(Press-News.org) Florida Atlantic University Christine E. Lynn College of Nursing’s Canines Providing Assistance to Wounded Warriors (C-P.A.W.W.) has received a new grant from the Human Animal Bond Research Institute (HABRI) for research that investigates the contribution of pet dog ownership to resilience and well-being in adolescent children of military families.
The grant was awarded to a team of researchers led by Laurie Martinez, Ph.D., an assistant professor, FAU College of Nursing; and co-led by Cheryl A. Krause-Parello, Ph.D., associate vice president for research, FAU Division of Research and a research professor in the College of Nursing.
This important study will provide insight into how pet dogs support well-being and resilience in adolescents while a parent or guardian is in the National Guard, Reserve, is a veteran or on active duty. Adolescents in military families face ubiquitous teen stressors and unique military challenges such as parental deployment and frequent relocations. Dog ownership is suggested as a contextual resource of strength to counter the effects of adolescent military-specific stressors and promote positive outcomes.
“With approximately 66 percent of households in the United States owning a pet, family military pet dogs are an understudied innovative resource that may mitigate military-connected adolescent stress and nurture resilience and well-being,” said Martinez, principal investigator of the study. “Exploring how pet dogs can serve as conduits to better mental health outcomes opens new pathways for daily health promotion.”
This longitudinal, observational pilot study will conduct scientifically validated surveys to investigate the role of pet dogs in the lives of military adolescents between the ages of 12 to 18. Researchers expect to find higher levels of resilience, improved well-being, reduced depression, and lower perceived stress in dog-owning adolescents compared to military adolescents who do not own a pet dog.
“We hope that this research will inform policies and programs aimed at improving health for children in military families,” said Steven Feldman, president, HABRI.
- FAU -
About C-P.A.W.W.:
Canines Providing Assistance to Wounded Warriors is a health research initiative for veterans in FAU’s Christine E. Lynn College of Nursing. The C-P.A.W.W. initiative was established in October 2013 to advance the health and well-being of members of the armed forces. C-P.A.W.W. is committed to the evolution of nursing knowledge within the context of research, education and practice in order to better assist the military population. Its mission is to comprehensively advance interdisciplinary research, education and practice protocols for wounded warriors and veterans through the development of evidence-based and restorative interventions, to support military-related health initiatives by building community partnerships, to investigate therapeutic interventions--particularly those involving canine assistance-- that positively influence health outcomes, and to emphasize system planning, innovative public policymaking, and thorough protocols of care development for the armed forces. To learn more, visit https://nursing.fau.edu/outreach/c-paww/.
About the Christine E. Lynn College of Nursing:
FAU’s Christine E. Lynn College of Nursing is nationally and internationally known for its excellence and philosophy of caring science. In 2024, the College was ranked No. 4 for the Family Nurse Practitioner Master’s concentration nationwide by U.S. News and World Report, No. 17 for Best Online Master’s in Nursing Administration and Financial Leadership Programs and No. 32 for the Best Online Master’s in Nursing Programs. In 2023, FAU graduates on the Boca Raton campus earned an 81% pass rate on the National Council Licensure Examination for Registered Nurses (NCLEX-RN®) and a 100% AGNP Certification Pass Rate. The baccalaureate, master’s and DNP programs at Florida Atlantic University’s Christine E. Lynn College of Nursing are accredited by the Commission on Collegiate Nursing Education. The College is the only one in the U.S. to have all degree programs endorsed by the American Holistic Nursing Credentialing Corporation.
About Florida Atlantic University:
Florida Atlantic University, established in 1961, officially opened its doors in 1964 as the fifth public university in Florida. Today, the University serves more than 30,000 undergraduate and graduate students across six campuses located along the southeast Florida coast. In recent years, the University has doubled its research expenditures and outpaced its peers in student achievement rates. Through the coexistence of access and excellence, FAU embodies an innovative model where traditional achievement gaps vanish. FAU is designated a Hispanic-serving institution, ranked as a top public university by U.S. News & World Report and a High Research Activity institution by the Carnegie Foundation for the Advancement of Teaching. For more information, visit www.fau.edu.
About HABRI:
HABRI is a not-for-profit organization that funds innovative scientific research to document the health benefits of companion animals; educates the public about human-animal bond research; and advocates for the beneficial role of companion animals in society. For more information, please visit http://www.habri.org.
END
DURHAM, N.C. – The unique circumstances arising from the COVID-19 pandemic altered a long-held convention that doctors provide care regardless of personal risk.
In a study assessing doctors’ tolerance for refusing care to COVID-19 patients, Duke Health researchers identified a growing acceptance to withhold care because of safety concerns.
