(Press-News.org) Social media. The climate crisis. Political polarization. The tumult of a pandemic and online learning. Teens today are dealing with unprecedented stressors, and over the past decade their mental health has been in sustained decline. Levels of anxiety and depression rose after the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic. Compounding the problem is a shortage of mental health providers — for every 100,000 children in the U.S., there are only 14 child and adolescent psychiatrists.
In response to this crisis, University of Washington researchers studied whether virtual reality might help reduce stress for teens and boost mental health. Working with adolescents, the team designed a snowy virtual world with six activities — such as stacking rocks and painting — based on practices shown to improve mental health.
In a 3-week study of 44 Seattle teens, researchers found that teens used the technology an average of twice a week without being prompted and reported lower stress levels and improved mood while using it, though their levels of anxiety and depression didn’t decline overall.
The researchers published their findings April 22 in the journal JMIR XR and Spatial Computing. The system is not publicly available.
“We know what works to help support teens, but a lot of these techniques are inaccessible because they’re locked into counseling, which can be expensive, or the counselors just aren’t available,” said lead author Elin Björling, a UW senior research scientist in the human centered design and engineering department. “So we tried to take some of these evidence-based practices, but put them in a much more engaging environment, like VR, so the teens might want to do them on their own.”
The world of Relaxation Environment for Stress in Teens, or RESeT, came from conversations the researchers had with groups of teens over two years at Seattle Public Library sites. From these discussions, the team built RESeT as an open winter world with a forest that users could explore by swinging their arms (a behavior known to boost mood) to move their avatar. A signpost with six arrows on it sent users to different activities, each based on methods shown to improve mental health, such as dialectical behavior therapy and mindfulness-based stress reduction.
In one exercise, “Riverboat,” users put negative words in paper boats and send them down a river. Another, “Rabbit Hole,” has players stand by a stump; the longer they’re still, the more rabbits appear.
“In the co-design process, we learned some teens were really afraid of squirrels, which I wouldn’t have thought of,” Björling said. “So we removed all the squirrels. I still have a Post-It in my office that says ‘delete squirrels.’ But all ages and genders loved rabbits, so we designed Rabbit Hole, where the reward for being calm and paying attention is a lot of rabbits surrounding you.”
To test the potential effects of RESeT on teens’ mental health, the team enrolled 44 teens between ages 14 and 18 in the study. Each teen was given a Meta Quest 2 headset and asked to use RESeT three to five times a week. Because the researchers were trying to see if teens would use RESeT regularly on their own, they did not give prompts or incentives to use the headsets after the start of the study. Teens were asked to complete surveys gauging their stress and mood before and after each session.
On average, the teens used RESeT twice a week for 11.5 minutes at a time. Overall, they reported feeling significantly less stressed while using RESeT, and also reported smaller improvements in mood. They said they liked using the headset in general. However, the study found no significant effects on anxiety and depression.
“Reduced stress and improved mood are our key findings and exactly what we hoped for,” said co-author Jennifer Sonney, an associate professor in the UW School of Nursing who works with children and families. “We didn't have a big enough participant group or a design to study long-term health impacts, but we have promising signals that teens liked using RESeT and could administer it themselves, so we absolutely want to move the project forward.”
The researchers aim to conduct a larger, longer-term study with a control group to see if a VR system could impart lasting effects on mood and stress. They’re also interested in incorporating artificial intelligence to personalize the VR experience and in exploring offering VR headsets in schools or libraries to improve community access.
Additional co-authors were Himanshu Zade, a UW lecturer and researcher at Microsoft; Sofia Rodriguez, a senior manager at Electronic Arts who completed this research as a UW master’s student in human centered design and engineering; Michael D. Pullmann, a research professor in psychiatry and behavioral sciences at the UW School of Medicine; and Soo Hyun Moon, a senior product designer at Statsig who completed this research as a UW master’s student in human centered design and engineering. This research was funded by the National Institute of Mental Health through the UW ALACRITY Center, which supports UW research on mental health.
For more information, contact Björling at bjorling@uw.edu and Sonney at jsonney@uw.edu.
END
Virtual reality environment for teens may offer an accessible, affordable way to reduce stress
2024-05-01
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Join us in honoring the 2024 American Gastroenterological Association Recognition Awards recipients
2024-05-01
Bethesda, MD (May 1, 2024) — The American Gastroenterological Association (AGA) has announced the 2024 recipients of its annual recognition prizes, given in honor of outstanding contributions and achievements in gastroenterology.
"AGA is delighted to present the recipients chosen for the 2024 AGA Recognition Prizes. We extend our gratitude to all the nominators for their submission of nomination letters, and to the diligent selection committee members for their work in identifying these exceptional individuals from ...
