(Press-News.org) About The Study: Racial and ethnic disparities were observed for almost all leading causes of injury and disease that were associated with recent increases in youth mortality rates. Addressing the increasing disparities affecting American Indian or Alaska Native and Black youth will require efforts to prevent homicide and suicide, especially those events involving firearms.
Authors: Elizabeth R. Wolf, M.D., M.P.H., of the Virginia Commonwealth University School of Medicine in Richmond, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2024.3908)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Media advisory: This study is being released to coincide with presentation at the Pediatric Academic Societies meeting.
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/10.1001/jama.2024.3908?guestAccessKey=964d2832-89ff-4409-a3a0-b96e343165cb&utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_content=tfl&utm_term=050424
END
Racial and ethnic disparities in all-cause and cause-specific mortality among US youth
JAMA
2024-05-04
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Ready to launch program introduces medical students to interventional cardiology field
2024-05-04
LONG BEACH (May 4, 2024) Interventional cardiology's future success relies on a diverse workforce that will help to positively impact patient outcomes. Now in its second year, SCAI’s Ready to Launch program introduces the interventional cardiology field to a diverse group of medical students at all levels, providing hands-on experience and mentorship opportunities. The program is hosted annually during SCAI Scientific Sessions with participation from local medical schools.
“This ...
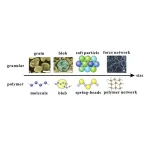
Variety in building block softness makes for softer amorphous materials
2024-05-04
Tokyo, Japan – Scientists from Tokyo Metropolitan University have created a new model for disordered materials to study how amorphous materials resist stress. They treated groups of atoms and molecules as squishy spheres with varying softness. Putting their model under a load, they discovered unexpected disparities between harder regions and where forces were concentrated, with areas in between such regions “hardening” to produce elongated “force chains”. Their findings promise new insights into designing better materials.
When it comes to building hard materials, using hard ingredients is not enough. For example, when concrete fails during ...
Tennis greats Chris Evert and Martina Navratilova honored at A Conversation With a Living Legend®
2024-05-04
HOUSTON ― Cancer survivors and tennis legends Chris Evert and Martina Navratilova participated in a fireside-style chat on Wednesday, May 1, at The University of Texas
MD Anderson Cancer Center’s signature event, A Conversation with a Living Legend ®, hosted at the Post Oak Hotel at Uptown Houston. The sold-out event raised more than $1.5 million for cell therapy research at MD Anderson with a ticketed audience of 800+.
Past Living Legend honoree and co-anchor of ABC’s Good Morning America, Robin Roberts, led the onstage interview with Evert and Navratilova, and ABC13 Houston’s ...
Seismic waves used to track LA’s groundwater recharge after record wet winter
2024-05-04
Record-setting storms in 2023 filled California’s major reservoirs to the brim, providing some relief in a decades-long drought, but how much of that record rain trickled underground?
Shujuan Mao of Stanford University and her colleagues used a surprising technique to answer this question for the greater Los Angeles metropolitan area. They analyzed changes in the velocity of seismic waves traveling through the LA basin, tracking these changes in space and time between January and October 2023.
As Mao reported at the Seismological Society of America (SSA)’s 2024 Annual Meeting, ...
When injecting pure spin into chiral materials, direction matters
2024-05-03
Researchers from North Carolina State University and the University of Pittsburgh studied how the spin information of an electron, called a pure spin current, moves through chiral materials. They found that the direction in which the spins are injected into chiral materials affects their ability to pass through them. These chiral “gateways” could be used to design energy-efficient spintronic devices for data storage, communication and computing.
Spintronic devices harness the spin of an electron, rather than its charge, to create current and move information through electronic devices.
“One of the goals in spintronics ...
New quantum sensing scheme could lead to enhanced high-precision nanoscopic techniques
2024-05-03
Researchers from the University of Portsmouth have unveiled a quantum sensing scheme that achieves the pinnacle of quantum sensitivity in measuring the transverse displacement between two interfering photons.
This new technique has the potential to enhance superresolution imaging techniques that already employ single-photon sources as probes for the localization and tracking of biological samples, such as single-molecule localization microscopy with quantum dots.
Traditionally, achieving ultra-high precision in nanoscopic techniques has been constrained by the limitations of standard imaging methods, such as the diffraction limit ...
New MSU research: Are carbon-capture models effective?
2024-05-03
MSU has a satellite uplink/LTN TV studio and Comrex line for radio interviews upon request.
