(Press-News.org)
“[...] these findings may help to advance our understanding of the pathogenesis of corneal endothelial disease and may lead to the discovery of new therapies targeting senescent cells.”
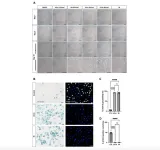
BUFFALO, NY- April 30, 2024 – A new research paper was published on the cover of Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 16, Issue 8, entitled, “Senescent characteristics of human corneal endothelial cells upon ultraviolet-A exposure.”
In this new study, researchers Kohsaku Numa, Sandip Kumar Patel, Zhixin A. Zhang, Jordan B. Burton, Akifumi Matsumoto, Jun-Wei B. Hughes, Chie Sotozono, Birgit Schilling, Pierre-Yves Desprez, Judith Campisi (1948-2024), and Koji Kitazawa from Buck Institute for Research on Aging, Kyoto Prefectural University of Medicine, University of Cambridge, and California Pacific Medical Center investigated the senescent phenotypes of human corneal endothelial cells (hCEnCs) upon treatment with ultraviolet (UV)-A.
“We assessed cell morphology, senescence-associated β-galactosidase (SA-β-gal) activity, cell proliferation and expression of senescence markers (p16 and p21) in hCEnCs exposed to UV-A radiation, and senescent hCEnCs induced by ionizing radiation (IR) were used as positive controls.”
The researchers performed RNA sequencing and proteomics analyses to compare gene and protein expression profiles between UV-A- and IR-induced senescent hCEnCs — they also compared the results to non-senescent hCEnCs. Cells exposed to 5 J/cm2 of UV-A or to IR exhibited typical senescent phenotypes, including enlargement, increased SA-β-gal activity, decreased cell proliferation and elevated expression of p16 and p21. RNA-Seq analysis revealed that 83.9% of the genes significantly upregulated and 82.6% of the genes significantly downregulated in UV-A-induced senescent hCEnCs overlapped with the genes regulated in IR-induced senescent hCEnCs. Proteomics also revealed that 93.8% of the proteins significantly upregulated in UV-A-induced senescent hCEnCs overlapped with those induced by IR. In proteomics analyses, senescent hCEnCs induced by UV-A exhibited elevated expression levels of several factors part of the senescence-associated secretory phenotype.
“In this study, where senescence was induced by UV-A, a more physiological stress for hCEnCs compared to IR, we determined that UV-A modulated the expression of many genes and proteins typically altered upon IR treatment, a more conventional method of senescence induction, even though UV-A also modulated specific pathways unrelated to IR.”
Read the full study: DOI: https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.205761
Corresponding Author: Koji Kitazawa - kkitazaw@koto.kpu-m.ac.jp
Keywords: cellular senescence, senescence-associated secretory phenotype, RNA-Seq proteomics, gene ontology analysis
Click here to sign up for free Altmetric alerts about this article.
About Aging:
Aging publishes research papers in all fields of aging research including but not limited, aging from yeast to mammals, cellular senescence, age-related diseases such as cancer and Alzheimer’s diseases and their prevention and treatment, anti-aging strategies and drug development and especially the role of signal transduction pathways such as mTOR in aging and potential approaches to modulate these signaling pathways to extend lifespan. The journal aims to promote treatment of age-related diseases by slowing down aging, validation of anti-aging drugs by treating age-related diseases, prevention of cancer by inhibiting aging. Cancer and COVID-19 are age-related diseases.
Aging is indexed by PubMed/Medline (abbreviated as “Aging (Albany NY)”), PubMed Central, Web of Science: Science Citation Index Expanded (abbreviated as “Aging‐US” and listed in the Cell Biology and Geriatrics & Gerontology categories), Scopus (abbreviated as “Aging” and listed in the Cell Biology and Aging categories), Biological Abstracts, BIOSIS Previews, EMBASE, META (Chan Zuckerberg Initiative) (2018-2022), and Dimensions (Digital Science).
Please visit our website at www.Aging-US.com and connect with us:
Facebook
X, formerly Twitter
Instagram
YouTube
LinkedIn
Reddit
Pinterest
Spotify, and available wherever you listen to podcasts
Click here to subscribe to Aging publication updates.
For media inquiries, please contact media@impactjournals.com.
Aging (Aging-US) Journal Office
6666 E. Quaker Str., Suite 1B
Orchard Park, NY 14127
Phone: 1-800-922-0957, option 1
###
END
Common household products containing nanoparticles – grains of engineered material so miniscule they are invisible to the eye – could be contributing to a new form of indoor air pollution, according to a Rutgers study.
