(Press-News.org) About The Study: The findings of this study of 26,000 participants from four large U.S. studies suggest that both individual- and area-level social determinants of health may be considered in future development of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease risk assessment tools, particularly among Black individuals.
Authors: Yiyi Zhang, Ph.D., of Columbia University Medical Center in New York, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.8584)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time http://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.8584?utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_term=042624
About JAMA Network Open: JAMA Network Open is an online-only open access general medical journal from the JAMA Network. On weekdays, the journal publishes peer-reviewed clinical research and commentary in more than 40 medical and health subject areas. Every article is free online from the day of publication.
END
Cardiovascular risk associated with social determinants of health at individual and area levels
JAMA Network Open
2024-04-26
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Experimental NIH malaria monoclonal antibody protective in Malian children
2024-04-26
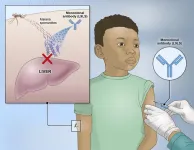
One injected dose of an experimental malaria monoclonal antibody was 77% effective against malaria disease in children in Mali during the country’s six-month malaria season, according to the results of a mid-stage clinical trial. The trial assessed an investigational monoclonal antibody developed by scientists at the National Institutes of Health (NIH), and results appear in The New England Journal of Medicine.
“A long-acting monoclonal antibody delivered at a single health care visit that rapidly provides high-level protection against malaria in these vulnerable populations would fulfill an unmet public health need,” said Dr. Jeanne ...
Energy trades could help resolve Nile conflict
2024-04-26
Scientists have shed light on a new, transformative approach that could help resolve a dispute over the Nile river’s water resources.
The Nile is one of the longest rivers globally and spreads over 11 countries in East Africa, supplying water, energy production, environmental quality and cultural wealth. However, the use of Nile resources has been a long-standing source of tension, often overshadowing opportunities for cooperation and mutual benefit.
But as the demand for energy, water, and food in Africa is steadily increasing, the study, led by The University of Manchester in collaboration with regional organisations, offers a glimmer of hope at a resolution.
The research, ...
Homelessness a major issue for many patients in the emergency department
2024-04-26
Housing insecurity is an issue for 1 in 20 patients who go to emergency departments at major medical centers in the Southeast, according to a Vanderbilt University Medical Center (VUMC) study published in JAMA Network Open.
These patients were more likely to present with a chief complaint of suicide, to be uninsured, and to have multiple visits during the study period from Jan. 5 to May 16, 2023.
“This points to the importance of prioritizing mental health care and homeless ...
Undocumented Latinx patients got COVID-19 vaccine at same rate as US citizens
2024-04-26
For undocumented Latinx patients who sought care in the emergency room during the pandemic, the reported rate of having received the COVID-19 vaccine was found to be the same as U.S. citizens, a new UCLA Health study found. These findings surprised researchers, given that COVID-19 disproportionately affected the Latinx community in infections, hospitalizations, and death.
Dr. Jesus R. Torres, lead study author and emergency medicine physician at UCLA Health, aimed to study undocumented people because they tend not to be identified in existing research even though they comprise approximately 3% of the ...
ETRI develops an automated benchmark for labguage-based task planners
2024-04-26
If instructed to “Place a cooled apple into the microwave,” how would a robot respond?
Initially, the robot would need to locate an apple, pick it up, find the refrigerator, open its door, and place the apple inside. Subsequently, it would close the refrigerator door, reopen it to retrieve the cooled apple, pick up the apple again, and close the door. Following this, the robot would need to locate the microwave, open its door, place the apple inside, and then close the microwave door. Evaluating how well these steps are executed exemplifies the essence of ...
Revolutionizing memory technology: multiferroic nanodots for low-power magnetic storage
2024-04-26
Traditional memory devices are volatile and the current non-volatile ones rely on either ferromagnetic or ferroelectric materials for data storage. In ferromagnetic devices, data is written or stored by aligning magnetic moments, while in ferroelectric devices, data storage relies on the alignment of electric dipoles. However, generating and manipulating magnetic fields is energy-intensive, and in ferroelectric memory devices, reading data destroys the polarized state, requiring the memory cell to be re-writing.
Multiferroic materials, which contain both ferroelectric and ferromagnetic orders, offer a promising solution for more efficient ...
