(Press-News.org) More than 100 years ago, scientists at The University of Manchester changed the world when they discovered the nucleus in atoms, marking the birth of nuclear physics.
Fast forward to today, and history repeats itself, this time in quantum computing.
Building on the same pioneering method forged by Ernest Rutherford – "the founder of nuclear physics" – scientists at the University, in collaboration with the University of Melbourne in Australia, have produced an enhanced, ultra-pure form of silicon that allows construction of high-performance qubit devices – a fundamental component required to pave the way towards scalable quantum computers.
The finding, published in the journal Communications Materials - Nature, could define and push forward the future of quantum computing.
Richard Curry, Professor of Advanced Electronic Materials at The University of Manchester, said:
“What we’ve been able to do is effectively create a critical ‘brick’ needed to construct a silicon-based quantum computer. It’s a crucial step to making a technology that has the potential to be transformative for humankind - feasible; a technology that could give us the capability to process data at such as scale, that we will be able to find solutions to complex issues such as addressing the impact of climate change and tackling healthcare challenges.
“It is fitting that this achievement aligns with the 200th anniversary of our University, where Manchester has been at the forefront of science innovation throughout this time, including Rutherford’s ‘splitting the atom’ discovery in 1917, then in 1948 with ‘The Baby’ - the first ever real-life demonstration of electronic stored-program computing, now with this step towards quantum computing.”
Overcoming a challenge
One of the biggest challenges in the development of quantum computers is that qubits – the building blocks of quantum computing - are highly sensitive and require a stable environment to maintain the information they hold. Even tiny changes in their environment, including temperature fluctuations can cause computer errors.
Another issue is their scale, both their physical size and processing power. Ten qubits have the same processing power as 1,024 bits in a normal computer and can potentially occupy much smaller volume. Scientists believe a fully performing quantum computer needs around one million qubits, which provides the capability unfeasible by any classical computer.
Silicon is the underpinning material in classical computing due to its semiconductor properties and the researchers believe it could be the answer to scalable quantum computers. Scientists have spent the last 60 years learning how to engineer silicon to make it perform to the best of its ability, but in quantum computing, it has its challenges.
Natural silicon is made up of three atoms of different mass (called isotopes) – silicon 28, 29 and 30. However the Si-29, making up around 5% of silicon, causes a ‘nuclear flip flopping’ effect causing the qubit to lose information.
In a breakthrough at The University of Manchester, scientists have come up with a way to engineer silicon to remove the silicon 29 and 30 atoms, making it the perfect material to make quantum computers at scale, and with high accuracy.
The result – the world’s purest silicon – provides a pathway to the creation of one million qubits, which may be fabricated to the size of pin head.
Ravi Acharya, a PhD researcher who performed experimental work in the project, explained: "The great advantage of silicon quantum computing is that the same techniques that are used to manufacture the electronic chips — currently within an everyday computer that consist of billions of transistors — can be used to create qubits for silicon-based quantum devices. The ability to create high quality Silicon qubits has in part been limited to date by the purity of the silicon starting material used. The breakthrough purity we show here solves this problem."
The new capability offers a roadmap towards scalable quantum devices with unparalleled performance and capabilities and holds promise of transforming technologies in ways hard to imagine.
Project co-supervisor, Professor David Jamieson, from the University of Melbourne, said: “Our technique opens the path to reliable quantum computers that promise step changes across society, including in artificial intelligence, secure data and communications, vaccine and drug design, and energy use, logistics and manufacturing.
“Now that we can produce extremely pure silicon-28, our next step will be to demonstrate that we can sustain quantum coherence for many qubits simultaneously. A reliable quantum computer with just 30 qubits would exceed the power of today's supercomputers for some applications,”
What is quantum computing and how does it work?
All computers operate using electrons. As well as having a negative charge, electrons have another property known as ‘spin’, which is often compared to a spinning top.
The combined spin of the electrons inside a computer’s memory can create a magnetic field. The direction of this magnetic field can be used to create a code where one direction is called ‘0’ and the other direction is called ‘1’. This then allows us to use a number system that only uses 0 and 1 to give instructions to the computer. Each 0 or 1 is called a bit.
In a quantum computer, rather than the combined effect of the spin of many millions of electrons, we can use the spin of single electrons, moving from working in the ‘classical’ world to the ‘quantum’ world; from using ‘bits’ to ‘qubits’.
While classical computers do one calculation after another, quantum computers can do all the calculations at the same time allowing them to process vast amounts of information and perform very complex calculations at an unrivalled speed.
While still in early stages of quantum computing, once fully developed, quantum computers will be used to solve real-world complex problems, such as drug design, and provide more accurate weather forecasts – calculations too difficult for today’s supercomputers.
This work was supprted by the UK Engineering and Physical Science Research Council (EPSRC), specifically the Programme Grant ‘Nanoscale Advanced Materials Engineering led by Prof. Curry. Professor Jamieson’s collaboration with the University of Manchester is supported by a Royal Society Wolfson Visiting Fellowship and the Australian Research Council. Ravi Acharya is a joint University of Manchester and University of Melbourne PhD student supported by a Cookson Scholarship.
END
Quantum breakthrough: World’s purest silicon brings scientists one step closer to scaling up quantum computers
2024-05-07
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New super-pure silicon chip opens path to powerful quantum computers
2024-05-07
Researchers at the Universities of Melbourne and Manchester have invented a breakthrough technique for manufacturing highly purified silicon that brings powerful quantum computers a big step closer.
