(Press-News.org) PULLMAN, Wash. – While increasingly visible among adults, polyamory also exists among adolescents, and as a new study indicates, so does the stigma that can come with it.
A Washington State University study of 323 youth ages 12 to 17 at an LGBTQ+ summer camp found that 54, or about 16.7%, identified as polyamorous or ambiamorous, meaning they were open to either monogamous or polyamorous relationships. These “poly” and “ambi” youth reported higher levels of depressive symptoms than their LGBTQ+ peers.
The study, one of the first to investigate polyamorous relationships in youth, was published in the journal Psychology & Sexuality.
“It was notable that many of the polyamorous teens said they wouldn't feel safe being out in their home communities,” said study author Traci Gillig, a WSU researcher. “They felt like they would be misunderstood or that people have stereotypes or judgments around what it means for them to be poly, like that they are promiscuous or don’t perceive cheating as a problem.”
Polyamory is a relationship structure that involves having more than one romantic partner at the same time with the consent and knowledge of all the partners, so as with monogamous relationships, the secrecy of cheating is considered a breach of trust. Again similar to monogamy, polyamory is primarily about relationships and does not necessarily have to involve sex at all.
This study was limited to a camp for LGBTQ+ youth called Brave Trails, which likely indicates the adolescents came from more accepting families, Gillig noted. However, 30 adolescents still reported they either would not feel safe, or felt unsure if they would be safe, if they were open about being poly in their home communities.
Gillig said it was encouraging that many also felt they would be supported, and 16 of the 54 poly or ambi campers said they were open about it at home.
Adult polyamory has been gaining attention in the news media and on TV with shows that feature poly people on Netflix and Showtime. It has also been the subject of research, which has found that more than 20% of adults have engaged in consensually non-monogamous relationships like polyamory. Another study also found that some poly adults began to understand their identity as poly when they were adolescents.
For this study, participants filled out questionnaires before and at the end of the camp, which included assessments of anxiety and depressive symptoms. They also answered questions about their preferred relationship structure and how comfortable they felt being open with others about it.
The survey allowed campers to write in explanations, and some who felt less safe said that being poly was “a touchy subject” and that even those who accept their LGBTQ+ identity would not be okay with it.
The poly and ambi kids as well as all the adolescents in the study showed improved mental health after experiencing the accepting environment of the LGBTQ+ camp, and Gillig emphasized that support is key for young people who have a marginalized identity.
“Youths’ experience with being polyamorous or ambiamorous is similar to being LGBTQ+ in that if they perceive that they won't be supported, then they’re not as likely to disclose their identity at home. We know from research with queer youth that this can cause elevated levels of depressive symptoms,” she said. “My hope is that parents would have an open mind, if their child comes to them and expresses that they identify as polyamorous or if they have questions about it.”
END
Polyamorous youth report facing stigma, heightened levels of depression
2024-04-29
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Competition from “skinny label” generics saved Medicare billions
2024-04-29
IMPORTANT UPDATE:
The article referenced in Tip #4 on color ultrasound for suspected GCA will not be published on April 30. If you had planned to cover this topic, please hold your stories until further notice. In its place, Annals will publish the following:
Sodium–Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitors and the Risk for Dialysis and Cardiovascular Disease in Patients With Stage 5 Chronic Kidney Disease
Abstract: https://www.acpjournals.org/doi/10.7326/M23-1874
Please contact Angela ...
Xavier Ochsner College of Medicine announces founding dean and location in downtown New Orleans at Benson Tower
2024-04-29
New Orleans, La. – Xavier University of Louisiana (Xavier), a leading undergraduate institution in preparing Black students to successfully complete medical school, has announced continued progress with Ochsner Health (Ochsner), the Gulf South’s leading academic medical center in training physicians, to launch their transformational Xavier Ochsner College of Medicine (XOCOM). This groundbreaking partnership marks a significant milestone in advancing medical education by addressing health disparities ...
Three Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute faculty members honored by AAAS
2024-04-29
Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute’s Boleslaw Szymanski, Ph.D., and Chunyu Wang, M.D. Ph.D., have been elected fellows of the American Association for the Advancement Science (AAAS). Steven Cramer, Ph.D., who was elected AAAS Fellow in 2017, was elected Council Member of the Section on Engineering.