In a study published in the journal Science of the Total Environment, a team of Rutgers researchers found people walking through a space, where a consumer product containing nanoparticles was recently sprayed, stirred residual specks off carpet fibers and floor surfaces, projecting them some three ...
An international team of researchers has successfully used NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope to map the weather on the hot gas-giant exoplanet WASP-43 b.
Precise brightness measurements over a broad spectrum of mid-infrared light, combined with 3D climate models and previous observations from other telescopes, suggest the presence of thick, high clouds covering the nightside, clear skies on the dayside, and equatorial winds upwards of 5,000 miles per hour mixing atmospheric gases around the planet.
The investigation is just the latest demonstration of the exoplanet science now possible with Webb’s ...
NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope has captured the sharpest infrared images to date of a zoomed-in portion of one of the most distinctive objects in our skies, the Horsehead Nebula. These observations show the top of the “horse’s mane” or edge of this iconic nebula in a whole new light, capturing the region’s complexity with unprecedented spatial resolution.
Webb’s new images show part of the sky in the constellation Orion (The Hunter), in the western side of a dense region known as the Orion B molecular cloud. Rising from turbulent waves of dust and gas is the Horsehead Nebula, otherwise known as ...
Proteins are the workhorses of life. Organisms use them as building blocks, receptors, processors, couriers and catalysts. A protein’s structure is critical to its function. Malformed proteins not only fail to carry out their tasks, they can accumulate and eventually gum up the inner workings of cells. As a result, misfolded proteins cause a variety of degenerative diseases, from Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s to the blinding disease retinitis pigmentosa. These disorders are currently incurable.
A paper out of UC Santa Barbara reveals a new connection between ...
Researchers from the University of California San Diego have revealed new trends in drug consumption that shed light on how people are adapting to the evolving risks associated with unregulated drug use in the United States. The findings could help policymakers and public health officials better tailor interventions to meet the needs of vulnerable populations and reduce the public health burden of substance-related harm.
Since the early 2010s, deaths from accidental overdoses have been on the rise ...
Speech is critical to detecting suicidal ideation and a key to understanding the mental and emotional state of people experiencing it. Suicide hotline counsellors are trained to quickly analyze speech variation to better help callers through a crisis.
But just as no system is perfect, there is room for error in interpreting a caller’s speech. In order to assist hotline counsellors to properly assess a caller’s condition, Concordia PhD student Alaa Nfissi has developed a model for speech emotion recognition (SER) using artificial intelligence tools. The model analyzes and codes waveform modulations in ...
April 30, 2024, ALEXANDRIA, Virginia —The American Academy of Otolaryngology–Head and Neck Surgery Foundation (AAO-HNSF) published the Clinical Practice Guideline: Age-Related Hearing Loss today in Otolaryngology–Head and Neck Surgery. This clinical practice guideline (CPG) sheds lights on a global public health problem affecting approximately 466 million people worldwide and identifies quality improvement opportunities and provide clinicians trustworthy, evidence-based recommendations regarding the identification and management of age-related hearing loss (ARHL) in patients 50 years and older.
“Age-related ...
The grazing of both domestic and wild animals is shaping landscapes across Europe. It can also contribute to multiple ecosystem services, such as providing habitat for biodiversity. Grazing systems with lower densities of animals and with minimal and only targeted applications of deworming and other medicinal treatments offer benefits for local biodiversity protection and various ecosystem services. However, this type of land management also poses a range of challenges, leading to a constant decline in the number of land users engaged in low-intensity grazing. A team of researchers led by iDiv, UL, and UFZ set out to investigate these ...
Philadelphia, April 30, 2024 – A genetic propensity to higher circulating levels of lipids containing arachidonic acid, an omega-6 polyunsaturated fatty acid found in eggs, poultry, and seafood, has been found to be linked with a lower risk for bipolar disorder, according to a new study in Biological Psychiatry, published by Elsevier. This new evidence paves the way for potential lifestyle or dietary interventions.
Bipolar disorder is a debilitating mood disorder characterized by recurring episodes of mania and depression. Although its etiology is still unclear, previous studies have shown that ...
In an effort to improve early detection of breast cancer and address disparities in outcomes, the US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) has issued updated breast cancer screening recommendations to now advise all women to undergo routine screening every other year starting at age 40 —representing a significant shift from previous guidelines, which recommended screening starting at age 50 and engaging in individualized decision-making for women aged 40 to 49.
The revised guidelines aim to enhance early detection of breast cancer and tackle disparities in breast cancer mortality, particularly among Black women, who are more likely to have aggressive ...