New Japanese lily species identified, 1st addition to sukashiyuri group in 110 years
Classification of these plants bloom to double the number of taxonomic groups through morphological study, DNA analysis
2024-05-01
(Press-News.org)
A new species of the Japanese lily known as sukashiyuri has been identified for the first time since 1914 by a research team led by Dr. Seita Watanabe, a specially appointed assistant professor at the Botanical Gardens and the Graduate School of Science at Osaka Metropolitan University.
Dr. Watanabe questioned the classification used up to now for sukashiyuri group, which usually has orange flowers. These lilies have high ornamental value, having been exported from Japan for more than two centuries. There have been only four taxonomic groups, but Dr. Watanabe and his team sought evidence to prove that there were more.
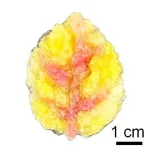
Traveling across Japan to observe the lilies, record images, gather specimens, and obtain DNA from plant materials, the research team members conducted a detailed analysis of the form and structure of the plants and their DNA. The results of their extensive work revises the conventional classification into eight taxons, including what they have named Lilium pacificum, the first new species of Japanese lily in 110 years.
Lilium pacificum grows on coastal areas facing the Pacific Ocean on Honshu from Ibaraki Prefecture south to Shizuoka Prefecture and the Izu Islands.
“It has an interesting characteristic: the tips of its leaves are curved into a claw-like shape,” Dr. Watanabe enthused. “Based on the new understanding of these eight taxonomic groups, we found that seven are endemic to Japan, each adapted to its environment, whether coastal or mountainous, and evolving unique traits.”
Dr. Watanabe added: “Our research shows that these plants have differentiated through complex processes, and we hope that our work will provide clues for speciation studies. In the past, individual differences may have been overlooked because of the apparent simplicity of the plants. Through this research, I was reminded of the importance of morphological observation.”
The findings were published in Taxon.
###
About OMU
Established in Osaka as one of the largest public universities in Japan, Osaka Metropolitan University is committed to shaping the future of society through “Convergence of Knowledge” and the promotion of world-class research. For more research news, visit https://www.omu.ac.jp/en/ and follow us on social media: X, Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-05-01
Due to a later melatonin onset and increased alertness in the evening, teenagers often find it hard to fall asleep at a time that would allow them to clock up the recommended eight to 10 hours of sleep each night.
It is also during teenage years when increasing school demands, activities, more independence from parents, and relationships with peers begin to compete with sleep. The role of social context, however, is often overlooked when studying adolescents’ sleep. Now, researchers in Sweden and Australia wanted to find out how popularity ...
2024-05-01
Patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) all have a unique and diverse set of antibodies that are involved in the development of the disease. Researchers at Utrecht University unveiled the complexity of these antibodies using powerful lab tools capable of analysing our immune system at molecular levels. Their discovery suggests that current assumptions about the origin of RA are too simple. Still, their findings may point towards improved diagnostics.
Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic autoimmune disease that primarily affects the joints, causing pain, stiffness, and swelling. It arises when the immune system mistakenly attacks the body’s own tissues, leading ...
2024-05-01
LOS ANGELES — Keck Hospital of USC earned an “A” Hospital Safety Grade from The Leapfrog Group, an independent national watchdog organization.
“This grade puts Keck Hospital among the safest in the nation, and is a testament to the hospital’s commitment to the highest standards of quality and safety protocols,” said Marty Sargeant, MBA, CEO of Keck Medical Center of USC.
The Leapfrog Group assigns an “A,” “B,” “C,” “D” or “F” grade to general hospitals across the country based on over 30 measures of errors, accidents, injuries and infections and the ...
2024-05-01
Orlando, Fla - A new national survey by the Orlando Health Cancer Institute finds nearly a third (32%) of Americans agree that a tan makes people look better and healthier, a dangerous beauty standard that experts say can lead to risky behavior when it comes to sun exposure.
“There is no such thing as a healthy tan, as it’s really just a visual manifestation of damage to the skin,” said Rajesh Nair, MD, an oncology surgeon at the Orlando Health Cancer Institute. “But we’re fighting against a perceived positive image and health benefits of something that actually has a totally opposite reality, which ...
2024-05-01
The body clock has a significant impact on the performance of NBA players, according to study published in the peer-reviewed journal Chronobiology International.
The authors say their findings, from more than 25,000 matches, show elite basketball coaches and teams should consider the physical and mental effects of time zone travel when planning games and preparing for games.
A first of its kind, the research is based on the achievements at home and away of NBA (National Basketball Association) league players across 21 consecutive seasons. Considered the most competitive in the world, NBA athletes frequently travel ...
2024-05-01
CLEVELAND, Ohio (May 1, 2024)—Musculoskeletal pain is a prevalent menopause symptom, which helps explain why women typically experience more pain than men, especially around the age of 50 years. Beyond pain, muscle function and mass are also affected by menopause. A new study suggests premature surgical menopause can lead to an increased risk of muscle disorders. Results of the survey are published online today in Menopause, the journal of The Menopause Society.
The highly publicized Study of Women’s Health Across the Nation spotlighted a number of symptoms that are common during the menopause ...
2024-05-01
Women are 40% more likely to experience depression in the perimenopause than those who aren’t experiencing any menopausal symptoms, finds a new study led by UCL researchers.
The research, published in the Journal of Affective Disorders, provided a meta-analysis of seven studies involving 9,141 women from across the world (including Australia, USA, China, Netherlands and Switzerland), to understand whether different stages of the menopause were associated with different risk of depression.
The perimenopause usually occurs around three to five years before the onset of menopause. During this stage women’s oestrogen and progesterone levels begin to fluctuate, ...
2024-05-01
How do planets form? How do galaxies evolve? And ultimately, how did the universe itself begin? A unique astronomical observatory that researchers hope will unravel some of the biggest mysteries out there marks its opening on April 30, 2024.
At an altitude of 5,640 meters, the University of Tokyo Atacama Observatory (TAO), built on the summit of a desert mountain in northern Chile, is the highest astronomical observatory in the world, which should give it unrivaled capabilities, but presents some novel challenges.
Astronomers will ...
2024-05-01
Illumina, a global genomics and human health company, has partnered with the Garvan Institute of Medical Research’s TenK10K project to help transform the treatment of complex diseases, starting with autoimmune diseases, with a joint investment of $27 million AUD.
The Garvan Institute plans to map 50 million human cells from 10,000 people to identify unique genomic fingerprints of autoimmune diseases, heart diseases and cancer, building on the early success of a clinical trial for Crohn’s disease.
Crohn’s disease affects more than 80,000 Australians. As with many autoimmune diseases, ...
2024-05-01
Head and abdominal trauma is a leading cause of death for children. About 1%–2% of children who come to emergency departments with head or abdominal injuries require immediate intervention. These injuries are diagnosed the world over by computed tomography (CT) scans. But CT-related radiation can cause cancers later in life, and accumulated evidence suggests that CT is overused.
“There is an urgent need for validated guidelines for the safe use of CT to diagnose injured children while preventing unnecessary radiation exposure,” says Pradip Chaudhari, MD, Director of Research and Scholarship, Division of Emergency and Transport Medicine, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] New Japanese lily species identified, 1st addition to sukashiyuri group in 110 years
Classification of these plants bloom to double the number of taxonomic groups through morphological study, DNA analysis







