(Press-News.org) Living at higher altitudes in India is linked to an increased risk of stunted growth, with children living in homes 2000 metres or more above sea level 40% more at risk than those living 1000 metres below, finds research published in the open access journal BMJ Nutrition Prevention & Health.
Children living in rural areas seem to be the most vulnerable, prompting the researchers to advocate prioritising nutritional programmes in hilly and mountainous regions of the country.
Despite various initiatives, childhood stunting, caused by chronic malnutrition, remains a major public health challenge in India, affecting over a third of 5-year olds, note the researchers.
While research from other countries indicates a link between residential altitude and stunting, it’s not clear if this might also be applicable in India, where a substantial number of people live more than 2500 metres above sea level.
To explore this further, the researchers drew on data from the 2015–16 National Family Health Survey (NFHS-4), a nationally representative household survey of India. Some 167,555 children under the age of 5 from across the country were included in the analysis.
GPS data were used to categorise altitude level while the World Health Organization (WHO) standard was used to define stunting.
Most (98%;164,874) of the children lived less than 1000 m above sea level; 1.4% (2346) lived between 1000 and 1999m above sea level; and 0.2% (335) lived at or above 2000m. Seven out of 10 lived in rural areas.
The overall prevalence of stunting among these children was 36%, with a higher prevalence among children aged 18–59 months (41%) than among those under 18 months of age (27%).
Stunting was more common among children of third or higher birth order (44%) than it was among firstborns (30%). And stunting rates were even higher among those children who had been small or very small (45%) at birth.
Mother’s education emerged as an influential factor: stunting prevalence fell as maternal educational attainment rose. The proportion of children whose mothers had had no schooling was more than double that of children whose mothers had had a higher education: 48% vs 21%.
Other protective factors included elements of antenatal care, such as clinic visits, tetanus vaccination, and iron and folic acid supplements; proximity to health facilities; and not belonging to a particular caste or indigenous tribe.
This is an observational study that captured a snapshot of the population at a specific point in time, making it difficult to confirm altitude as a cause of stunting, acknowledge the researchers.
But there are plausible explanations for their findings, they suggest. For example, chronic exposure to high altitude can reduce appetite, restrict oxygen delivery to tissues, and limit nutrient absorption.
Food insecurity also tends to be greater at higher elevations where crop yields are lower and the climate is harsher. Similarly, healthcare provision, including implementing nutritional programmes, and healthcare access are also more challenging, they suggest.
“In summary, concerted efforts are needed across health and nutrition sectors to address stunting, tailored to focus on higher-risk children in vulnerable areas,” they conclude.
“A multipronged approach should combine reproductive health initiatives, women’s nutrition programmes, infant and young child feeding interventions, and food security measures. Continued research, monitoring, and evaluation will be key to guide evidence-based policies and targeted action to ensure every Indian child has the opportunity for healthy growth and development.”
Professor Sumantra Ray, Executive Director of the NNEdPro Global Institute for Food, Nutrition and Health, which co-owns BMJ Nutrition Prevention & Health with BMJ, adds:
“In recent decades public health interventions in India have effectively tackled previously prevalent nutritional problems, such as Iodine deficiency, which are associated with living at higher altitudes.
“But this study highlights the complexities of malnutrition in hilly regions where wider determinants of malnutrition among the under 5s require further study to elucidate the relative contributions of heredity, environment, lifestyle, and socioeconomic factors.”
END
Living at higher altitudes in India linked to increased risk of childhood stunting
Children living at 2000+ m above sea level 40% more at risk than those living 1000m below. Children in rural areas seem to be the most vulnerable
2024-04-26
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Scientists discover a new signaling pathway and design a novel drug for liver fibrosis
2024-04-26
A healthy liver filters all the blood in your body, breaks down toxins and digests fats. It produces collagen to repair damaged cells when the liver is injured. However, a liver can produce too much collagen when an excess accumulation of fat causes chronic inflammation, a condition called metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH). In an advanced state, MASH can lead to cirrhosis, liver cancer and liver-related death.
