(Press-News.org) Psilocybin - the active ingredient in “magic” mushrooms - is a more effective treatment for symptoms of depression than controls, providing further support for its potential as an antidepressant, suggests a study published by The BMJ today.
The researchers say the findings are encouraging but “further research is needed to clarify the factors that maximise psilocybin’s treatment potential for symptoms of depression.”
Depression affects an estimated 300 million people worldwide and is a leading cause of disability.
Psilocybin has shown promise in reducing symptoms of depression after one or two doses with few side effects and no current evidence of causing addiction. However, studies published to date have not investigated factors that may moderate psilocybin’s effects, including type of depression, past use of psychedelics, dosage, and publication biases.
To address this, a team of UK researchers examined databases looking for randomised controlled trials that compared psilocybin as a treatment for symptoms of depression with controls, such as placebo, niacin (vitamin B), or micro doses of psychedelics.
They included studies where psychotherapy was present in both the experimental and the control conditions, so that the effects of psilocybin could be distinguished from those of psychotherapy.
They found seven relevant trials for analysis involving 436 participants with depression (52% female; 90% white). Changes in depression scores were measured using a statistical method called Hedges’ g. A Hedges’ g of 0.2 indicates a small effect, 0.5 a moderate effect, and 0.8 or more a large effect.
The change in depression scores was significantly greater after treatment with psilocybin than with a comparator treatment, with an overall Hedge’s g of 1.64 indicating a large effect size favouring psilocybin.
Further analyses to account for trial differences indicated that having secondary depression (related to an underlying disease) rather than primary depression, being assessed with a self-reported scale rather than a clinician assessed scale, older age, and previous use of psychedelics, were correlated with greater improvements.
The study authors acknowledge that high levels of variation (heterogeneity) between trials resulted in a low certainty of evidence to support a strong antidepressant effect of psilocybin, and generalisability of findings were limited by the lack of participant diversity.
Pre-treatment expectations and the extent to which participants knew they were being treated with psilocybin or placebo, were also not measured.
Furthermore, in clinical trials, patients receive psilocybin in a calm living room with soothing music, supervised by a psychotherapist, which is unlikely to be achievable in a healthcare system.
As such, the authors conclude that, although this review’s findings are encouraging for psilocybin’s potential as an effective antidepressant, issues such as cost, lack of regulatory guidelines and legal safeguards associated with psilocybin treatment need to be dealt with before it can be established in clinical practice.
This study is an important contribution to the evidence base for the use of psilocybin in depression, but it cannot answer several questions, say researchers unconnected to the study in a linked editorial.
For instance, they argue that it cannot provide evidence for psilocybin’s effectiveness (performance under 'real-world' conditions) in depression until more information about potential effect modifiers is gathered, and that pragmatic clinical trials and real world data could help to deliver that.
Furthermore, there is still ongoing debate on whether psychedelics can express antidepressant activity on their own rather than by assisting specific forms of psychotherapy.
Finally, and perhaps most importantly, the editorial authors say that, as per all analyses using aggregate data, we cannot differentiate between those individuals most likely to benefit from psilocybin and those who might instead experience adverse events.
As such, they conclude that these promising findings “support a prudent approach in both scholarly and public settings, because more and better evidence is needed before any clinical recommendation can be made about therapeutic use of psilocybin.”
[Ends]
END
New study supports psilocybin’s potential as an antidepressant
Findings are encouraging but further evidence is needed before any clinical recommendations can be made, say experts
2024-05-02
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
The Lancet Public Health: Global study reveals stark differences between females and males in major causes of disease burden, underscoring the need for gender-responsive approaches to health
2024-05-02
Global and regional analyses reveal persistent health differences between females and males across the 20 leading causes of disease burden (illness and death—quantified as health loss) over the past 30 years.
Overall, health loss is higher in males, particularly driven by premature death; but females, despite tending to live longer, endure higher levels of illness over their lives—underscoring the diverse and evolving health needs of men and women at different stages of their lives.
These health differences emerge in adolescence highlighting the importance of early interventions and measures to prevent the onset and exacerbation ...
Revealed: face of 75,000-year-old female Neanderthal from cave where species buried their dead
2024-05-02
A new Netflix documentary has recreated the face of a 75,000-year-old female Neanderthal whose flattened skull was discovered and rebuilt from hundreds of bone fragments by a team of archaeologists and conservators led by the University of Cambridge.
The team excavated the female Neanderthal in 2018 from inside a cave in Iraqi Kurdistan where the species had repeatedly returned to lay their dead to rest. The cave was made famous by work in the late 1950s that unearthed several Neanderthals which appeared ...
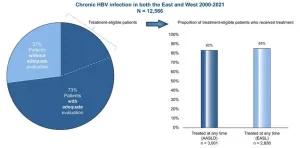
Hepatitis B is globally underassessed and undertreated, especially among women and Asian minorities in the West
2024-05-02
Amsterdam, May 2, 2024 – New evidence reveals global underassessment and undertreatment of chronic hepatitis B (HBV), especially among women and Asian minorities in the West, a new study in the Journal of Hepatology, published by Elsevier, details.
"In clinical practice we continue to see patients with advanced liver disease due to HBV despite having vaccines for prevention and excellent oral therapy for those who are treatment eligible. Simplifying and broadening HBV management is crucial," according to the researchers.
With the World Health Organization's goal to eliminate viral hepatitis by 2030 fast approaching, targeted outreach is needed to reduce new infections ...
