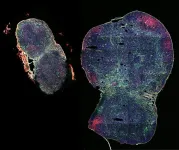
(Press-News.org) A pattern of brain activity that helps prevent us from getting lost has been identified in a new study, published in Nature Human Behaviour.
Researchers at the University of Birmingham and Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich have for the first time been able to pinpoint the location of an internal neural compass which the human brain uses to orientate itself in space and navigate through the environment.
The research identifies finely tuned head direction signals within the brain. The results are comparable to neural codes identified in rodents and have implications for understanding diseases such as Parkinson’s and Alzheimers, where navigation and orientation are often impaired.
Measuring neural activity in humans while they are moving is challenging as most technologies available require participants to remain as still as possible. In this study, the researchers overcame this challenge by using mobile EEG devices and motion capture.
First author Dr Benjamin J. Griffiths said: “Keeping track of the direction you are heading in is pretty important. Even small errors in estimating where you are and which direction you are heading in can be disastrous. We know that animals such as birds, rats and bats have neural circuitry that keeps them on track, but we know surprisingly little about how the human brain manages this out and about in the real world.”
A group of 52 healthy participants took part in a series of motion-tracking experiments while their brain activity was recorded via scalp EEG. These enabled the researchers to monitor brain signals from the participants as they moved their heads to orientate themselves to cues on different computer monitors.
In a separate study, the researchers monitored signals from 10 participants who were already undergoing intercranial electrode monitoring for conditions such as epilepsy.
All the tasks prompted participants to move their heads, or sometimes just their eyes, and brain signals from these movements were recorded from EEG caps, which measure signals from the scalp, and the intracranial EEG (iEEG), which records data from the hippocampus and neighbouring regions.
After accounting for ‘confounds’ in the EEG recordings from factors such as muscle movement or position of the participant within the environment, the researchers were able to show a finely tuned directional signal, which could be detected just before physical changes in head direction among participants.
Dr Griffiths added: “Isolating these signals enables us to really focus on how the brain processes navigational information and how these signals work alongside other cues such as visual landmarks. Our approach has opened up new avenues for exploring these features, with implications for research into neurodegenerative diseases and even for improving navigational technologies in robotics and AI.”
In future work, the researchers plan to apply their learning to investigate how the brain navigates through time, to find out if similar neuronal activity is responsible for memory.
END
Human ‘neural compass’ pinpointed in new study
2024-05-06
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Personalized screening early in pregnancy may improve preeclampsia detection
2024-05-06
Research Highlights:
A personalized screening algorithm for preeclampsia in the first trimester of pregnancy may help clinicians better predict who is at risk for developing the condition and who may benefit from treatment with a daily, low-dose aspirin.
In this study of more than 7,000 women, the new screening method, which combined maternal history, biomarker tests and ultrasound tests, was better at identifying preeclampsia risk in than current risk factor-based guidelines.
Embargoed until 4 a.m. CT/5 a.m. ET Monday, May 6, 2024
DALLAS, May 6, 2024 — A new screening algorithm for preeclampsia combining maternal history, ...
Expanding a lymph node, boosting a vaccine
2024-05-06
Expanding a lymph node, boosting a vaccine
A biomaterial vaccine enhances and sustains lymph node expansion following vaccination, boosting anti-tumor immunity in an animal model.
By Benjamin Boettner
(BOSTON) — Each one of us has around 600 lymph nodes (LNs) – small, bean-shaped organs that house various types of blood cells and filter lymph fluid – scattered throughout our bodies. Many of us have also experienced some of our LNs to temporarily swelling during infections with viruses or other pathogens. This LN expansion and subsequent contraction can also result from vaccines injected nearby, and in fact ...
GIST-MIT CSAIL researchers develop a biomechanical dataset for badminton performance analysis
2024-05-06
In sports training, practice is the key, but being able to emulate the techniques of professional athletes can take a player’s performance to the next level. AI-based personalized sports coaching assistants can make this a reality by utilizing published datasets. With cameras and sensors strategically placed on the athlete's body, these systems can track everything, including joint movement patterns, muscle activation levels, and gaze movements.