The new technique to engineer ultra-pure silicon makes it the perfect material to make quantum computers at scale and with high accuracy, the researchers say.
Project co-supervisor Professor David Jamieson, from the University of Melbourne, said the innovation – published today in Communication Materials, a Nature journal – uses qubits of phosphorous atoms implanted ...
Millions in costs due to discharge of scrubber water into the Baltic Sea
2024-05-07
Discharge from ships with so-called scrubbers cause great damage to the Baltic Sea. A new study from Chalmers University of Technology, Sweden, shows that these emissions caused pollution corresponding to socio-economic costs of more than EUR 680 million between 2014 and 2022. At the same time, the researchers note that the shipping companies' investments in the much-discussed technology, where exhaust gases are "washed" and discharged into the sea, have already been recouped for most of the ships. This means that the industry is now making billions ...
Bio-inspired materials’ potential for efficient mass transfer boosted by a new twist on a century-old theory
2024-05-07
The natural vein structure found within leaves – which has inspired the structural design of porous materials that can maximise mass transfer – could unlock improvements in energy storage, catalysis, and sensing thanks to a new twist on a century-old biophysical law.
An international team of researchers, led by the NanoEngineering Group at the Cambridge Graphene Centre, has developed a new materials theory based on ‘Murray’s Law’, applicable to a wide range of next-generation functional ...
Small pump for kids awaiting heart transplant shows promise in Stanford Medicine-led trial
2024-05-07
A small, implantable cardiac pump that could help children await heart transplants at home, not in the hospital, has performed well in the first stage of human testing.
The pump, a new type of ventricular assist device, or VAD, is surgically attached to the heart to augment its blood-pumping action in individuals with heart failure, allowing time to find a donor heart. The new pump could close an important gap in heart transplant care for children.
In a feasibility trial of seven children who received the new pump to support their failing hearts, six ultimately underwent heart transplants ...
Time flies, but your hands tell: Haut.AI cracks the age code with hand analysis
2024-05-07
Tallinn, Estonia – 7th May 2024, 10 AM CET – Haut.AI, a leader in responsible skincare artificial intelligence (AI) development, today announced a breakthrough research paper demonstrating the effectiveness of using hand images for accurate age prediction. This innovative approach offers a viable alternative to traditional facial photo methods and promotes fairer AI solutions.
The study, titled “Predicting human chronological age via AI analysis of dorsal hand versus facial images: A study in a cohort of Indian females,” shows that AI models trained on hand images achieve comparable accuracy to those using facial images, with an average error of ...
Babraham Institute receives £48M strategic investment from BBSRC for a four-year programme of work to promote lifelong health
2024-05-07
Following a quinquennial review by the Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council (BBSRC), the Babraham Institute will receive £48m for the period 2024-2028 to advance research on the mechanisms that maintain the health of our cells, tissues and organs across the life course.
This work is key in driving BBSRC’s strategic research priorities around an integrated understanding of health, developing and applying transformative technologies and advancing our understanding of the rules of life.
As one of eight UK bioscience ...
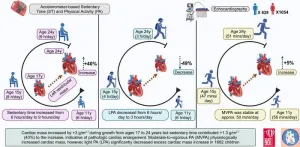
Childhood sedentariness linked to premature heart damage – light physical activity reversed the risk
2024-05-07
An increase in sedentary time from childhood caused progressing heart enlargement, a new study shows. However, light physical activity could reduce the risk. The study was conducted in collaboration between the Universities of Bristol and Exeter, and the University of Eastern Finland, and the results were published in the prestigious European Journal of Preventive Cardiology.
Left ventricular hypetrophy refers to an excessive increase in heart mass and size. In adults, it is known to increase the risk for heart attacks, stroke, and premature death.
In the present study, 1,682 children ...
Parents’ watchful eye may keep young teens from trying alcohol, drugs: Study
2024-05-07
PISCATAWAY, NJ – Teenagers are less likely to drink, smoke or use drugs when their parents keep tabs on their activities--but not necessarily because kids are more likely to be punished for substance use, suggests a new study in the Journal of Studies on Alcohol and Drugs.
Researchers found that, contrary to common belief, parents’ “monitoring” does not seem to boost the odds of catching their kids using substances. However, when kids simply are aware that their parents are monitoring behavior, they avoid trying alcohol or drugs in the first place.
It is the fear of being caught, rather than actually being punished.
Many studies ...
A triumph of galaxies in three new images from the VST
2024-05-07
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
Distant, far away galaxies. Interacting galaxies, whose shape has been forged by the mutual gravitational influence, but also galaxies forming groups and clusters, kept together by gravity. They are the protagonists of three new images released by the VLT Survey Telescope (VST).
VST is an optical telescope with a 2,6 diameter mirror, entirely built in Italy, that has been operating since 2011 at the European Southern Observatory’s (ESO) Paranal Observatory in Chile. Since 2022, the telescope has been fully managed by INAF through the National Coordination Centre for VST, ...
Smart labs for bespoke synthesis of nanomaterials are emerging
2024-05-07
In the early 20th century, the development of a catalyst for ammonia synthesis by the Haber-Bosch method took more than 10,000 experiments before it was successful. The development of new materials is a time-consuming and costly process from design to commercialization. However, in recent years, researchers have been working to shorten the development period by using artificial intelligence (AI). When combined with robots, it is possible to conduct material development research 24 hours a day, 365 days a year without human ...