In medieval England, leprosy spread between red squirrels and people, genome evidence shows
2024-05-03
(Press-News.org) Evidence from archaeological sites in the medieval English city of Winchester shows that English red squirrels once served as an important host for Mycobacterium leprae strains that caused leprosy in people, researchers report May 3 in the journal Current Biology.
“With our genetic analysis we were able to identify red squirrels as the first ancient animal host of leprosy,” says senior author Verena Schuenemann of the University of Basel in Switzerland. “The medieval red squirrel strain we recovered is more closely related to medieval human strains from the same city than to strains isolated from infected modern red squirrels. Overall, our results point to an independent circulation of M. leprae strains between humans and red squirrels during the Medieval Period.”
“Our findings highlight the importance of involving archaeological material, in particular animal remains, into studying the long-term zoonotic potential of this disease, as only a direct comparison of ancient human and animal strains allows reconstructions of potential transmission events across time,” says Sarah Inskip of the University of Leicester, UK, a co-author on the study.
Leprosy is one of the oldest recorded diseases in human history and is still prevalent to this day in Asia, Africa, and South America. While scientists have traced the evolutionary history of the mycobacterium that causes it, they didn’t know how it may have spread to people from animals in the past beyond some hints that red squirrels in England may have served as a host.
In the new study, the researchers studied 25 human and 12 squirrel samples to look for M. leprae at two archaeological sites in Winchester. The city was well known for its leprosarium (a hospital for people with leprosy) and connections to the fur trade. In the Middle Ages, squirrel fur was widely used to trim and line garments. Many people also kept squirrels trapped wild squirrels as kits in the wild and raised them as pets.
The researchers sequenced and reconstructed four genomes representing medieval strains of M. leprae, including one from a red squirrel. An analysis to understand their relationships found that all of them belonged to a single branch on the M. leprae family tree. They also showed a close relationship between the squirrel strain and a newly constructed one isolated from the remains of a medieval person. They report that the medieval squirrel strain is more closely related to human strains from medieval Winchester than to modern squirrel strains from England, indicating that the infection was circulating between people and animals in the Middle Ages in a way that hadn’t been detected before.
“The history of leprosy is far more complex than previously thought,” Schuenemann said. “There has been no consideration of the role that animals might have played in the transmission and spread of the disease in the past, and as such, our understanding of leprosy’s history is incomplete until these hosts are considered. This finding is relevant to today as animal hosts are still not considered, even though they may be significant in terms of understanding the disease’s contemporary persistence despite attempts at eradication.”
“In the wake of COVID-19, animal hosts are now becoming a focus of attention for understanding disease appearance and persistence,” Inskip said. “Our research shows that there is a long history of zoonotic diseases, and they have had and continue to have a big impact on us.”
###
This work was supported by the Swiss State Secretariat for Education, Research and Innovation SERI funded ERC Consolidator Project “RESERVOIR,” the University of Zurich’s University Research Priority Program “Evolution in Action: From Genomes to Ecosystems,” and the Fondation Raoul Follereau and the Heiser Program of the New York Community Trust for Research in Leprosy.
Current Biology, Urban, Blom, and Avanzi et al.: “Ancient Mycobacterium leprae genome reveals medieval English red squirrels as animal leprosy host.” https://www.cell.com/current-biology/fulltext/S0960-9822(24)00446-9
Current Biology (@CurrentBiology), published by Cell Press, is a bimonthly journal that features papers across all areas of biology. Current Biology strives to foster communication across fields of biology, both by publishing important findings of general interest and through highly accessible front matter for non-specialists. Visit http://www.cell.com/current-biology. To receive Cell Press media alerts, contact press@cell.com.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-05-03
The first panoramic view of infection pathways in the human placenta has been created, which could highlight potential drug targets to develop pregnancy-safe therapies for malaria, toxoplasmosis and listeria, all diseases that can cause severe pregnancy complications.
Researchers from the Wellcome Sanger Institute, the University of Cambridge, the University of Dundee, and collaborators, used novel ‘mini placenta’ models to map the placental response to infections in early development. This ...
2024-05-03
Researchers at the University of Basel and the University of Zurich have been able to prove that British squirrels carried leprosy bacteria as early as the Middle Ages. Further results revealed a link between the pathogens found in the medieval rodents and those in the local human population during that period.
