(Press-News.org) The eventual prevalence of a piece of misinformation may depend on its topic and the country in which it spreads, with notable differences between the UK, Germany, France and Italy, according to a study published May 8, 2024 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Fabiana Zollo from the Ca’ Foscari University of Venice, Italy, and colleagues. This finding suggests that policies to combat misinformation and polarization may need to be context-specific in order to be effective, the authors say.
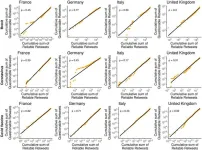
Researchers analyzed news activity on Twitter (now X) in France, Germany, Italy and the UK from 2019 to 2021, including a focus on news about Brexit, the coronavirus, and the Covid vaccines. Each news source they analyzed was rated as either “Reliable” or “Questionable” based upon their NewsGuard (a tool that evaluates the reliability of news outlets based on nine journalistic criteria) score.
Across all four countries, the vast majority of users only ever consumed reliable news sources on each of the three topics. But in every country and in each topic, there were always a small percentage of users who only ever consumed questionable news sources — with very few people consuming a mix of both reliable and questionable sources.
The ratio of questionable news vs reliable news consumption and spread varied between countries. Overall, Germany had the highest ratio of questionable news retweets to reliable news retweets on all three topics, with France in second, followed by Italy, and the UK had the lowest proportion of questionable news retweets overall. However, measures of misinformation varied by topic. Italy, for example, had the lowest proportion of questionable news retweets for the topic of the coronavirus – but had the highest percentage of people consuming only questionable news sources on Brexit. These kinds of differences could emphasize that “cultural nuances” will be important when it comes to fighting misinformation, the authors write.
#####
In your coverage please use this URL to provide access to the freely available article in PLOS ONE: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0302473
Citation: Baqir A, Galeazzi A, Zollo F (2024) News and misinformation consumption: A temporal comparison across European countries. PLoS ONE 19(5): e0302473. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0302473
Author Countries: Italy
Funding: F.Z. acknowledges financial support from the European Union’s Rights, Equality and Citizenship project EUMEPLAT grant no. 101004488. A.G. and F.Z. acknowledge partial support from the IRIS Academic Research Coalition (UK government, grant no. SCH-00001-3391). F.Z. acknowledges the partial support received from SERICS (PE00000014), which is funded under the MUR National Recovery and Resilience Plan by the European Union’s NextGenerationEU initiative. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript. There was no additional external funding received for this study.
END
The spread of misinformation varies by topic and by country in Europe
A few people in Germany, France, Italy and the UK primarily rely on questionable news sources, though most read only trustworthy news
2024-05-08
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Pacific Oyster density has increased up to 32-fold across a decade in some California waters, and coincides with summer seawater temperature increases of 2-4°C
2024-05-08
Pacific Oyster density has increased up to 32-fold across a decade in some California waters, and coincides with summer seawater temperature increases of 2-4°C
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0302935
Article Title: Intra-decadal increase in globally-spread Magallana gigas in southern California estuaries
Author Countries: USA
Funding: “Funding was provided by CSU Fullerton and via subcontracts with Merkel & Associates, Inc. and Port of San Diego to DCZ. Funders had no involvement in the study design or data collection process.” The funders had no role in study design, data collection ...
The EU could mitigate climate change equivalent to 13% of its agricultural greenhouse gas emissions by planting cover crops on bare soil before maize
2024-05-08
The EU could mitigate climate change equivalent to 13% of its agricultural greenhouse gas emissions by planting cover crops on bare soil before maize
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0302139
Article Title: Cover crops support the climate change mitigation potential of agroecosystems
Author Countries: Germany
Funding: The research was funded by the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research within the Project "CATCHY", project number: 031B1060C. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision ...
Strengthening CAR-T therapy to work against solid tumors
2024-05-08
May 8, 2024—(BRONX, NY)—Researchers at the National Cancer Institute-designated Montefiore Einstein Comprehensive Cancer Center (MECCC) have shown that a breakthrough therapy for treating blood cancers can be adapted to treat solid tumors—an advance that could transform cancer treatment. The promising findings, reported today in Science Advances, involve CAR-T cell therapy, which supercharges the immune system to identify and attack cancer cells.
“CAR-T cell therapy has revolutionized ...
Exercise, new drug class recommended for management of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
2024-05-08
The American College of Cardiology (ACC) and the American Heart Association (AHA) today released a new clinical guideline for effectively managing individuals diagnosed with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM). The guideline reiterates the importance of collaborative decision-making with patients who have HCM and provides updated recommendations for the most effective treatment pathways for adult and pediatric patients.