Resource-appropriate cancer care, including coexisting health issues of HIV and cancer, to be addressed during meeting in Nairobi
2024-05-01
NAIROBI, KENYA [May 1, 2024] — Local and global experts are meeting in Nairobi, Kenya to update clinical practice guidelines as part of ongoing work with Allied Against Cancer—a collaboration between the National Comprehensive Cancer Network® (NCCN®), African Cancer Coalition (ACC), American Cancer Society (ACS), and Clinton Health Access Initiative (CHAI). The meeting brings together subject matter experts to update NCCN Harmonized Guidelines™ for Sub-Saharan Africa, featuring updates for treating cancer in people with HIV and other important ...
Marriage of synthetic biology and 3D printing produces programmable living materials
2024-05-01
Scientists are harnessing cells to make new types of materials that can grow, repair themselves and even respond to their environment. These solid “engineered living materials” are made by embedding cells in an inanimate matrix that’s formed in a desired shape. Now, researchers report in ACS Central Science that they have 3D printed a bioink containing plant cells that were then genetically modified, producing programmable materials. Applications could someday include biomanufacturing and sustainable construction.
Recently, researchers have been developing engineered living materials, primarily relying on bacterial ...
Friends with health benefits: How the buddy system pays off when pursuing goals
2024-05-01
Weekly targets, annual resolutions, five-year plans—all of them so troublingly elusive. With best intentions, most of us fail to stick with the goals we set.
Next time, consider pursuing them with a friend.
New field research by Assistant Professor Rachel Gershon, published in Management Science, suggests that pursuing our goals with friends may make them more attainable. Gershon, along with Cynthia Cryder of Washington University and Katy Milkman of the University of Pennsylvania, ...
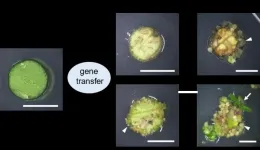
Novel genetic plant regeneration approach without the application of phytohormones
2024-05-01
For ages now, plants have been the primary source of nutrition for animals and mankind. Additionally, plants are used for the extraction of various medicinal and therapeutic compounds. However, their indiscriminate use, along with the rising demand for food, underscores the need for novel plant breeding practices. Advances in plant biotechnology can address the problems associated with food scarcity in the future by enabling the production of genetically modified (GM) plants with higher productivity and resilience to the changing climate.
Naturally, plants can regenerate an entire new plant from a single ‘totipotent’ cell (a cell that ...
ACS inaugural report shows mortality for preventable cancers among native Hawaiian and other Pacific Islanders in U.S. is 2-3 times as high as white people
2024-05-01
ATLANTA, May 1, 2024 — The American Cancer Society (ACS) today released a first-of-its-kind Cancer Facts & Figures for Asian American, Native Hawaiian, & Other Pacific Islander People, 2024-2026. This report shows that despite limited disaggregated data, there is wide variation in the cancer burden among ethnic groups that make up this fast-growing population. Cancer is the second-leading cause of death in the United States nationally but ranks first in Chinese, Filipino, Korean, and Vietnamese individuals, with lung cancer the leading cause of death in men of every Asian American, Native ...
ChatGPT fails at heart risk assessment
2024-05-01
SPOKANE, Wash. – Despite ChatGPT’s reported ability to pass medical exams, new research indicates it would be unwise to rely on it for some health assessments, such as whether a patient with chest pain needs to be hospitalized.
In a study involving thousands of simulated cases of patients with chest pain, ChatGPT provided inconsistent conclusions, returning different heart risk assessment levels for the exact same patient data. The generative AI system also failed to match the traditional ...
Improved AI process could better predict water supplies
2024-05-01
PULLMAN, Wash. -- A new computer model uses a better artificial intelligence process to measure snow and water availability more accurately across vast distances in the West, information that could someday be used to better predict water availability for farmers and others.
Publishing in the Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, the interdisciplinary group of Washington State University researchers predict water availability from areas in the West where snow amounts aren’t being physically measured.
Comparing ...
A blood test for stroke risk? Study finds network of inflammatory molecules may act as biomarker for risk of future cerebrovascular disease
2024-05-01
A simple blood test could allow doctors to determine whether a person may be at higher risk for stroke or cognitive decline during their lifetime, according to a new UCLA Health study.
The study, published in the journal Stroke, found that measuring concentrations of a network of inflammatory molecules in the blood could allow doctors to calculate a risk score for susceptibility for cerebral small vessel disease – a common cause of stroke and a contributor to cognitive decline found especially among the elderly.
Currently, the only way to determine a person’s risk for cerebral vascular diseases has been ...
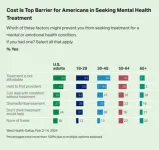
New survey finds 75% of Americans feel mental health takes back seat to physical health within U.S. healthcare system
2024-05-01
WASHINGTON, DC – May 1, 2024 – Three-quarters of Americans feel mental health conditions are identified and treated much worse than physical health issues within the U.S. healthcare system, even as more than 80% perceive a dramatic rise in prevalence of mental health issues in the last five years, according to a new survey from West Health and Gallup released at the start of Mental Health Awareness Month and Older Americans Month.
Nearly identical percentages believe mental health is handled either “much” (38%) or “somewhat” worse (37%) than physical health ailments, while 15% say they are dealt with “about the same.” ...