(Press-News.org) ITHACA, N.Y. – Cornell University researchers and collaborators have developed a new framework that allows scientists to predict crop yield without the need for enormous amounts of high-quality data – which is often scarce in developing countries, especially those facing heightened food insecurity and climate risk.
In many parts of the world, crop yields are dropping, largely due to the effects of climate change. According to a recent Cornell study, over the last four decades, for every 1 degree Celsius of warming, net farm income decreased by 66%.
Farmers in developed countries can often rely on big datasets and risk management tools to help reduce the impacts of extreme heat on their yield and income. But in developing countries, data is scarce, and it is often difficult to accurately measure crop yield.
In a paper accepted in Environmental Research Letters in March, the scientists suggest using satellite photos to remotely measure solar-induced chlorophyll fluorescence (SIF) as a way of assessing and predicting crop yield. Using sample fields of corn in the U.S. and wheat in India, the scientists have hit upon an approach that should, in principle, work universally for any crop, according to Ying Sun, a co-author and associate professor of soil and crop sciences.
Chlorophyll fluorescence is the reddish light re-emitted by photosynthetic tissues and organisms, she said, a measurement that serves as a proxy of photosynthetic energy conversion in plants.
“It won’t tell you how many ears of corn are in a field,” she said, “but step one is to model photosynthesis from fluorescence. Crop yield depends on photosynthesis. Here we have a mechanistic model, which is very important.”
This approach could be valuable for making policy decisions, establishing crop insurance and even forecasting areas of poverty. It could be employed to help food assistance organizations and nongovernmental agencies be more fleet of foot in providing aid.
The strategy takes advantage of the growing availability of satellite data and is cheaper to use and faster to access than other yield-prediction methods.
Sun said she and her colleagues are working on further research that would allow this kind of tool to be used in real time to allow farmers to react, adjusting things like soil amendments or irrigation strategies to improve a current harvest’s health and productivity.
For additional information, see this Cornell Chronicle story.
END
Satellite images of plants’ fluorescence can predict crop yields
2024-05-01
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Machine learning tool identifies rare, undiagnosed immune disorders through patients’ electronic health records
2024-05-01
Researchers say a machine learning tool can identify many patients with rare, undiagnosed diseases years earlier, potentially improving outcomes and reducing cost and morbidity. The findings, led by researchers at UCLA Health, are described in Science Translational Medicine.
“Patients who have rare diseases may face prolonged delays in diagnosis and treatment, resulting in unnecessary testing, progressive illness, psychological stresses, and financial burdens,” said Manish Butte, MD, PhD, a UCLA professor in pediatrics, human genetics, and microbiology/immunology who cares for these patients in his clinic at UCLA. “Machine learning and other artificial intelligence ...
MD Anderson researcher Sharon Dent elected to prestigious National Academy of Sciences
2024-05-01
HOUSTON ― Sharon Dent, Ph.D., professor of Epigenetics and Molecular Carcinogenesis at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, has been elected to the National Academy of Sciences (NAS). Dent is a global leader in the field of chromatin research whose foundational work has helped define the role of chromatin in cancer growth and development.
Dent is one of 120 members and 24 international members elected this year in recognition of their distinguished and continuing achievements in original research. The NAS, established in 1863 by President Abraham Lincoln, is a private, nonprofit society of distinguished scholars engaged in scientific and engineering research.
With ...
Nonmotor seizures may be missed in children, teens
2024-05-01
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL 4 P.M. ET, WEDNESDAY, MAY 1, 2024
MINNEAPOLIS – Children and teens may experience nonmotor seizures for months or years before being seen in an emergency department for a more obvious seizure that includes convulsions, according to a study published in the May 1, 2024, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology. Even then, the history of nonmotor seizures may not be recognized.
“Early diagnosis of epilepsy is of the utmost importance because epileptic seizures can lead to injury and even death,” said study author Jacqueline French, MD, of NYU Grossman School of Medicine ...
