(Press-News.org) Pradipta Ghosh, M.D., sat down in her office at the University of California San Diego School of Medicine and considered a request from the other side of the world.
Ghosh, a professor in the Departments of Medicine and Cellular and Molecular Medicine at UC San Diego School of Medicine, received an email from Dennis McGonagle, Ph.D., professor of investigative rheumatology at the University of Leeds in the United Kingdom. It began an international collaboration, one that uncovered a previously overlooked COVID-related syndrome and resulted in a paper in eBioMedicine, a journal published by The Lancet.
McGonagle asked if she was interested in collaborating on a COVID-related mystery. “He told me they were seeing mild COVID cases,” Ghosh said. “They had vaccinated around 90 percent of the Yorkshire population, but now they were seeing this very rare autoimmune disease called MDA5 — autoantibody associated dermatomyositis (DM) in patients who may or may not have contracted COVID, or even remember if they were exposed to it.”
McGonagle told of patients with severe lung scarring, some of whom presented rheumatologic symptoms — rashes, arthritis, muscle pain — that often accompany interstitial lung disease. He was curious to know if there was a connection between MDA5-positive dermatomyositis and COVID-19.
“DM is more common in individuals of Asian descent, particularly Japanese and Chinese,” Ghosh said. “However, Dr. McGonagle was noting this explosive trend of cases in Caucasians.”
“But that's the least of the problem,” Ghosh said. “Because he said, ‘Oh, and by the way, some of these patients are progressing rapidly to death.’”
Ghosh is the founding director of the Institute for Network Medicine at UC San Diego School of Medicine, home to the Center for Precision Computational Systems Network (PreCSN — the computational pillar within the Institute for Network Medicine). PreCSN’s signature asset is BoNE — the Boolean Network Explorer, a powerful computational framework for extracting actionable insights from any form of big-data.
“BoNE is designed to ignore factors that differentiate patients in a group while selectively identifying what is common (shared) across everybody in the group,” Ghosh explained. Previous applications of BoNE allowed Ghosh and her team to identify other COVID-related lung and heart-afflicting syndromes in adults and children, respectively.
As a rheumatologist, McGonagle specializes in inflammatory and autoimmune conditions. His expertise, combined with the computational power of the Institute for Network Medicine, proved to be an excellent collaboration for probing the post-pandemic upsurge in inflammatory and autoimmune diagnoses. Ghosh said that McGonagle’s roster of patients, all within the U.K.’s National Health System (NHS), helped to facilitate the investigation.
“The NHS has a centralized health care database with comprehensive medical records for a large population, making it easier to access and analyze health data for research purposes,” Ghosh explained.
Ghosh and McGonagle put together a team to probe what they found was indeed an entirely new syndrome. The UC San Diego team included Saptarshi Sinha, Ph.D., interim director of PreCSN, who was a co-first author on the paper, along with Paula David Ramos, M.D., who was conducting research fellowship in experimental rheumatology, at the Leeds Institute of Rheumatic and Musculoskeletal Medicine. The UC San Diego team also included two PreCSN-affiliated students, Ella McLaren, an undergraduate student and aspiring physician-scientist, and Sahar Taheri, a graduate student in the Jacobs School of Engineering Department of Computer Science and Engineering.
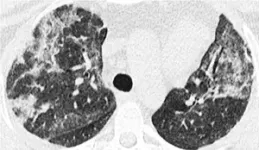
The study began with McGonagle lab’s detection of autoantibodies to MDA5 — an RNA-sensing enzyme whose functions include detecting COVID-19 and other RNA viruses. A total of 25 patients from the group of 60 developed lung scarring, also known as interstitial lung disease. Ghosh noted that the lung scarring was bad enough to cause eight people in the group to die due to progressive fibrosis. She said that there are established clinical profiles of MDA5 autoimmune diseases.
“But this was different,” Ghosh said. “It was different in behavior and rate of progression — and in the number of deaths.”
