Researchers discover "topological hall effect" in two-dimensional quantum magnets
2024-05-13
(Press-News.org)
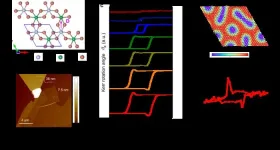
In a recent study published in Nature Physics, researchers from the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, together with researchers of University of Science and Technology of China, have introduced the concept of the "Topological Kerr Effect" by using the low-temperature magnetic field microscopy system and the magnetic force microscopy imaging system supported by the steady-state high magnetic field experimental facility.
The study holds great promise for advancing our understanding of topological magnetic structures.
Originating in particle physics, skyrmions are unique topological excitations found in condensed matter magnetic materials. Characterized by their vortex- or ring-like arrangement of spins, these structures possess non-trivial properties that make them potential candidates for next-generation magnetic storage and logic devices. However, the detection of skyrmions has traditionally relied on the Topological Hall Effect, which is limited to metallic systems. As the field of topological magnetic materials expands, there's an urgent need for characterization techniques applicable to a broader range of systems, including non-metallic skyrmions.
Building on the discovery of two-dimensional ferromagnetic materials in 2017, the researchers predicted a new class of such materials, CrMX6 (M=Mn, V; X=I, Br), which exhibit non-trivial topological electronic states.
They synthesized high-quality two-dimensional CrVI6 single crystals and performed precise micro-area magneto-optical Kerr effect (MOKE) measurements. Remarkably, the MOKE hysteresis loop revealed distinctive "cat ear"-shaped prominences within certain thickness ranges and temperature intervals, resembling the electrical topological Hall effect observed in magnetic skyrmion systems.
Further theoretical analysis revealed that the coexistence of Cr and V atoms breaks the central inversion symmetry, and the strong Dzyaloshinskii-Moriya exchange leads to the generation of topological magnetic structures-skyrmions.
Atomic-scale magnetic dynamics simulations and theoretical calculations revealed the scattering of conducting electrons by the "topological charge" of skyrmions under a photoelectric field, elucidating the microscopic mechanism behind the optical Kerr signal during magnetization reversal.
Based on these findings, the researchers proposed a new scheme for the non-destructive detection of topological magnetic structures by optical methods using alternating photoelectric fields and high magnetic field spectroscopy.
This scheme offers spatially resolved, non-contact detection of skyrmions and other topological excitations, providing valuable insights into their microscopic mechanisms and broadening their range of applications, according to the team.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-05-13
In a new study, led by Charles Underwood from the Max Planck Institute for Plant Breeding Research (MPIPZ) in Cologne, Germany, scientists established a system to generate clonal sex cells in tomato plants and used them to design the genomes of offspring. The fertilization of a clonal egg from one parent by a clonal sperm from another parent led to plants containing the complete genetic information of both parents. The study is now published in Nature Genetics.
Hybrid seeds, combining two different parent lines with specific favorable traits, are popular in agriculture as they give rise to robust crops with enhanced productivity, and have been utilized by farmers ...
2024-05-13
DURHAM, N.C. – Nature gave ticks, mosquitos and leaches a quick-acting way to keep blood from clotting while they extract their meal from a host.
Now the key to that method has been harnessed by a team of Duke researchers as a potential anti-clotting agent that could be used as an alternative to heparin during angioplasty, dialysis care, surgeries and other procedures.
Publishing in the journal Nature Communications, the researchers describe a synthetic molecule that mimics the effects of compounds in the saliva of blood-sucking critters. Importantly, the new molecule can also ...
2024-05-13
Toronto, ON - A new national study found that transgender preteens, 12 and13 years old, reported 13 hours of daily recreational screen time, which was 4.5 hours more than their cisgender peers. Data were collected from 2019 to 2021, overlapping with the COVID-19 pandemic, and the study was published in Annals of Epidemiology.
