(Press-News.org) CCU (Carbon Capture & Utilization), which captures CO2 and converts it into useful compounds, is crucial for rapidly transitioning to a carbon-neutral society. While CCS (Carbon Capture & Storage), which only involves CO2 storage, has entered the initial commercialization stage due to its relatively simple process and low operational costs, CCU has only been explored at the research level due to the complexity of conversion processes and high production costs of compounds.
Dr. Lee Ung's team at the Clean Energy Research Center of the Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST, Director Oh Sang Rok) announced the development of a novel CCU process that converts CO2 into formic acid. Formic acid, an organic acid, is a high-value compound used in various industries such as leather, food, and pharmaceuticals. Currently formic acid retains a large market consuming around one million tons annually, which is expected to grow in the future owing to its potential use as a hydrogen carrier. Moreover, it has a higher production efficiency compared to other CCU-based chemicals, as it can be produced from a single CO2 molecule.
The research team selected 1-methylpyrrolidine, which exhibited the highest CO2 conversion rate among various amines mediating formic acid production reactions, and optimized the operating temperature and pressure of the reactor containing a ruthenium (Ru)-based catalyst, thereby increasing the CO2 conversion rate to over twice the current level of 38%. Furthermore, to address the excessive energy consumption and formic acid decomposition issues during CO2 separation from air or exhaust gases and formic acid purification, the team developed a simultaneous capture-conversion process that directly converts CO2 captured within the amine without separating it. As a result, they significantly reduced the formic acid production cost from around $790 per ton to $490 per ton while mitigating CO2 emissions, compared to conventional formic acid production.
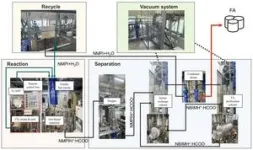
To evaluate the commercialization potential of the developed formic acid production process, the research team constructed the world's largest pilot plant capable of producing 10 kg of formic acid per day. Previous CCU studies were conducted on a small scale in laboratories and did not consider the product purification process required for large-scale production. However, the research team developed processes and materials to minimize corrosion and formic acid decomposition, and optimized operating conditions that led to successful production of formic acid with a purity exceeding 92%.
The team plans to complete a 100 kg per day pilot plant by 2025 and conduct process verification, aiming for commercialization by 2030. Success in process verification with the 100 kg pilot plant is expected to enable transportation and sales to demand companies.
Dr. Lee Ung stated, "Through this research, we have confirmed the commercialization potential of our process that converts CO2 to formic acid, which is a huge breakthrough considering that most CCU technologies are being conducted at lab-scale." He further expressed his intention to contribute to achieving the country's carbon neutrality goal by accelerating the commercialization of CCU. .
###
KIST was established in 1966 as the first government-funded research institute in Korea. KIST now strives to solve national and social challenges and secure growth engines through leading and innovative research. For more information, please visit KIST’s website at https://eng.kist.re.kr/
This research was supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT (Minister Lee Jong-Ho) as part of KIST's major projects and the Carbon-to-X project(2020M3H7A1098271). The research results were published in the latest issue of the international journal "Joule" (IF 39.8, JCR top 0.9%).
END
The commercialization of CO2 utilization technology to produce formic acid is imminent
Development of a CCU process for formic acid production with both economic and environmental viability. Expected to expedite the commercialization of CCU through the world's largest-scale demonstration.
2024-05-07
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Multisite review shows serious adverse events occur frequently in outpatient care
2024-05-06
Embargoed for release until 5:00 p.m. ET on Monday 6 May 2024
Annals of Internal Medicine Tip Sheet
@Annalsofim
Below please find summaries of new articles that will be published in the next issue of Annals of Internal Medicine. The summaries are not intended to substitute for the full articles as a source of information. This information is under strict embargo and by taking it into possession, media representatives are committing to the terms of the embargo not only on their own behalf, but also on behalf of the ...
Study highlights need for improvement of patient safety in outpatient settings
2024-05-06
KEY TAKEAWAYS
In a study of outpatient sites, researchers found that 7% of patients experienced at least one adverse event and 1.9% of patients experienced at least one preventable adverse event.
The most common adverse events in the outpatient setting were adverse drug events.
The findings highlight an urgent need to develop interventions to prevent both inpatient and outpatient harm.
Over the last several decades, research has brought nationwide awareness to issues of patient harm in the “inpatient” setting, where patients ...
Sylvester researchers develop a nanoparticle that can penetrate the blood-brain barrier
2024-05-06
MIAMI, FLORIDA (EMBARGOED UNTIL MAY 6, 2024 AT 3:00 P.M. EDT) – Researchers at Sylvester Comprehensive Cancer Center at the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine have developed a nanoparticle that can penetrate the blood-brain barrier. Their goal is to kill primary breast cancer tumors and brain metastases in one treatment, and their research shows the method can shrink breast and brain tumors in laboratory studies.
