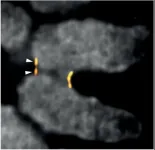
(Press-News.org) Researchers from the Kops group in collaboration with researchers from the University of Edinburgh, made a surprising new discovery in the structure of the centromere, a structure that is involved in ensuring that chromosomes are segregated properly when a cell divides. Mistakes in chromosome segregation can lead to cell death and cancer development. The researchers discovered that the centromere consists of two subdomains. This fundamental finding has important implications for the process of chromosome segregation and provides new mechanisms underlying erroneous divisions in cancer cells. The research was published in Cell on May 13th 2024.
Our bodies consist of trillions of cells, most of which have a limited life span and therefore need to reproduce to replace the old ones. This reproduction process is referred to as cell division or mitosis. During mitosis, the parent cell will duplicate its chromosomes in order to pass down the genetic material to the daughter cells. The resulting identical pairs of chromosomes, the sister chromatids, are held together by a structure called the centromere. The sister chromatids then need to be evenly split over the two daughter cells to ensure that each daughter cell is an exact copy of the parent cell. If errors happen during the segregation, one daughter cell will have too many chromosomes, while the other has too few. This can lead to cell death or cancer development.
The role of the centromere
The centromere is a part of the chromosome that plays a vital role in chromosome segregation during mitosis. The process of dividing the sister chromatids over the cells is guided by the interaction between the centromeres and structures known as spindle microtubules. These spindle microtubules are responsible for pulling the chromatids apart and thus separating the two sister chromatids. Carlos Sacristan Lopez, the first author of this study, explains: ‘If the attachment of the centromere to the spindle microtubules does not occur properly it leads to chromosome segregation mistakes which are frequently observed in cancer.’ Understanding the structure of the centromere can contribute to more insights into the function of the centromere and its role in erroneous chromosomal segregation.
A surprising discovery
To investigate the centromere structure, the researchers used a combination of imaging and sequencing techniques. The super-resolution microscopy imaging took place at the Hubrecht Institute, while the group of Bill Earnshaw performed the sequencing. This collaboration led to a surprising new discovery in the centromere structure. Previously believed to consist of a compact structure attaching to multiple spindle microtubules, it was instead revealed that the centromere consists of two subdomains. Carlos explains: ‘This discovery was very surprising, as subdomains bind microtubules independently of each other. Yet, to form correct attachments, they must remain closely connected. In cancer cells, however, we often observe that subdomains uncouple, resulting in erroneous attachments and chromosome segregation errors.'
This very exciting and fundamental discovery contributes to our understanding of the origin of chromosome segregation errors which are frequently seen in cancer.
Publication
Vertebrate centromeres in mitosis are functionally bipartite structures stabilized by cohesin. Carlos Sacristan, Kumiko Samejima, Lorena Andrade Ruiz, Moonmoon Deb, Maaike L.A. Lambers, Adam Buckle, Chris A. Brackley, Daniel Robertson, Tetsuya Hori, Shaun Webb, Robert Kiewisz, Tristan Bepler, Eloïse van Kwawegen, Patrik Risteski, Kruno Vukušić, Iva M. Tolić, Thomas Müller-Reichert, Tatsuo Fukagawa, Nick Gilbert, Davide Marenduzzo, William C. Earnshaw, and Geert J.P.L. Kops.
***************************************************************************************************************************************************************************************************************************
About Geert Kops:
Geert Kops is director of the Hubrecht Institute, group leader, professor of Molecular Tumor Cell Biology at the University Medical Center Utrecht and Oncode Investigator.
About the Hubrecht Institute:
The Hubrecht Institute is a research institute focused on developmental and stem cell biology. Because of the dynamic character of the research, the institute has a variable number of research groups, around 20, that do fundamental, multidisciplinary research on healthy and diseased cells, tissues and organisms. The Hubrecht Institute is a research institute of the Royal Netherlands Academy of Arts and Sciences (KNAW), situated on Utrecht Science Park. Since 2008, the institute is affiliated with the UMC Utrecht, advancing the translation of research to the clinic. The Hubrecht Institute has a partnership with the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL). For more information, visit www.hubrecht.eu.
END
Research on centromere structure yields new insights into the mechanisms of chromosome segregation errors
2024-05-13
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Ochsner Medical Center-Baton Rouge earns Acute Stroke Ready Certification from Joint Commission
2024-05-13
BATON ROUGE, La. – Ochsner Medical Center - Baton Rouge has earned The Joint Commission’s Gold Seal of Approval® and the American Stroke Association’s Heart-Check mark for Acute Stroke Ready Certification.
The designation means OMC-Baton Rouge meets The Joint Commission's designation for readiness to treat patients who experience severe stroke.
