gastroenterology (including hepatology, pancreatology, esophagology, and gastrointestinal surgery).
For more information, please visit: egastroenterology.bmj.com and follow us on Twitter (@eGastro_BMJ).
Sign-up to Email Alerts for eGastroenterology: https://emails.bmj.com/k/Bmj/jausu/egastroenterology
END
The Speech Accessibility Project, which aims to make automatic speech recognition technology more accessible to people with speech differences and disabilities, is now sharing some of its voice recordings and related data with universities, nonprofits and companies.
The project team is accepting signed data use agreements and one-page proposals for 211 recordings of people with Parkinson’s. The download also includes text of the original speech prompts and a transcript of the participants’ responses. A subset includes annotations ...
DALLAS, April 22, 2024 — Scientific researchers in Missouri and Virginia have been awarded nearly $1.4 million each in grants to study ways to extend the life expectancy and improve the quality of life for children with a transplanted heart. These two research awards mark the latest round of funding for a joint $3 million scientific research initiative between the American Heart Association, celebrating 100 years of lifesaving service as the world’s leading nonprofit organization focused on heart and brain health for all, and Enduring Hearts, the only non-profit organization solely dedicated ...
A University of Melbourne researcher has spotted a rare evolutionary phenomenon happening rapidly in real time in bats living in the Solomon Islands.
Dr Tyrone Lavery reports in a paper published in Evolution that two groups of leaf-nosed bats with vastly different body sizes that were thought to be separate species are an example of a rare type of parallel evolution. Parallel evolution is when different populations living in similar environments evolve similar features independently.
The smaller bat, Hipposideros diadema, is found across its six main islands and many smaller islands. It is ...
The SARS-CoV-2 virus that causes COVID has the unsettling ability of often generating variants of itself. Other viruses also mutate, but as SARS-CoV-2 quickly spread throughout the entire human population during the pandemic, killing millions, the virus’ dynamic evolution posed a serious problem: it repeatedly challenged our bodies’ immune response fighting the virus and hindered the process of getting updated vaccines ready.
Understanding the genetic mechanism fueling SARS-CoV-2’s ability to generate variants can go a long way in keeping COVID at bay. In this study published in Nature Microbiology, researchers at Baylor College of Medicine and collaborating institutions developed ...
Governments in the Mesoamerican Reef region are exploring the use of nature-based solutions to strengthen coral health and societal benefits for coastal communities. A new study led by Stanford researchers in collaboration with scientists from the World Wildlife Fund, the Healthy Reefs Initiative, and others from the Smart Coasts project quantified the outcomes of different watershed interventions to support coral health at regional versus national scales, and identified target areas that could improve both ecosystem and societal benefits nationally and across the region.
The nature-based approaches evaluated as key ...
An international team led by researchers at the University of Toronto has mapped the movement of proteins encoded by the yeast genome throughout its cell cycle. This is the first time that all the proteins of an organism have been tracked across the cell cycle, which required a combination of deep learning and high-throughput microscopy.
The team applied two convolutional neural networks, or algorithms, called DeepLoc and CycleNet, to analyze images of millions of live yeast cells. The result was a comprehensive map identifying where proteins are located and how they move and change in abundance ...
Physical cues in the womb, and not just genetics, influence the normal development of neural crest cells, the embryonic stem cells that form facial features, finds a new study led by UCL researchers.
The study published in Nature Cell Biology found that an increase in hydrostatic pressure sensed by the embryo can hinder the healthy development of facial features in mouse and frog embryos and in human embryoids (cell structures grown in the lab from human stem cells), suggesting that differences in pressure might affect the risk of facial malformations.
The ...
Artificial intelligence (AI) can quickly and accurately predict the path and intensity of major storms, a new study has demonstrated.
The research, based on an analysis of November 2023’s Storm Ciaran, suggests weather forecasts that use machine learning can produce predictions of similar accuracy to traditional forecasts faster, cheaper, and using less computational power.
Published in npj Climate and Atmospheric Science, the University of Reading study highlights the rapid progress and transformative potential of AI in weather prediction.
Professor Andrew Charlton-Perez, ...
Feedback loop that is melting ice shelves in West Antarctica revealed
New research has uncovered a feedback loop that may be accelerating the melting of the floating portions of the West Antarctic Ice Sheet, pushing up global sea levels.
The study, published in Science Advances, sheds new light on the mechanisms driving the melting of ice shelves beneath the surface of the ocean, which have been unclear until now.
The West Antarctic Ice Sheet has been losing mass in recent decades, contributing to global sea level rise. If it were to melt entirely, global sea levels would rise by around five meters.
It’s known that Circumpolar Deep Water (CDW), ...
Long-term daily use of aspirin can help to prevent the development and progression of colorectal cancer, but the mechanisms involved have been unclear. New research has revealed that aspirin may exert these protective effects by boosting certain aspects of the body’s immune response against cancer cells. The findings are published by Wiley online in CANCER, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Cancer Society.
To investigate the effects of aspirin (a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug) on colorectal cancer, investigators in Italy obtained tissue samples from 238 patients who underwent surgery for colorectal cancer in 2015–2019, 12% of whom were aspirin ...