Skin spots, deformed noses, ulcers: leprosy, is an infectious disease that can bring about some serious symptoms. The bacterium responsible, Mycobacterium leprae, which still infects around 200,000 people each year especially in the Global South, also has a long history in Europe. The international research group led by paleogeneticist Professor Verena Schünemann ...
2024-05-03
The Foundational Questions Institute, FQxI, a philanthropically-funded science funding agency and think tank, is delighted to announce that Dr Pinar Emirdag has been appointed to the Institute’s Board of Directors.
Emirdag, a financial services executive and entrepreneur, is currently director of Hupomone Ventures, having previously spearheaded industry-changing initiatives at institutions such as JP Morgan, Citi and the London Stock Exchange and at start-ups including Lava Trading and Clearmatics. FQxI’s Chief Operating Officer Kavita ...
2024-05-03
A first-ever stretchy electronic skin could equip robots and other devices with the same softness and touch sensitivity as human skin, opening up new possibilities to perform tasks that require a great deal of precision and control of force.
The new stretchable e-skin, developed by researchers at The University of Texas at Austin, solves a major bottleneck in the emerging technology. Existing e-skin technology loses sensing accuracy as the material stretches, but that is not the case with this new version.
"Much like human skin has to stretch and bend ...
2024-05-03
A common challenge in shipping occurs when ships arrive promptly at their destination, only to find a crowded harbour. Subsequently, they are often required to wait outside the harbour or anchor until port services and a quayside become available.
According to a report from the International Maritime Organization (IMO), it is not uncommon for ships to spend between 5-10% of their time waiting to enter port. Excessive speeds followed by extended waiting times with engines running result in a notable increase in fuel consumption. This is a problem that impacts both the climate and the economy.
Several European universities, ports, shipping companies and technology firms have now joined forces ...
2024-05-03
The interest in antimicrobial solutions for personal and multi-user touch screens, such as tablets and mobile devices, has grown in recent years. Traditional methods like sprayable alcohols or wipes are not ideal for these delicate displays. Antimicrobial coatings applied directly to the glass are a promising alternative, but only if they are transparent and long-lasting. Previous proposed coating solutions, such as photocatalytic metal oxides (e.g., TiO2 and ZnO), have posed some challenges. Additionally, these coatings typically require light and moisture to be antimicrobial and eliminate the microbes present on the surface.
Copper ...
2024-05-03
The number of male students at the University of Oxford from elite schools declined significantly by the middle of the twentieth century, a new study shows.
In contrast the proportion of female students remained steady. Those with fathers with professional jobs rose dramatically by the 1960s, according to the analysis.
At the beginning of the century around 25 to 35 per cent had fathers in professional occupations. This had risen to around 50 per cent among those arriving at Oxford in the 1960s.
The research, published in the journal Gender & History, was ...
2024-05-03
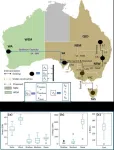
A model charts the most cost-efficient path to a fully renewable electricity grid for Australia. Raheel Ahmed Shaikh and colleagues modeled possible scenarios for Australia’s eastern and western grids, using solar and wind generation, short-to-long-term energy storage, and financial input data to explore low-cost capacity mix. Going completely renewable would require significant expansion of both generation and storage. Interconnecting the two grids would reduce generation capacity needs by 6% and storage power capacity needs by 14%. The least cost renewable-only grid would be dominated by wind, ...
2024-05-03
East Hanover, NJ – May 3, 2024 – John DeLuca, PhD, of Kessler Foundation was named recipient of the 2024 Giants of Multiple Sclerosis® award for rehabilitation. He was one of seven inductees announced by NeurologyLive® and the Consortium of Multiple Sclerosis Centers (CMSC) this week. Dr. DeLuca is senior vice president, Research and Training at the Foundation and a professor in the departments of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation and Neurology at Rutgers New Jersey Medical School.
Established in 2021, the Giants of Multiple Sclerosis award honors trailblazers, innovators, and visionaries ...
2024-05-03
Waltham — April 30, 2024 — One-third of patients undergoing surgery for adult spinal deformity (ASD) also have severe osteoarthritis (OA) of the hip – which is associated with worse spinal alignment and physical functioning, reports a study in The Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery. The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio in partnership with Wolters Kluwer.
These differences persist even following operative treatment of ASD, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] In medieval England, leprosy spread between red squirrels and people, genome evidence shows