Efficient stochastic parallel gradient descent training for on-chip optical processors
2024-05-01
A new publication from Opto-Electronic Advances; DOI 10.29026/oea.2024.230182 , discusses efficient stochastic parallel gradient descent training for on-chip optical processors.
With the explosive growth of global data volume, space-division multiplexing (SDM) technology has been emerged as a promising solution to enhance the communication capacity. Over the past few decades, SDM has been realized in few-mode fibers, multi-core fiber and free-space optical communication systems. However, all of above solutions face challenges of signal crosstalk because of the mixing between different channels during the ...
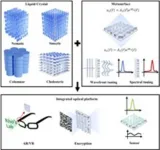
Liquid crystal-integrated metasurfaces for an active photonic platform
2024-05-01
A new publication from Opto-Electronic Advances; DOI 10.29026/oea.2024.230216 , discusses liquid crystal-integrated metasurfaces for an active photonic platform.
In the field of optical science, the exploration of metasurfaces has garnered significant attention over the last few decades. Metasurfaces represent a sophisticated evolution of traditional optical components, comprising nanostructures meticulously arranged to enable precise control over light manipulation. These nanostructures function as building blocks, allowing for the creation of lenses with unique ...
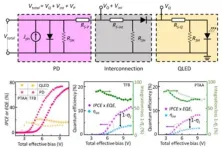
Unraveling the efficiency losses and improving methods in quantum dot-based infrared up-conversion photodetectors
2024-05-01
A new publication from Opto-Electronic Science; DOI 10.29026/oes.2024.230029 discusses unraveling the efficiency losses and improving methods in quantum dot-based infrared up-conversion photodetectors.
Traditional infrared imagers are usually constructed by bonding an infrared PD with each pixel of a thin film transistor (TFT)-based active-matrix backplane. A feasible way to avoid the costly pixilation is to use infrared up-conversion photodetector, in which an infrared photodetector (PD) and a light-emitting diode (LED) with large effective areas are back-to-back ...
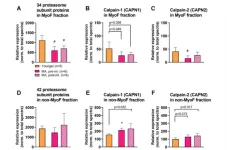
A novel deep proteomic approach unveils molecular signatures affected by aging and resistance training
2024-05-01
“Resistance training can reverse certain aspects of skeletal muscle aging.”
BUFFALO, NY- May 1, 2024 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 16, Issue 8, entitled, “A novel deep proteomic approach in human skeletal muscle unveils distinct molecular signatures affected by aging and resistance training.”
The skeletal muscle proteome alterations to aging and resistance training have been reported in prior studies. However, ...
High-intensity spatial-mode steerable frequency up-converter toward on-chip integration
2024-05-01
A new publication from Opto-Electronic Science; DOI 10.29026/oes.2024.230036 discusses high-intensity spatial-mode steerable frequency up-converter toward on-chip integration.
Integrated photonic devices consisting of micro-lasers, amplifiers, optical waveguides, frequency converters, and modulators on a single chip, enabling control over photon's spatial modes, frequencies, angular momenta, and phases, are essential for preparing high-dimensional quantum entangled states, high-capacity photon information processing, all-optical communication, and miniaturization of photonic computing. However, ...
Study indicates that cancer patients gain important benefits from genome-matched treatments
2024-05-01
In 2016, The Jackson Laboratory (JAX), a National Cancer Institute-designated Cancer Center and at the forefront of cancer research, launched the Maine Cancer Genomics Initiative (MCGI) to bring the latest progress in cancer care to rural Maine patients. Now, after successfully expanding access to genome tumor testing and targeted cancer treatments throughout Maine, the MCGI team provides compelling evidence that genome-matched treatments can provide significant patient benefit.
The MCGI report, published recently in npj Precision Oncology, ...
Gift to UCR clinic aims to assist local unhoused population
2024-05-01
RIVERSIDE, Calif. -- The Hulen Place Clinic, which UCR Health, the clinical arm of the School of Medicine (SOM) at the University of California, Riverside, opened in September 2023 to address the health and well-being of the unhoused and underserved populations in the County of Riverside has received a gift of $500,000 from the San Manuel Band of Mission Indians, a sovereign American Indian tribe of Serrano people in San Bernardino County, California.
Located about two miles from downtown Riverside and adjacent to an emergency shelter and temporary ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Mining the dark transcriptome: University of Toronto Engineering researchers create the first potential drug molecules from long noncoding RNA
IU researchers identify clotting protein as potential target in pancreatic cancer
Human moral agency irreplaceable in the era of artificial intelligence
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
Analysis of ancient parrot DNA reveals sophisticated, long-distance animal trade network that pre-dates the Inca Empire
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
GLP-1RA switching and treatment persistence in adults without diabetes
Gnaw-y by nature: Researchers discover neural circuit that rewards gnawing behavior in rodents
Research alert: How one receptor can help — or hurt — your blood vessels
Lamprey-inspired amphibious suction disc with hybrid adhesion mechanism
A domain generalization method for EEG based on domain-invariant feature and data augmentation
Bionic wearable ECG with multimodal large language models: coherent temporal modeling for early ischemia warning and reperfusion risk stratification
JMIR Publications partners with the University of Turku for unlimited OA publishing
Strange cosmic burst from colliding galaxies shines light on heavy elements
Press program now available for the world's largest physics meeting
New release: Wiley’s Mass Spectra of Designer Drugs 2026 expands coverage of emerging novel psychoactive substances
[Press-News.org] New study supports psilocybin’s potential as an antidepressantFindings are encouraging but further evidence is needed before any clinical recommendations can be made, say experts