The mission of the AAAS is to “advance science, engineering, and innovation throughout the world for the benefit of all.” Each year, AAAS elects fellows whose “efforts… are scientifically or socially distinguished.”
Over RPI’s 200-year history, 70 RPI faculty members have been ...
STRONG STAR Consortium secures $17 million in DOD research funding for brain injuries, PTSD and more
2024-04-29
SAN ANTONIO, April 29, 2024 – In a recent round of grant awards, the STRONG STAR Consortium based at The University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio (UT Health San Antonio) was selected by the U.S. Department of Defense for a total of $17 million in funding to launch eight new research projects focused on traumatic brain injury and psychological health.
The combined projects will enable the consortium to take a big step forward in its mission to advance the care of military personnel and veterans recovering from war-related trauma ...
Scientists harness the wind as a tool to move objects
2024-04-29
Researchers have developed a technique to move objects around with a jet of wind. The new approach makes it possible to manipulate objects at a distance and could be integrated into robots to give machines ethereal fingers.
‘Airflow or wind is everywhere in our living environment, moving around objects like pollen, pathogens, droplets, seeds and leaves. Wind has also been actively used in industry and in our everyday lives – for example, in leaf blowers to clean leaves. But so far, we can’t control the direction the leaves move – we can only blow them together into a pile,’ says Professor Quan Zhou from Aalto University, who led the study.
The first ...
Long snouts protect foxes when diving headfirst in snow
2024-04-29
ITHACA, N.Y. – When hunting for mice in winter, red and arctic fox are known to plunge headfirst at speeds of 2-4 meters per second, but their sharp noses reduce the impact force in snow and protect them from injury, according to a new Cornell University study.
The fundamental research sheds light on the biomechanics of the unique hunting behavior (known as mousing), advances our understanding of animal adaptations and offers insights into snow injuries people experience during snowboarding or skiing.
The study published April 29 in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
While ...
Laser imaging could offer early detection for at-risk artwork
2024-04-29
DURHAM, N.C. -- Look closely at Impressionist paintings in museums compared with photos of them taken 50 years ago, and you might notice something odd: some are losing their bright yellow hues.
Take the dramatic sunset in Edward Munch’s famous painting “The Scream.” Portions of the sky that were once a vivid orangish yellow have faded to off-white.
Likewise, some of the sunny yellow that Henri Matisse brushed between the reclining nudes in his painting “The Joy of Life” is now more of a drab beige.
Several other paintings from this period are facing ...
"BioBlitz" citizen science reveals urban biodiversity, guides management
2024-04-29
Citizen scientists are uncovering rare animal, plant, and fungi species in areas where they have never been seen before, increasing our knowledge of urban biodiversity and proving the existence of local species long thought extinct. The approach used is called a BioBlitz, a biological census in which citizen scientists contribute photographs or audio of living organisms they can see or hear in a designated area over a particular period, creating a snapshot of an area’s biodiversity.
In a recently published article in the journal BioScience, Dr. Esti Palma (University of Melbourne) ...
Haiti study suggests early-onset heart failure is prevalent form of heart disease in low-income countries
2024-04-29
Early-onset heart failure is alarmingly common in urban Haiti—over 15-fold higher than previously estimated—according to a study conducted by Weill Cornell Medicine researchers in partnership with the Haitian medical organization GHESKIO. Heart failure occurs when the heart muscle can no longer pump an adequate amount of blood throughout the body.
The study indicates that the nature of cardiovascular disease in Haiti, and perhaps other low- and middle-income nations, differs from wealthier countries where ischemic heart disease, also called coronary heart disease, is prevalent. This condition, ...
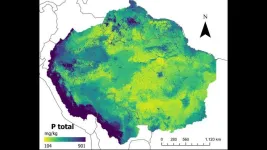
Maps developed with artificial intelligence confirm low levels of phosphorus in Amazonian soil
2024-04-29
As the impacts of climate change increasingly affect the daily lives of residents in several countries, including Brazil, the resilience of forests, especially tropical ones such as the Amazon, has become a frequent topic of research. In addition to studying various factors that influence the way vegetation reacts to global warming, scientists are seeking to improve vegetation models – tools that play a crucial role in understanding and managing ecosystems, contributing to biodiversity conservation and sustainable development.
And it is exactly this combination that is described in research published in the journal Earth System Science Data by a group associated ...