Ghosh and the UC San Diego team explored McGonagle’s data with BoNE. They found that the patients who showed the highest level of MDA5 response also showed high levels of interleukin-15.
“Interleukin-15 is a cytokine that can cause two major immune cell types,” she explained. “These can push cells to the brink of exhaustion and create an immunologic phenotype that is very, very often seen as a hallmark of progressive interstitial lung disease, or fibrosis of the lung.”
BoNE allowed the team to establish the cause of the Yorkshire syndrome — and pinpoint a specific single nucleotide polymorphism that is protective. By right of discovery, the group was able to give the condition a name: MDA5-autoimmunity and Interstitial Pneumonitis Contemporaneous with COVID-19. It’s MIP-C for short, “Pronounced ‘mipsy,’” Ghosh said, adding that the name was coined to make a connection with MIS-C, a separate COVID-related condition of children.
Ghosh said that it’s extremely unlikely that MIP-C is confined to the United Kingdom. Reports of MIP-C symptoms are coming from all over the world. She said she hopes the team’s identification of interleukin-15 as a causative link will jump start research into treatment.
University of California San Diego co-authors are all noted above.
This work was supported in part by the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) Leeds Biomedical Research Centre (BRC), and in part by the National Institutes for Health (NIH) grant R01-AI155696 and pilot awards from the University of California Office of the President Research Grants Program Office (R00RG2628, R00RG2642 and R01RG3780) to Pradipta Ghosh. Saptarshi Sinha was supported in part by R01-AI141630 (to Pradipta Ghosh) and in part through funds from the American Association of Immunologists (AAI) Intersect Fellowship Program for Computational Scientists and Immunologists.
# # #
END
An entirely new COVID-related syndrome
UC San Diego joins forces with UK researchers in a retrospective observational study to solve a medical mystery
2024-05-09
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Improved wildfire smoke model identifies areas for public health intervention
2024-05-09
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — The Canadian wildfires of June 2023 exposed a large portion of the Northeastern United States to unprecedented levels of smoke. A new model that combines wildfire smoke forecasts and data from ground-based sensors may help public health officials plan targeted interventions in areas most at risk for the negative health effects of unexpected smoke events and air pollution, according to a team led by Penn State scientists.
The researchers reported their findings in the journal Science of the Total Environment.
“Statistical analyses suggest that situations like last year’s ...
Highly drug-resistant infections from stem cell treatments in Mexico identified by National Jewish Health
2024-05-09
DENVER (May 9, 2024) – Experts in mycobacterial diseases at National Jewish Health, in collaboration with local health departments and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), are investigating a potential outbreak of a highly drug-resistant mycobacterium (germ) after U.S. patients who traveled to Mexico for stem cell injections became sick. Genetically identical Mycobacterium abscessus subspecies massiliense infections following stem cell injections at various clinics in Mexico prompted this investigation. Early results of the study were ...
Causal inference about the effects of interventions from observational studies in medical journals
2024-05-09
About The Study: Adoption of the proposed framework to identify when causal interpretation is appropriate in observational studies promises to facilitate better communication between authors, reviewers, editors, and readers. Practical implementation will require cooperation between editors, authors, and reviewers to operationalize the framework and evaluate its effect on the reporting of empirical research.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Issa J. Dahabreh, M.D., Sc.D., email idahabreh@hsph.harvard.edu.
To ...
Turning trash into treasure: breakthrough innovations in PET plastic upcycling
2024-05-09
A recent review has unveiled revolutionary methods to recycle and transform everyday polyethylene terephthalate (PET) plastic into valuable materials. By harnessing cutting-edge enzymes and catalysts, the review dramatically improves how we break down and reuse PET, slashing energy use and emissions. These game-changing techniques are poised to redefine plastic waste management and boost the circular economy.