EAST LANSING, Mich. – Reforestation efforts to restock depleted forests are important for addressing climate change and for both capturing and restoring carbon from the Earth’s atmosphere. These types of solutions to mitigate carbon emissions are critical after 2023 proved to be the warmest year on record. However, some models have been found to be inaccurate.
New research from Michigan State University has found the carbon removal potential of some reforestation models have been over exaggerated ...
One vaccine, many cancers
2024-05-03
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a type of blood cancer that forms in the soft marrow of the bones, typically attacking cells that would otherwise form the key component of the body’s immunodefense system, white blood cells.
In a new study published in Blood Advances, researchers from the UChicago Pritzker School of Molecular Engineering’s Hubbell Lab created with a novel approach to develop in-situ cancer vaccines that could increase the effectiveness of immunotherapies in AML and other blood ...
nTIDE April 2024 Jobs Report: Post-pandemic gains seen in employment for people with disabilities appear to continue
2024-05-03
East Hanover, NJ – May 3, 2024 – Following a two-month decline, the employment of individuals with disabilities returns to near historic highs reported by nTIDE in late 2023, reaffirming the significance of those prior highs. That’s according to today’s National Trends in Disability Employment – semi-monthly update (nTIDE), issued by Kessler Foundation and the University of New Hampshire’s Institute on Disability (UNH-IOD).
Month-to-Month nTIDE Numbers (comparing March 2024 to April 2024)
“Following two months of decline, individuals with disabilities are now edging back towards their near ...
Exploring oncogenic driver molecular alterations in Hispanic/Latin American cancer patients
2024-05-03
“[...] this editorial underscores the complex molecular diagnosis landscape of cancer in the [Latin American] population.”
BUFFALO, NY- May 3, 2024 – A new editorial paper was published in Oncoscience (Volume 11) on April 22, 2024, entitled, “Exploring oncogenic driver molecular alterations in Hispanic/Latin American cancer patients: A call for enhanced molecular understanding.”
In this new editorial, researcher Rafael Parra-Medina from Fundación Universitaria de Ciencias de la Salud and Instituto Nacional de Cancerología begins by discussing Latin America’s (LA) population — a heterogeneous mix ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Further evidence of developmental risks linked to epilepsy drugs in pregnancy
Cosmetic procedures need tighter regulation to reduce harm, argue experts
How chaos theory could turn every NHS scan into its own fortress
Vaccine gaps rooted in structural forces, not just personal choices: SFU study
Safer blood clot treatment with apixaban than with rivaroxaban, according to large venous thrombosis trial
Turning herbal waste into a powerful tool for cleaning heavy metal pollution
Immune ‘peacekeepers’ teach the body which foods are safe to eat
AAN issues guidance on the use of wearable devices
In former college athletes, more concussions associated with worse brain health
Racial/ethnic disparities among people fatally shot by U.S. police vary across state lines
US gender differences in poverty rates may be associated with the varying burden of childcare
3D-printed robotic rattlesnake triggers an avoidance response in zoo animals, especially species which share their distribution with rattlers in nature
Simple ‘cocktail’ of amino acids dramatically boosts power of mRNA therapies and CRISPR gene editing
Johns Hopkins scientists engineer nanoparticles able to seek and destroy diseased immune cells
A hidden immune circuit in the uterus revealed: Findings shed light on preeclampsia and early pregnancy failure
Google Earth’ for human organs made available online
AI assistants can sway writers’ attitudes, even when they’re watching for bias
Still standing but mostly dead: Recovery of dying coral reef in Moorea stalls
3D-printed rattlesnake reveals how the rattle is a warning signal
Despite their contrasting reputations, bonobos and chimpanzees show similar levels of aggression in zoos
Unusual tumor cells may be overlooked factors in advanced breast cancer
Plants pause, play and fast forward growth depending on types of climate stress
University of Minnesota scientists reveal how deadly Marburg virus enters human cells, identify therapeutic vulnerability
Here's why seafarers have little confidence in autonomous ships
MYC amplification in metastatic prostate cancer associated with reduced tumor immunogenicity
The gut can drive age-associated memory loss
Enhancing gut-brain communication reversed cognitive decline, improved memory formation in aging mice
Mothers exposure to microbes protect their newborn babies against infection
How one flu virus can hamper the immune response to another
Researchers uncover distinct tumor “neighborhoods”, with each cell subtype playing a specific role, in aggressive childhood brain cancer
[Press-News.org] Racial and ethnic disparities in all-cause and cause-specific mortality among US youthJAMA