Emergency departments frequently miss signs of epilepsy in children
2024-05-01
A subtle type of seizure goes undetected two thirds of the time in pediatric emergency departments, a new study shows.
The work focuses on “nonmotor” seizures, which cause children to “zone out” and stare into space or fidget. They may also feel sudden changes in emotions, thoughts, or sensations, as opposed to motor seizures, which cause muscles to move in abrupt, jerking motions.
According to the authors, improving recognition of nonmotor seizures may speed up the diagnosis and treatment of epilepsy in children, ...
Unraveling the roles of non-coding DNA explains childhood cancer’s resistance to chemotherapy
2024-05-01
(MEMPHIS, Tenn. – May 01, 2024) St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital scientists have identified specific DNA variants in the non-coding regions of the genome contributing to chemotherapy resistance in acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). The results guided the team to unravel the mechanism behind a previously unknown contributor to therapeutic resistance. The discovery was enabled by combining new technologies to overcome previous limitations in understanding the non-coding genome, which could be adapted to other ...
Marshall University announces new clinical trial studying the effect of ACL reconstruction on return to play in sports
2024-05-01
HUNTINGTON, W.Va. – The Marshall University Joan C. Edwards School of Medicine is now accepting applicants for an observational trial focused on fertilized anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) reconstruction.
Unlike traditional ACL repairs, fertilized ACL surgery uses a biologic concentrate of the patient’s stem cells, bone marrow and autograft bone along with an internal brace with the goal of stabilizing and expediting the healing process.
“Past patients of the fertilized ACL have already shown shorter recovery times with no known additional risks to the patient,” said Chad D. Lavender, M.D., ...
New York State is vulnerable to increasing weather-driven power outages, with vulnerable people in the Bronx, Queens and other parts of New York City being disproportionately affected
2024-05-01
New York State is vulnerable to increasing weather-driven power outages, with vulnerable people in the Bronx, Queens and other parts of New York City being disproportionately affected.
####
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/climate/article?id=10.1371/journal.pclm.0000364
Article Title: Powerless in the storm: Severe weather-driven power outages in New York State, 2017–2020
Author Countries: United States
Funding: This work was supported by the National Institute for Environmental Health Sciences (NIEHS) P30 ES009089 ...
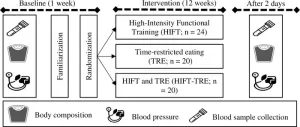
Time-restricted eating and high-intensity exercise might work together to improve health
2024-05-01
Combining time-restricted eating with high-intensity functional training may improve body composition and cardiometabolic parameters more than either alone, according to a study published May 1, 2024 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Ranya Ameur and Rami Maaloul from the University of Sfax, Tunisia, and colleagues.
Changes in diet and exercise are well-known ways to lose weight and improve cardiometabolic health. However, finding the right combination of lifestyle changes to produce sustainable results can be challenging. Prior studies indicate that time-restricted eating (which limits when, but not what, individuals eat) and ...
Simulations of agriculture on Mars using pea, carrot and tomato plants suggest that intercropping, growing different crops mixed together, could boost yields in certain conditions
2024-05-01
Simulations of agriculture on Mars using pea, carrot and tomato plants suggest that intercropping, growing different crops mixed together, could boost yields in certain conditions
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0302149
Article Title: Intercropping on Mars: A promising system to optimise fresh food production in future martian colonies
Author Countries: The Netherlands
Funding: The author(s) received no specific funding for this work. END ...
New computer algorithm supercharges climate models and could lead to better predictions of future climate change
2024-05-01
Earth System Models – complex computer models which describe Earth processes and how they interact – are critical for predicting future climate change. By simulating the response of our land, oceans and atmosphere to manmade greenhouse gas emissions, these models form the foundation for predictions of future extreme weather and climate event scenarios, including those issued by the UN Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC).
However, climate modellers have long faced a major problem. Because Earth System Models integrate many complicated processes, they cannot immediately run a simulation; they must first ensure that it has reached a stable equilibrium ...