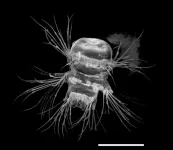
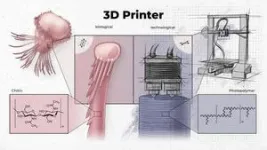
(Press-News.org) A new interdisciplinary study led by molecular biologist Florian Raible from the Max Perutz Labs at the University of Vienna provides exciting insights into the bristles of the marine annelid worm Platynereis dumerilii. Specialized cells, so-called chaetoblasts, control the formation of the bristles. Their mode of operation is astonishingly similar to that of a technical 3D printer. The project is a collaboration with researchers from the University of Helsinki, Vienna University of Technology and Masaryk University in Brno. The study was recently published in the renowned journal Nature Communications.
Chitin is the primary building material both for the exoskeleton of insects and for the bristles of bristle worms such as the marine annelid worm Platynereis dumerilii. However, the bristle worms have a somewhat softer chitin – the so-called beta chitin – which is particularly interesting for biomedical applications. The bristles allow the worms to move around in the water. How exactly the chitin is formed into distinct bristles has so far remained enigmatic. The new study now provides exciting insight into this special biogenesis. Florian Raible explains: "The process begins with the tip of the bristle, followed by the middle section and finally the base of the bristles. The finished parts are pushed further and further out of the body. In this development process, the important functional units are created one after the other, piece by piece, which is similar to 3D printing."
A better understanding of processes such as these also holds potential for the development of future medical products or for the production of naturally degradable materials. Beta-chitin from the dorsal shell of squid, for example, is currently used as a raw material for the production of particularly well-tolerated wound dressings. "Perhaps in the future it will also be possible to use annelid cells to produce this material," says Raible.
The exact biological background to this: so-called chaetoblasts play a central role in this process. Chaetoblasts are specialized cells with long surface structures, so-called microvilli. These microvilli harbor a specific enzyme that the researches could show to be responsible for the formation of chitin, the material from which the bristles are ultimately made. The researchers' results show a dynamic cell surface characterized by geometrically arranged microvilli.
The individual microvilli have a similar function to the nozzles of a 3D printer. Florian Raible explains: "Our analysis suggests that the chitin is produced by the individual microvilli of the chaetoblast cell. The precise change in the number and shape of these microvilli over time is therefore the key to shaping the geometric structures of the individual bristles, such as individual teeth on the bristle tip, which are precise down to the sub-micrometer range." The bristles usually develop within just two days and can have different shapes; depending on the worm's stage of development, they are shorter or longer, more pointed or flatter.
In addition to the local collaboration with the Vienna University of Technology and imaging specialists from the University of Brno, the cooperation with the Jokitalo laboratory at the University of Helsinki proved to be a great benefit for the researchers at the University of Vienna. Using their expertise in serial block-face scanning electron microscopy (SBF-SEM), the researchers investigated the arrangement of microvilli in the bristle formation process and proposed a 3D model for the synthesis of bristle formation. First author Kyojiro Ikeda from the University of Vienna explains: "Standard electron tomography is very labor-intensive, as the cutting of the samples and their examination in the electron microscope must be done manually. With this approach, however, we can reliably automate the analysis of thousands of layers."
The Raible group is currently working on improving the resolution of the observation in order to reveal even more details about bristle biogenesis.
END
Nature's 3D printer: bristle worms form bristles piece by piece
Better understanding of this natural formation process offers potential for technical developments
2024-05-13
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Research shows that ‘softer’ proteins can cross into the nucleus quicker
2024-05-13
Researchers at the Francis Crick Institute and King’s College London have discovered that how soft or rigid proteins are in certain regions can dictate how fast or slow they enter the nucleus.
Proteins need to come in and out of the nucleus, the control centre of the cell, to give different functions, such as telling the nucleus to switch on or off certain genes. These proteins cross using a channel on the edge of the nucleus called the ‘nuclear pore complex’.
Previous research has shown that the size and composition of these proteins change how easily they can cross, but now this research, published today in Nature Physics, has shown that mechanical properties can also ...
Birth by C-section more than doubles odds of measles vaccine failure
2024-05-13
PRESS RELEASE FROM THE UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE
EMBARGOED UNTIL 10:00 LONDON TIME (BST)/ 05:00 US ET ON MONDAY 13 MAY 2024
A copy of the paper and photographs are available at:
https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/1Rfv2ywq7jhHLPuhKZ_ihs6TinuLHCJmU?usp=sharing
Peer-reviewed / Meta-analysis / People
A study by the University of Cambridge, UK, and Fudan University, China, has found that a single dose of the measles jab is up to 2.6 times more likely to be completely ineffective in children born by C-section, compared to those born naturally.
Failure of the vaccine means that the child’s immune system does not produce antibodies to fight ...
How do obesity and metabolic syndrome affect women’s risks of breast cancer and cancer-related death?
2024-05-13
In the Women’s Health Initiative (WHI) randomized trial, a low-fat diet reduced breast cancer mortality, especially in women with more metabolic syndrome (MetS) components (obesity, high blood pressure, elevated blood sugar, and abnormal cholesterol). A recent analysis of WHI findings indicates that MetS and obesity each have different associations with breast cancer subtypes and mortality risk. The findings are published by Wiley online in CANCER, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Cancer Society.
The analysis ...
KITECH develops deformable energy storage device via laser technology
2024-05-13
The joint research team, led by Dr. Chanwoo Yang and Researcher Seong Ju Park from Korea Institute of Industrial Technology(KITECH), along with Prof. Jin Kon Kim and Dr. Keon-Woo Kim from POSTECH, has successfully developed a compact energy storage device with excellent elasticity. This research was published in the world-renowned journal in the field of electronic engineering, 'npj Flexible Electronics'.