“All the papers throughout history have shown that physicians broadly believed they should treat infectious disease patients,” said the study’s lead author, Braylee Grisel, a fourth-year student at Duke University ...
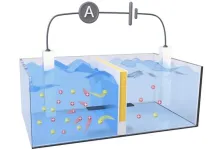
Estuaries — where freshwater rivers meet the salty sea — are great locations for birdwatching and kayaking. In these areas, waters containing different salt concentrations mix and may be sources of sustainable, “blue” osmotic energy. Researchers in ACS Energy Letters report creating a semipermeable membrane that harvests osmotic energy from salt gradients and converts it to electricity. The new design had an output power density more than two times higher than commercial membranes in lab demonstrations.
Osmotic energy can be generated anywhere salt gradients are ...
In February, OpenAI released videos created by its generative artificial intelligence program Sora. The strikingly realistic content, produced via simple text prompts, is the latest breakthrough for companies demonstrating the capabilities of AI technology. It also raised concerns about generative AI’s potential to enable the creation of misleading and deceiving content on a massive scale. According to new research from Drexel University, current methods for detecting manipulated digital media will not be effective against AI-generated video; but a machine-learning approach could be the key to unmasking these synthetic creations.
In a paper accepted ...
PULLMAN, Wash. – Political conservatives who watched a documentary on Syrian refugees with a virtual reality headset had far more sympathy for the people depicted in the film than those who viewed the same film on a two-dimensional computer screen.
Higher sympathy levels among the conservatives who watched the VR version of the documentary, “Clouds over Sidra,” resulted in a greater willingness to donate to the crisis, according to a study on the research published in New Media & Society.
Liberal participants in the study reported high levels of sympathy and ...
Setting the stage for a new era of immersive displays, researchers are one step closer to mixing the real and virtual worlds in an ordinary pair of eyeglasses using high-definition 3D holographic images, according to a study led by Princeton University researchers.
Holographic images have real depth because they are three dimensional, whereas monitors merely simulate depth on a 2D screen. Because we see in three dimensions, holographic images could be integrated seamlessly into our normal view of the everyday world.
The result is a virtual and augmented reality display that has the potential to be truly immersive, the kind where you can move your head ...
The need for sustainable and environment-friendly solutions has accelerated the global demand for green and renewable technologies. In this regard, semiconductor photocatalysts have emerged as an attractive solution, owing to their potential in mitigating pollutants and harnessing solar energy efficiently. Photocatalysts are materials that initiate chemical reactions when exposed to light. Despite their progress, commonly used photocatalysts suffer from reduced photocatalytic activity and a narrow operation range within the visible ...
Researchers at the Centre for Genomic Regulation in Barcelona and the University of Cologne in Germany have developed a new experimental strategy to tackle scarring and fibrosis. Experiments with patient-derived human cells and animal models showed the strategy was effective, non-toxic and its effects reversible. The findings are published today in the journal Nature Communications.
Scarring occurs from the secretion and accumulation of various components – primarily proteins known as collagens – into the space between individual cells, usually occurring as a response to injury or damage. Excessive collagen secretion can also cause the buildup of fibrotic ...
A new collaboration brings together a world-leading interdisciplinary team with skills across quantum computing, genomics, and advanced algorithms. They aim to tackle one of the most challenging computational problems in genomic science: building, augmenting and analysing pangenomic datasets for large population samples. Their project sits at frontiers of research in both biomedical science and quantum computing.
The project, which involves researchers based at the University of Cambridge, the Wellcome Sanger Institute and EMBL’s European ...
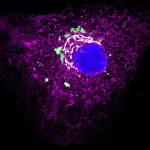
When pathogens invade the body, the immune system must react immediately to prevent or contain an infection. But how do our defence cells stay ready when no attacker is in sight? Scientists from Vienna have found a surprising explanation: They are constantly stimulated by healthy tissue. This keeps them active and ready to respond to pathogens. Based on this insight, future medications could be devised to selectively enhance our immune system’s attention. The study has been published in the journal Nature Immunology (DOI: 10.1038/s41590-024-01804-1).
Communication is crucial in immune defence. When ...
“Our new study shows that renewable-scarce countries like parts of the EU, Japan and South Korea could save between 18 to 38 percent in production costs”, explains Philipp Verpoort, scientist at the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research (PIK) and lead author of the study published in Nature Energy. “They could do so by relocating their production of industrial basic materials like green steel and chemicals based on green hydrogen to countries where renewable energy is cheap.” The use of renewable electricity and green hydrogen is ...