Researchers propose groundbreaking framework for future network systems
2024-04-26
In a new study published in Engineering, Academician Wu Jiangxing’s research team unveils a theoretical framework that could revolutionize the landscape of network systems and architectures. The paper titled “Theoretical Framework for a Polymorphic Network Environment,” addresses a fundamental challenge in network design—achieving global scalability while accommodating the diverse needs of evolving services.
For decades, the quest for an ideal network capable of seamlessly scaling across various dimensions has remained elusive. The team, however, has identified a critical barrier known as the “impossible service-level ...
New favorite—smart electric wheel drive tractor: realizes efficient drive with ingenious structure and intelligent control
2024-04-26
Electric tractors are intended to be used in the field instead of traditional fuel tractors and can be used in greenhouse planting, indoor farming, mountainous operations, and other special operating scenarios. Unlike traditional fuel tractors, electric tractors have no exhaust emissions, rapid drive system response, flexible power output, or other advantages. These scenarios require electric tractors to be able to adapt to complex drive and operating environments, putting higher requirements on the design of electric tractors and their control systems. Therefore, ...
Using stem cell-derived heart muscle cells to advance heart regenerative therapy
2024-04-26
Regenerative heart therapies involve transplanting cardiac muscle cells into damaged areas of the heart to recover lost function. However, the risk of arrhythmias following this procedure is reportedly high. In a recent study, researchers from Japan tested a novel approach that involves injecting ‘cardiac spheroids,’ cultured from human stem cells, directly into damaged ventricles. The highly positive outcomes observed in primate models highlight the potential of this strategy.
Cardiovascular diseases are still among the top causes of death worldwide, and especially prevalent ...
Damon Runyon Cancer Research Foundation awards Quantitative Biology Fellowships to four cutting-edge scientists
2024-04-26
Damon Runyon has announced its 2024 Quantitative Biology Fellows, four exceptional early-career scientists who are bringing cutting-edge computational tools to bear on some of the most important questions in cancer biology. From the packaging of DNA to mechanisms of chemotherapy resistance, their projects aim to shed light on these fundamental questions through large-scale data collection, mathematical modeling, and quantitative analysis.
“In the five years since we named the first class of Quantitative Biology Fellows, it has only become more evident that these scientists bring fresh perspectives and creative ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Convergence in the Canopy: Why the Gracixalus weii treefrog sounds like a songbird
Subway systems are uncomfortably hot — and worsening
Granular activated carbon-sorbed PFAS can be used to extract lithium from brine
How AI is integrated into clinical workflow lowers medical liability perception
New biotech company to accelerate treatments for heart disease
One gene makes the difference: research team achieves breakthrough in breeding winter-hardy faba beans
Predicting brain health with a smartwatch
How boron helps to produce key proteins for new cancer therapies
Writing the catalog of plasma membrane repair proteins
A comprehensive review charts how psychiatry could finally diagnose what it actually treats
Thousands of genetic variants shape epilepsy risk, and most remain hidden
First comprehensive sex-specific atlas of GLP-1 in the mouse brain reveals why blockbuster weight-loss drugs may work differently in females and males
When rats run, their gut bacteria rewrite the chemical conversation with the brain
Movies reconstructed from mouse brain activity
Subglacial weathering may have slowed Earth's escape from snowball Earth
Simple test could transform time to endometriosis diagnosis
Why ‘being squeezed’ helps breast cancer cells to thrive
Mpox immune test validated during Rwandan outbreak
Scientists pinpoint protein shapes that track Alzheimer’s progression
Researchers achieve efficient bicarbonate-mediated integrated capture and electrolysis of carbon dioxide
Study reveals ancient needles and awls served many purposes
Key protein SYFO2 enables 'self-fertilization’ of leguminous plants
AI tool streamlines drug synthesis
Turning orchard waste into climate solutions: A simple method boosts biochar carbon storage
New ACP papers say health care must be more accessible and inclusive for patients and physicians with disabilities
Moisture powered materials could make cleaning CO₂ from air more efficient
Scientists identify the gatekeeper of retinal progenitor cell identity
American Indian and Alaska native peoples experience higher rates of fatal police violence in and around reservations
Research alert: Long-read genome sequencing uncovers new autism gene variants
Genetic mapping of Baltic Sea herring important for sustainable fishing
[Press-News.org] Cardiovascular risk associated with social determinants of health at individual and area levelsJAMA Network Open