The cells that produce collagen in livers are called hepatic stellate cells (HSC). In a new paper published in Cell ...
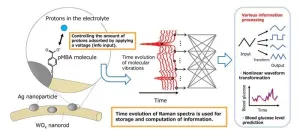
High-precision blood glucose level prediction achieved by few-molecule reservoir computing
2024-04-26
1. A collaborative research team from NIMS and Tokyo University of Science has successfully developed a cutting-edge artificial intelligence (AI) device that executes brain-like information processing through few-molecule reservoir computing. This innovation utilizes the molecular vibrations of a select number of organic molecules. By applying this device for the blood glucose level prediction in patients with diabetes, it has significantly outperformed existing AI devices in terms of prediction accuracy.
2. With the expansion of machine learning applications in various industries, there's an escalating demand for AI devices that are not only highly ...
The importance of communicating to the public during a pandemic, and the personal risk it can lead to
2024-04-26
**ECCMID has now changed its name to ESCMID Global, please credit ESCMID Global Congress (formerly ECCMID, Barcelona, Spain, 27-30 April) in all future stories**
In global crises like the COVID-19 pandemic, it is vital that scientists step forward to engage with the public and help deliver medical and scientific advice in a friendly, digestible and open format. While the traditional way for scientists to do this is by responding to media requests, alternatives, including collaborating with illustrators and local communities, will be discussed in a new ...
Improving health communication to save lives during epidemics
2024-04-26
During epidemics of Ebola, COVID-19, Zika and other public health emergencies, effective communication of public health messages is crucial to control the spread of disease, maintain public trust, and encourage compliance with health measures. In a new evidence review to be given at this year’s ESCMID Global Congress (formerly ECCMID) in Barcelona, Spain (27-30 April), Dr Benjamin Djoudalbaye from the Africa Centres for Disease Control and Prevention (AFRICA CDC) in Ethiopia, will discuss the challenges and lessons learnt from public health communication strategies during multiple epidemics across ...
Antimicrobial-resistant hospital infections remain at least 12% above pre-pandemic levels, major US study finds
2024-04-26
Hospital-related infections resistant to carbapenems, considered the antibiotics of last resort for treating severe infections, remain at least 35% higher than before the pandemic.
Findings also reveal that during the pandemic, hospitals experiencing surges due to high volumes of severely ill COVID-19 patients had the greatest increases in hospital-acquired antimicrobial-resistant infections, as did larger hospitals with increased bed capacity.
**ECCMID has now changed its name to ESCMID Global, please credit ...
German study finds antibiotic use in patients hospitalised with COVID-19 appears to have no beneficial effect on clinical outcomes
2024-04-26
Findings underscore need for rational antibiotic use especially during viral pandemics like COVID-19.
*ECCMID has now changed its name to ESCMID Global, please credit ESCMID Global Congress (formerly ECCMID, Barcelona, Spain, 27-30 April) in all future stories**
Antibiotic treatment of adults hospitalised with moderate COVID-19 is associated with clinical deterioration, despite the drugs being given to over 40% of patients, according to new research being presented at this year’s ESCMID Global Congress (formerly ECCMID) in Barcelona, Spain (27-30 April)
The findings underscore the need to discourage indiscriminate prescribing ...
Targeting specific protein regions offers a new treatment approach in medulloblastoma
2024-04-25
Targeting specific protein regions offers a new treatment approach in medulloblastoma
Scientists at St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital discovered a new compound that selectively targets parts of a cancer-related protein, EP300/CBP, in Group 3 medulloblastoma.
(MEMPHIS, Tenn. – April 25, 2024) Medulloblastoma (the most common malignant childhood brain tumor) is separated into four molecular groups, with Group 3 bearing the worst prognosis. By studying EP300 and CBP, critical proteins in Group 3 medulloblastoma cells, scientists at St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital designed a way to enhance anti-tumor ...