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) plastic into valuable materials. By harnessing cutting-edge PET, a prevalent form of plastic, poses significant environmental risks due to its durability and resistance to natural degradation. Traditional recycling methods often result in inferior-quality ...
Keck Medicine of USC launches institute to promote excellence in nursing
2024-05-09
LOS ANGELES — Keck Medicine of USC has launched the USC Nursing Institute to promote education, leadership development, clinical expertise and research among nurses.
The institute will support nurses across the health system’s four hospitals and more than 100 clinic locations to ensure nurses have access to the tools, education and training to provide exceptional patient care, facilitate collaboration and encourage career growth and leadership opportunities.
“Nurses are the backbone of our health system. The USC Nursing Institute supports a culture of excellence where nurses feel empowered to expand ...
Deep learning empowers reconfigurable intelligent surface in terahertz communication
2024-05-09
The escalating demand for wireless data traffic, driven by the proliferation of internet-of-things devices and broadband multimedia applications, has intensified the search for innovative solutions in wireless communication. A significant breakthrough has been reported in the application of reconfigurable intelligent surfaces for terahertz communications. In a research article published on Mar. 13 in Intelligent Computing, a team of researchers led by Zhen Gao of Beijing Institute of Technology has introduced a novel physical signal processing method that leverages deep learning to enhance ...
Scientists pinpoint new vaccine “booster” that promotes potent anti-tumour immunity
2024-05-09
Scientists from Trinity College Dublin have made an important breakthrough that offers promise for developing new immune therapies for cancer. They have discovered that a vaccine adjuvant – or “booster” – called C100 promotes potent anti-tumour immunity when it is injected directly into tumours in an animal model.
The scientists found that C100, derived from chitin – one of the most common building materials in nature, and which gives strength to the exoskeletons of crustaceans, insects, and the cell walls of fungi – is highly effective at stimulating a key sensing and signalling molecule which regulates ...
Study finds patients with limited English proficiency have poorer experiences with virtual health care
2024-05-09
People with limited English proficiency have a worse experience with virtual healthcare visits than those who are proficient in English, according to a new study led by a team of investigators at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, a founding member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare system. The study highlights the importance of designing telehealth platforms and processes that better serve people who face day-to-day language barriers.
The study, published in JAMA Network Open, analyzed results ...
Declination of treatment, racial and ethnic disparity, and overall survival in patients with breast cancer
2024-05-09
About The Study: This cross-sectional study highlights racial and ethnic disparities in treatment declination and overall survival, suggesting the need for equity-focused interventions, such as patient education on treatment benefits and improved patient-clinician communication and shared decision-making, to reduce disparities and improve patient survival.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Dezheng Huo, M.D., Ph.D., email dhuo@bsd.uchicago.edu.
To ...
Place-based measures of inequity and vision difficulty and blindness
2024-05-09
About The Study: Residential measures of inequity through segregation, income inequality, or persistent poverty were associated with a greater number of residents living with vision difficulty and blindness in this cross-sectional study. It is essential to understand and address how neighborhood characteristics can impact rates of vision difficulty and blindness.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Patrice M. Hicks, Ph.D., M.P.H., email pmhicks@med.umich.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2024.1207)
Editor’s ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Children with poor oral health more often develop cardiovascular disease as adults
GLP-1 drugs associated with reduced need for emergency care for migraine
New knowledge on heritability paves the way for better treatment of people with chronic inflammatory bowel disease
Under the Lens: Microbiologists Nicola Holden and Gil Domingue weigh in on the raw milk debate
Science reveals why you can’t resist a snack – even when you’re full
Kidney cancer study finds belzutifan plus pembrolizumab post-surgery helps patients at high risk for relapse stay cancer-free longer
Alkali cation effects in electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction
Test platforms for charging wireless cars now fit on a bench
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
[Press-News.org] An entirely new COVID-related syndromeUC San Diego joins forces with UK researchers in a retrospective observational study to solve a medical mystery