Beyond foldable and rollable devices, the era of stretchable IT devices is arriving. For these devices, the development of small, elastic energy storage devices is essential. In this respect, micro supercapacitors ...
Deeply entrenched school psychology practices can be ‘harmful to children’
2024-05-13
Many programs ‘deeply entrenched in school culture’ are harmful to children and can cause potentially lasting damage, psychologists have warned.
They say these practices, from abstinence-only sex education to zero tolerance policies, can direct considerable funds away from evidence-based strategies, as well as giving pupils misleading information.
In new book Investigating School Psychology, researchers have carried out an exhaustive review of current literature to look at practices that continue to exist with little to no scientific ...
Projected estimates of cancer in Canada in 2024
2024-05-13
The number of cancer cases and deaths in Canada is expected to increase because of a growing and aging population, but the overall rates of people being diagnosed with and dying from cancer will continue to decline, according to the latest cancer trends research in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) https://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.240095.
The study is the result of a collaboration between the Canadian Cancer Society, Statistics Canada, and the Public Health Agency of Canada. It provides estimates of the number ...
Private health plans paid hospitals 254% of what Medicare would pay during 2022
2024-05-13
Prices paid to hospitals during 2022 by employers and private insurers for both inpatient and outpatient services averaged 254% of what Medicare would have paid, with wide variation in prices among states, according to a new RAND report.
Some states (Arkansas, Iowa, Massachusetts, Michigan, Mississippi) had relative prices under 200% of Medicare, while other states (California, Florida, Georgia, New York, South Carolina, West Virginia, Wisconsin) had relative prices that were above 300% of Medicare.
Even as the number of hospitals and insurance claims analyzed has grown across multiple rounds of the RAND Hospital ...
World-first regulations to combat sedentary behaviour among children in China show global promise
2024-05-13
Pioneering measures to tackle sedentary behaviour among children in China have proved effective, according to new research.
The study, led by the University of Bristol, reveals regulations recently introduced by the Chinese government to reduce school children’s sedentary behaviour by restricting online gaming companies catering for this age group, limiting the amount of homework schoolteachers can assign, and curtailing when private tuition businesses can provide lessons, significantly reduced total sedentary time as well as how long they spent on different sedentary activities. The measures were associated with a 13.8% daily sedentary drop overall, ...
Randomized trial reveals anti-inflammatory power of aerobic exercise in adults with obesity—helping to mitigate risks of metabolic diseases
2024-05-13
New research being presented at this year’s European Congress on Obesity (ECO) in Venice, Italy (12-15 May), reveals the anti-inflammatory power of moderate-to-vigorous aerobic exercise in adults living with the low-grade inflammation of obesity, shedding light on its potential to help prevent multiple metabolic diseases including type 2 diabetes and atherosclerosis (clogged arteries).
Excessive fat accumulation in adipose tissue (fat cells) leads to chronic low-grade inflammation, characterised by chronically elevated levels of ...
UK study in over 80,000 adults finds smokers tend to eat less and have a less healthy diet than non-smokers
2024-05-13
New research being presented at this year’s European Congress on Obesity (ECO) in Venice, Italy (12-15 May), suggests that smokers tend to eat less and have less healthy eating habits than non-smokers, which could help explain why smokers often gain weight when they quit.
The study, involving over 80,000 UK adults, underscores the importance of providing nutritional and weight management support to smokers, particularly those who are attempting to quit smoking.
People who smoke typically have a lower body weight and body mass index (BMI) than their non-smoking counterparts, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Emerging class of antibiotics to tackle global tuberculosis crisis
Researchers create distortion-resistant energy materials to improve lithium-ion batteries
Scientists create the most detailed molecular map to date of the developing Down syndrome brain
Nutrient uptake gets to the root of roots
Aspirin not a quick fix for preventing bowel cancer
HPV vaccination provides “sustained protection” against cervical cancer
Many post-authorization studies fail to comply with public disclosure rules
GLP-1 drugs combined with healthy lifestyle habits linked with reduced cardiovascular risk among diabetes patients
Solved: New analysis of Apollo Moon samples finally settles debate about lunar magnetic field
University of Birmingham to host national computing center
Play nicely: Children who are not friends connect better through play when given a goal
Surviving the extreme temperatures of the climate crisis calls for a revolution in home and building design
The wild can be ‘death trap’ for rescued animals
New research: Nighttime road traffic noise stresses the heart and blood vessels
Meningococcal B vaccination does not reduce gonorrhoea, trial results show
AAO-HNSF awarded grant to advance age-friendly care in otolaryngology through national initiative
Eight years running: Newsweek names Mayo Clinic ‘World’s Best Hospital’
Coffee waste turned into clean air solution: researchers develop sustainable catalyst to remove toxic hydrogen sulfide
Scientists uncover how engineered biochar and microbes work together to boost plant-based cleanup of cadmium-polluted soils
Engineered biochar could unlock more effective and scalable solutions for soil and water pollution
Differing immune responses in infants may explain increased severity of RSV over SARS-CoV-2
The invisible hand of climate change: How extreme heat dictates who is born
Surprising culprit leads to chronic rejection of transplanted lungs, hearts
Study explains how ketogenic diets prevent seizures
New approach to qualifying nuclear reactor components rolling out this year
U.S. medical care is improving, but cost and health differ depending on disease
AI challenges lithography and provides solutions
Can AI make society less selfish?
UC Irvine researchers expose critical security vulnerability in autonomous drones
Changes in smoking status and their associations with risk of Parkinson’s, death
[Press-News.org] Nature's 3D printer: bristle worms form bristles piece by pieceBetter understanding of this natural formation process offers potential for technical developments