Brain metastases, as these secondary tumors are called, most commonly arise from solid tumors like breast, lung and colon cancer and are often associated with a poor prognosis. When cancer breaches ...
Caterbot? Robatapillar? It crawls with ease through loops and bends
2024-05-06
Engineers at Princeton and North Carolina State University have combined ancient paperfolding and modern materials science to create a soft robot that bends and twists through mazes with ease.
Soft robots can be challenging to guide because steering equipment often increases the robot’s rigidity and cuts its flexibility. The new design overcomes those problems by building the steering system directly into the robot’s body, said Tuo Zhao, a postdoctoral researcher at Princeton.
In an article published May 6 in the journal PNAS, the researchers describe how they created the robot out ...
Geologists, biologists unearth the atomic fingerprints of cancer
2024-05-06
Scientists at the University of Colorado Boulder and Princeton University have, for the first time, employed a tool often used in geology to detect the atomic fingerprints of cancer.
In a case of medicine meets earth science, the researchers discovered that cancer cells may be made from a different assortment of hydrogen atoms than healthy tissue. The findings could give doctors new strategies for studying how cancer grows and spreads—and may even, one day, lead to new ways to spot cancer early on in the body.
The team, led by CU Boulder geochemist Ashley Maloney, will publish its findings this week ...
Purdue pharmacy researcher receives $2.4 million NIH grant to fight antimicrobial-resistant lung infections
2024-05-06
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. — Qi “Tony” Zhou, a researcher in Purdue University’s College of Pharmacy has received a $2.4 million grant from the National Institutes of Health to fight lung infections that have established a resistance to antimicrobial drugs.
Zhou is an associate professor in the Department of Industrial and Molecular Pharmaceutics, a Faculty Scholar and a faculty member of the Purdue Institute for Drug Discovery and the Purdue Institute of Inflammation, Immunology and Infectious Disease. He leads a team of multinational experts from Australia, Thailand and the United States in developing novel, patent-pending ...
The Clues for Cleaner Water
2024-05-06
Researchers at the University of Pittsburgh and Drexel University in Philadelphia, along with Brookhaven National Laboratory, are working to solve a multipart mystery to make water disinfection treatments more sustainable.
Scalable electrochemical ozone production (EOP) technologies to disinfect dirty water may someday replace centralized chlorine treatments used today, whether in modern cities or remote villages. However, little is understood about EOP at the molecular level and how technologies that make it possible can be made to be efficient, economical, and sustainable.
Their research, “Interplay between Catalyst Corrosion and Homogeneous Reactive Oxygen Species ...
New $14.5 million center to help US Navy overcome emerging challenges
2024-05-06
Images
The U.S. Office of Naval Research is tapping academic expertise at the University of Michigan to solve current and future problems, Secretary of the Navy Carlos Del Toro announced during his visit to campus over graduation weekend.
The $14.5M Center for Naval Research and Education will also help train an engineering research community familiar with naval and marine applications.
"I am incredibly proud of the partnership between the University of Michigan and the Department of the Navy. Michigan is a key teammate in rebuilding our shipbuilding industry and restoring the comprehensive—commercial ...
Now available from Penn Nursing: innovative, online psychedelic course
2024-05-06
PHILADELPHIA (May 6, 2024) – Penn Nursing is proud to launch a groundbreaking new online course – Educating Nurses in Psychedelic Assisted Therapy – via Open Canvas. This free comprehensive course is designed to prepare nursing professionals for the pioneering field of psychedelic assisted therapy (PAT), aligning with the latest advancements in mental health treatment and Penn Nursing's commitment to social justice in healthcare.
With this new modality of care on the horizon, the need for well-educated, ...
Greet receives funding for Abstraction in the Andes, 1950 - 1970
2024-05-06
Michele Greet, Director, Art History Program, received funding for: “Abstraction in the Andes, 1950-1970.”
She will examine the emergence of abstract painting in Andean countries (Peru, Ecuador, and Bolivia) in the 1950s and 1960s. She will explore artists’ newfound interest in pre-Columbian art as source material as well as the circulation of ideas from Europe and the United States.
Although abstract art rapidly gained acceptance throughout Latin America after World War II, until recently, studies of abstract painting in the region have focused on the geometric styles that emerged in Brazil, Argentina, and Venezuela. Different variants of abstraction ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
[Press-News.org] The commercialization of CO2 utilization technology to produce formic acid is imminentDevelopment of a CCU process for formic acid production with both economic and environmental viability. Expected to expedite the commercialization of CCU through the world's largest-scale demonstration.