Using this data, personalized feedback is provided on player technique, along with improvement recommendations. Athletes can access this feedback anytime, and anywhere, making these systems versatile for athletes at ...
Study sheds light on 11th century Arab-Muslim optical scientist whose work laid ground for modern-day physics
2024-05-06
Scientists from the University of Sharjah and the Warburg Institute are poring over the writings of an 11th century Arab-Muslim polymath to demonstrate their impact on the development of optical sciences and how they have fundamentally transformed the history of physics from the Middle Ages up to modern times in Europe.
Their research focuses on the legacy of al-Ḥasan Ibn al-Haytham known in Latin as “Alhazen” and particularly his most influential work titled Book of Optics, reputed in Arabic as Kitab al-Manazir and first circulated in Europe via its Latin translation dubbed ‘Perspectiva’. Ibn ...
Rethinking “socially admitted” patients
2024-05-06
Labelling vulnerable patients in hospital as “socially admitted” may prevent treatment of medical issues, according to new research in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) https://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.231430.
Emergency departments are the last resort for some socially vulnerable people who may not have an acute or new medical issue. They may be seeking care because of a breakdown of supports or the inability of the patient, or their family, to cope with living at home. These people are known colloquially as “social admissions,” and other labels such as “orphan patient,” “failure ...
A better way to ride a motorcycle
2024-05-06
Motorcycles are designed to accommodate the average-sized rider, leaving taller and shorter riders vulnerable to discomfort.
A new study from the University of Waterloo used software that predicted realistic motorcycle riding behaviours, considering human factors and ergonomic trade-offs. It found that shorter and taller statures require joint adjustments to achieve their preferred riding posture.
Taller riders are required to flex their ankles, knees, hips and elbows more to interact with the motorcycle properly, ...
Survey of US parents highlights need for more awareness about newborn screening, cystic fibrosis and what to do if results are abnormal
2024-05-05
A national survey led by Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago found that parents have insufficient knowledge of newborn screening in general and of cystic fibrosis (CF) in particular. Researchers asked specific questions about CF based on studies showing that initial CF follow-up visits after a positive newborn screening often occur after 4 weeks of age, which is later than the recommended timeframe for best outcomes. Later follow-up is associated with worse nutrition in childhood, a predictor of long-term health in CF. Parents ...
Outcomes of children admitted to a pediatric observation unit with a psychiatric comanagement model
2024-05-05
About The Study: The findings of this study show a significantly lower pediatric emergency department length of stay and inpatient psychiatric admission rate following pediatric observation unit care and potential savings in inpatient psychiatric resources without contributing to 30-day readmission rates.
Authors: Rachel G. Kasdin, M.S., of the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamapediatrics.2024.1123)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, ...
SCAI announces 2024-25 SCAI-WIN CHIP Fellowship Recipient
2024-05-05
LONG BEACH (May 4, 2024) Mariem A. Sawan, MBBS, chief interventional cardiology fellow at Emory University, has been selected as the recipient of the SCAI-Women in Innovations (SCAI-WIN) CHIP Fellowship, the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions announced today.
The $115,000 fellowship opportunity was made possible by support from Abiomed (founding supporter), Boston Scientific, Medtronic, and Shockwave Medical, Inc., and is offered to interventional cardiology (IC) fellows or practicing interventional cardiologists ...
SCAI’s 30 in Their 30’s Award recognizes the contributions of early career interventional cardiologists
2024-05-05
LONG BEACH (May 4, 2024) During SCAI 2024 Scientific Sessions, the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography & Interventions (SCAI) presented its "30 in Their 30’s" award to thirty early-career interventional cardiologists.
This award program recognizes the excellence of these members for their outstanding leadership and demonstration of SCAI's core values and is designed to encourage and support young interventional cardiologists who have already made a significant impact in the field.
Recipients include:
Aakash Garg, MD, FSCAI
Adnan Khalif, MD, FSCAI
Alejandro ...