“Transgender adolescents are more likely to experience school-based bullying and exclusion from peer groups due to their gender identity, leading them to spend less time in traditional school activities and more time on screens,” says lead author, Jason Nagata, MD, associate professor of pediatrics at the University of California, San Francisco. ...
2024-05-13
For release: May 13, 2024
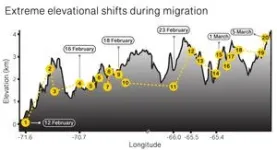
Ithaca, NY—The Giant Hummingbird of western South America is not one species but two, according to an international group of researchers. The northern population stays in the high Andes year-round while the southern population migrates from sea level up to 14,000 feet for the nonbreeding months. The two species appear identical. But looks deceive—their genomes and behaviors tell a different story. The paper announcing the find was published this week in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
“These ...
2024-05-13
In the weeks before and after the 2020 presidential election, researchers ran a number of tests to try to understand how much Facebook and its corporate cousin, Instagram, may be contributing to the nation's political divide.
One of those experiments — led by Matthew Gentzkow and Hunt Allcott, economics professors at Stanford University — centered on more than 35,000 Facebook and Instagram users who were paid to stay off the platforms in the run-up to Election Day. There’s a lot that researchers could glean from the social media hiatus, including whether people’s political attitudes shifted and in what ways. If views changed dramatically, that ...
2024-05-13
Researchers from UNM’s Museum of Southwestern Biology (MSB) have uncovered the giant hummingbird’s extreme long-distance migration for the first time. Their eight-year study, Extreme elevational migration spurred cryptic speciation in giant hummingbirds published this week in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, led them to another important discovery: The world’s largest hummingbird is a new species.
The team, led by Jessie Williamson, UNM Ph.D., 2022, included the Museum of Southwestern Biology at UNM, Pontificia Universidad Católica de Chile in Chile, and Centro de Ornitología ...
2024-05-13
A newly discovered Zika virus-specific synthetic molecule is capable of differentiating Zika-immune patient samples from samples of patients previously infected with the related dengue virus. The technology may lead to the development of better diagnostics and vaccine candidates, scientists announced today in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
The study, led by researchers at the University of Pittsburgh School of Public Health and The Herbert Wertheim UF Scripps Institute for Biomedical Innovation & Technology, is the first to apply an innovative “epitope surrogate” technology to Zika. Until now, researchers and clinicians have lacked diagnostic ...
2024-05-13
A way to curb nagging insects has been flying under our radar—an enzyme from fruit fly testes.
The compound could control bugs that carry disease and harm crops by stunting their ability to procreate, Johns Hopkins University researchers found.
“We have a toe in the door to control fruit fly populations with this enzyme,” said Steven Rokita, a professor of chemistry at Johns Hopkins who led the research. “It could offer a good way to control fertility of all kinds of biological and agricultural pests, starting with mosquito populations.”
The findings are set to publish ...
2024-05-13
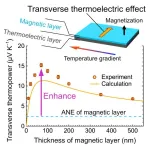
1. A NIMS research team has demonstrated for the first time ever that a simple stack of thermoelectric and magnetic material layers can exhibit a substantially larger transverse thermoelectric effect—energy conversion between electric and heat currents that flow orthogonally to each other within it—than existing magnetic materials capable of exhibiting the anomalous Nernst effect. This mechanism may be used to develop new types of thermoelectric devices useful in energy harvesting and heat flux sensing.
2. Seebeck effect-based ...
2024-05-13
CORVALLIS, Ore. – Today’s rate of atmospheric carbon dioxide increase is 10 times faster than at any other point in the past 50,000 years, researchers have found through a detailed chemical analysis of ancient Antarctic ice.
The findings, just published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, provide important new understanding of abrupt climate change periods in Earth’s past and offer new insight into the potential impacts of climate change today.
“Studying the ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Researchers discover "topological hall effect" in two-dimensional quantum magnets