HCM is an inherited cardiac condition most often caused by a gene mutation that makes the heart muscle too thick (hypertrophy), which impairs its ability to adequately pump blood throughout ...
Study: Heavy snowfall and rain may contribute to some earthquakes
2024-05-08
When scientists look for an earthquake’s cause, their search often starts underground. As centuries of seismic studies have made clear, it’s the collision of tectonic plates and the movement of subsurface faults and fissures that primarily trigger a temblor.
But MIT scientists have now found that certain weather events may also play a role in setting off some quakes.
In a study appearing today in Science Advances, the researchers report that episodes of heavy snowfall and rain likely contributed to ...
USC study reveals role of iron in allergic asthma and points to potential new therapies
2024-05-08
New USC research shows that iron serves as a gas pedal driving certain immune cells that cause inflammation in the lungs during an allergic asthma attack – and blocking or limiting iron may reduce the severity of symptoms.
During an attack, immune cells known as group 2 innate lymphoid cells (ILC2s) can become overactive, causing excessive inflammation and a tightening of the airways, making it difficult to breath. However, the underlying biology is poorly understood.
Now, researchers from the Keck School ...
SARS-CoV-2 and type 1 diabetes in children: new study aims to explore the relationship
2024-05-08
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease that leads to disrupted glucose metabolism. It requires lifelong insulin therapy. The Global Platform for the Prevention of Autoimmune Diabetes (GPPAD) collaborates within a European network to develop new methods to prevent this condition which is, to date incurable. AVAnT1A is GPPAD's third intervention study. It will investigate whether vaccination against SARS-CoV-2 in the first year of life can protect children who have an increased genetic risk for type 1 diabetes from developing the condition. The study is supported by funding from The Leona M. and Harry B. Helmsley ...
ECOG-ACRIN adds another trial to the ComboMATCH precision oncology study platform
2024-05-08
Another ECOG-ACRIN Cancer Research Group (ECOG-ACRIN) treatment trial is open as part of the ComboMATCH precision medicine study platform. ComboMATCH-E5 is evaluating treatment for patients with KRAS G12C-mutated advanced solid tumors with two different targeted drugs given together. The two drugs include the KRAS G12C inhibitor sotorasib and panitumumab, a human monoclonal antibody antagonist specific to the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR). Each drug is approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) as single-agent therapy for particular cancer types.
"Given the preclinical data demonstrating EGFR over-dependency ...
UT Institute of Agriculture invests in premier poultry research facility
2024-05-08
Poultry production and processing is a $10 billion industry in Tennessee, with more investment expected. To support the future of the industry, the University of Tennessee Institute of Agriculture is investing in the construction of a state-of-the-art, next generation poultry research and education facility at its Middle Tennessee AgResearch and Education Center in Spring Hill.
On Thursday, May 2, nearly 100 state and local officials and members of the poultry production and processing industry joined university officials to celebrate the official groundbreaking for the new project. Four commercial-size (54’ ...
ESMO Breast Cancer 2024: Event announcement
2024-05-08
Lugano, Switzerland, 8 May 2024 – ESMO Breast Cancer 2024 will be held in Berlin, Germany, between 15-17 May where the latest research in breast cancer will be presented. Participants from all over the world are expected to come to Berlin to listen to renowned experts presenting key innovative areas – including new agents, molecular and functional diagnostics, biomarkers and cutting-edge research applications – and providing perspectives on how transformative new data can find a clear path to the clinic.
The congress can be attended in person and online.
The scientific programme is ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
Political polarization can spur CO2 emissions, stymie climate action
Researchers develop new strategy for improving inverted perovskite solar cells
Yes! The role of YAP and CTGF as potential therapeutic targets for preventing severe liver disease
Pancreatic cancer may begin hiding from the immune system earlier than we thought
Robotic wing inspired by nature delivers leap in underwater stability
A clinical reveals that aniridia causes a progressive loss of corneal sensitivity
Fossil amber reveals the secret lives of Cretaceous ants
Predicting extreme rainfall through novel spatial modeling
The Lancet: First-ever in-utero stem cell therapy for fetal spina bifida repair is safe, study finds
Nanoplastics can interact with Salmonella to affect food safety, study shows
Eric Moore, M.D., elected to Mayo Clinic Board of Trustees
NYU named “research powerhouse” in new analysis
New polymer materials may offer breakthrough solution for hard-to-remove PFAS in water
[Press-News.org] The spread of misinformation varies by topic and by country in EuropeA few people in Germany, France, Italy and the UK primarily rely on questionable news sources, though most read only trustworthy news