$2.7 million grant to explore hypoxia’s impact on blood stem cells
2024-04-25
INDIANAPOLIS — Indiana University School of Medicine scientists are on a mission to understand why hematopoietic stem cells, responsible for producing all types of mature blood cells, exhibit better responses in a low-oxygen environment within the bone marrow, also known as hypoxia. Their discoveries and innovative approaches could influence treatment options like bone marrow transplantation for conditions such as bone marrow failure and rare blood diseases involving gene corrected stem cells.
A new four-year, ...
Cardiovascular societies propel plans forward for a new American Board of Cardiovascular Medicine
2024-04-25
CV Societies Propel Plans Forward for a New American Board of Cardiovascular Medicine
Planning enters next phase as ABMS announces open comment period
WASHINGTON (April 25, 2024) – Efforts by the American College of Cardiology, American Heart Association, Heart Failure Society of America, Heart Rhythm Society and The Society for Cardiovascular Angiography & Interventions to create a new, independent American Board of Cardiovascular Medicine under the American Board of Medical Specialties (ABMS) are closer to becoming a reality with the creation of a formal Board of Directors and the announcement by the ABMS Advisory Board on Specialty Board Development of an open comment ...
Hebrew SeniorLife selected for nationwide collaborative to accelerate system-wide spread of age-friendly care for older adults
2024-04-25
Hebrew SeniorLife is among the 30 US health systems nationally, and the only one in Massachusetts selected to participate in the Age-Friendly System-Wide Spread Collaborative.
This first-of-its-kind Collaborative, led by the Institute for Healthcare Improvement (IHI), will accelerate and spread the adoption of evidence-based, high-quality care for older adults across all of their sites and care settings.
The Collaborative is the latest endeavor of the Age-Friendly Health Systems initiative, which promotes four evidence-based elements of high-quality care known as ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
GLP-1RA switching and treatment persistence in adults without diabetes
Gnaw-y by nature: Researchers discover neural circuit that rewards gnawing behavior in rodents
Research alert: How one receptor can help — or hurt — your blood vessels
Lamprey-inspired amphibious suction disc with hybrid adhesion mechanism
A domain generalization method for EEG based on domain-invariant feature and data augmentation
Bionic wearable ECG with multimodal large language models: coherent temporal modeling for early ischemia warning and reperfusion risk stratification
JMIR Publications partners with the University of Turku for unlimited OA publishing
Strange cosmic burst from colliding galaxies shines light on heavy elements
Press program now available for the world's largest physics meeting
New release: Wiley’s Mass Spectra of Designer Drugs 2026 expands coverage of emerging novel psychoactive substances
Exposure to life-limiting heat has soared around the planet
New AI agent could transform how scientists study weather and climate
New study sheds light on protein landscape crucial for plant life
New study finds deep ocean microbes already prepared to tackle climate change
ARLIS partners with industry leaders to improve safety of quantum computers
Modernization can increase differences between cultures
Cannabis intoxication disrupts many types of memory
Heat does not reduce prosociality
Advancing brain–computer interfaces for rehabilitation and assistive technologies
Detecting Alzheimer's with DNA aptamers—new tool for an easy blood test
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal study develops radiomics model to predict secondary decompressive craniectomy
New molecular switch that boosts tooth regeneration discovered
Jeonbuk National University researchers track mineral growth on bioorganic coatings in real time at nanoscale
Convergence in the Canopy: Why the Gracixalus weii treefrog sounds like a songbird
Subway systems are uncomfortably hot — and worsening
Granular activated carbon-sorbed PFAS can be used to extract lithium from brine
[Press-News.org] Living at higher altitudes in India linked to increased risk of childhood stuntingChildren living at 2000+ m above sea level 40% more at risk than those living 1000m below. Children in rural areas seem to be the most vulnerable