To achieve certification, OMC-Baton Rouge underwent a rigorous, unannounced onsite. During the visit, a team of Joint Commission reviewers evaluated compliance with numerous certification standards, including ...
CEHD researchers studying family-led early childhood systems change for educational equity
2024-05-13
CEHD Researchers Studying Family-Led Early Childhood Systems Change For Educational Equity
Colleen Vesely, Associate Professor, College of Education and Human Development (CEHD); Bethany Letiecq, Associate Professor, Research Methods, CEHD; Rochelle Davidson Mhonde, Assistant Professor, Global and Community Health; and Jung Yeon Park, Assistant Professor of Quantitative Research Methods, School of Education, received funding for the project: “Family-Led Early Childhood Systems Change ...
Raz receives funding for Intent-Based Orchestration In Distributed Command & Control (IBODC2) software
2024-05-13
Raz Receives Funding For Intent-Based Orchestration In Distributed Command & Control (IBODC2) Software
Ali ...
Kelly receives funding for civil war graffiti preservation
2024-05-13
Kelly Receives Funding For Civil War Graffiti Preservation
Mills Kelly, Senior Scholar and Former Director, Roy Rosenzweig Center for History and New Media (RRCHNM); Professor, History, has received funding from the National Endowment for the Humanities for: “Off the Wall: Digital Preservation of Civil War Graffiti Houses.”
Kelly will use the funding to support the building and publishing of a digital archive focused on soldiers’ graffiti found in Civil War-era structures located in the ...
New viruses on the horizon
2024-05-13
Suddenly they appear and - like the SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus - can trigger major epidemics: Viruses that nobody had on their radar. They are not really new, but they have changed genetically. In particular, the exchange of genetic material between different virus species can lead to the sudden emergence of threatening pathogens with significantly altered characteristics. This is suggested by current genetic analyses carried out by an international team of researchers. Virologists from the German Cancer Research Center (DKFZ) were in charge of the large-scale study.
“Using a new computer-assisted analysis method, we discovered 40 previously ...
SIAM Conference on Mathematics of Planet Earth (MPE24)
2024-05-13
Climate change, biodiversity, infectious diseases, sustainability, and the associated socio-economic impacts are among the areas of greatest global concern. The SIAM Conference on Mathematics of Planet Earth (MPE24) provides a forum for interdisciplinary researchers to discuss mathematical, statistical, and computational strategies for addressing these problems. The discussion at MPE24 will range from the development of quantitative techniques and algorithms to providing policy makers with tools for qualitative decision support.
This year, MPE24 is especially interested in sessions and presentations that address fundamental ...
SIAM Conference on Nonlinear Waves and Coherent Structures (NWCS24)
2024-05-13
Theoretical and computational aspects of applied mathematical research on nonlinear waves and coherent structures are relevant to subjects as diverse as general relativity, high-energy particle and plasma physics, fluid and solid mechanics, nonlinear electrical circuits, materials science (including metamaterials), Bose-Einstein condensation, nonlinear optics, random media, atmosphere and ocean dynamics, chemical reactions, and biology. Relevant predictions are often tested against physical experiments and open avenues for collaborations and interactions ...
Zampieri receives funding for doctoral consortium
2024-05-13
Marcos Zampieri, Assistant Professor, Information Sciences and Technology, received funding for: “Doctoral Consortium at Student Research Workshop at the Annual Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics (NAACL).”
Zampieri will use this funding to subsidize travel, conference, and housing expenses of students selected to participate in the NAACL 2024 Student Research Workshop, which will take place during the main NAACL conference on June 16-21, 2024 in Mexico City, Mexico.
The student research workshop welcomes contributions in two categories: 1) thesis proposals, for advanced students who have ...
Study shows natural shorelines support greater biodiversity in the chicago river
2024-05-13
New research published today sheds light on the positive effects of maintaining natural shoreline structure on freshwater ecosystems, as opposed to armoring them with steel walls or piles of rocks. The study, conducted by Shedd Aquarium, Illinois Department of Natural Resources and Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources, revealed important trends in fish diversity and abundance along various types of shorelines in the Chicago Area Waterway System (CAWS). The findings indicated both fish species richness and the numbers of fish grew with increasing proportions of natural shoreline.
Shoreline armoring, ...
New study shows certain combinations of antiviral proteins are responsible for lupus symptoms and affect treatment outcomes
2024-05-13
In a new study, researchers from Johns Hopkins Medicine say they have uncovered insights as to why lupus symptoms and severity present differently in individuals with the autoimmune condition, which affects up to 1.5 million Americans. The team says this is a crucial step forward in understanding biological mechanisms behind lupus, and may also lead to shifts in how clinicians treat patients with the condition.
The full report, published in Cell Reports Medicine on May 13, concludes that specific combinations and elevated levels of immune system proteins, known as interferons, are associated with ...