(Press-News.org) By studying how bubbles form in a drop of biodiesel, researchers at the University of Gothenburg can help future engines get the most energy out of the fuel.
In an internal combustion engine, the fuel is distributed in small droplets in injection valves to maximise combustion.
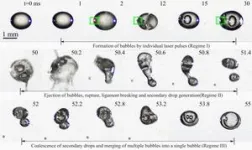
In the engine, the fuel droplets are pressurised to turn into gas and burn. When gas is formed, bubbles form inside the droplets and it is these that the researchers at the University of Gothenburg have studied using femtosecond lasers.
Less emissions
“The bubbles have a significant impact on the atomisation of biodiesel in engines. Therefore, our research is very important to address fundamental questions about the efficiency of the biodiesel engine,” says Dr. Yogeshwar Nath Mishra, who led the study at the University of Gothenburg together with Professor Dag Hanstorp.
Researchers are trying to understand how and when the bubbles form in the fuel droplets. In the long term, this knowledge could lead to the development of a more efficient engine that burns more fuel than today, resulting in less environmentally harmful emissions.
“Research on biodiesel is crucial in our transition from fossil fuels to combat climate change. In engines, bubbling affects fuel combustion and contributes to the formation of larger droplets that do not evaporate and burn completely, leading to increased emissions,” says Dr. Yogeshwar Nath Mishra.
The droplet is levitated acoustically
Studying bubble formation in engine injection valves is difficult because of their structure, with narrow channels in metal bodies. But with the latest technology, physicists can set up an experiment in the lab that allows them to study the process in a millimetre-sized drop of biodiesel. First, a fuel droplet is levitated, i.e. trapped in the air, using a standing sound wave.
“We then energise the droplet with our femtosecond laser, which focuses light energy at a point inside the droplet for a very short time, 100 femtoseconds, 10-13 seconds. This forms the gas bubbles, the number, growth and fine distribution of which are studied using a high-speed camera,” explains Dag Hanstorp, Professor of Physics at the University of Gothenburg.
Many applications
The results, published in Nature Scientific Reports, have provided significant insights into the phenomenon of bubble formation that are not only useful in the development of more efficient fuels and combustion engines.
“Bubble formation is important in industries such as chemical engineering for example carbonated drinks, ultrasonic imaging, boiling processes for heat transfer and processes such as gas release from water bodies and cloud formation. But what we have achieved is basic research. There is still a lot of development to be done before it can be used,” says Dag Hanstorp.
Video clip: How bubbles form in a drop of biodiesel. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QNeOsuKDXRY
END
Studying bubbles can lead to more efficient biofuel motors
2024-05-15
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
AACR releases Cancer Disparities Progress Report 2024
2024-05-15
PHILADELPHIA – The American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) today released its Cancer Disparities Progress Report 2024. First published in 2020, this biennial report raises awareness of the enormous toll that cancer exacts on racial and ethnic minority groups and other medically underserved populations in the United States; highlights underlying causes of cancer disparities as well as promising trends in reducing these inequities; and emphasizes the need for continued research and collaborations to ensure that advances against cancer benefit ...
Using AI to improve building energy use and comfort
2024-05-15
University of Waterloo researchers have developed a new method that can lead to significant energy savings in buildings. The team identified 28 major heat loss regions in a multi-unit residential building with the most severe ones being at wall intersections and around windows. A potential energy savings of 25 per cent is expected if 70 per cent of the discovered regions are fixed.
Building enclosures rely on heat and moisture control to avoid significant energy loss due to airflow leakage, which makes buildings less comfortable and more costly to maintain. This problem will likely be compounded by climate change due to volatile temperature ...
Check and checkmethane
2024-05-15
Kyoto, Japan -- As global temperatures rise to record highs, the pressure to curb greenhouse gas emissions has intensified. Methane is particularly targeted because its significant global-warming potential in the short term exceeds carbon dioxide by over 80-fold.
However, monitoring methane emissions and compiling their quantities have been challenging due to limiting trade-offs with existing detection methods.
Now, a research team including Kyoto University and Geolabe, USA has developed a method to automatically detect methane emissions at a global ...
UNH receives $8M NSF grant to advance New Hampshire’s science and technology leadership
2024-05-15
DURHAM, N.H.—New Hampshire will boost its research leadership as an innovator in science and technology and increase its STEM workforce with investments across the state’s institutions of higher education, thanks to an $8 million grant to the University of New Hampshire from the National Science Foundation. The cooperative agreement award, one of just three of its type in the nation, aims to increase research opportunities, mentoring, training and partnerships between New Hampshire’s community colleges, four-year colleges and universities and industry.
“With this support, UNH will collaborate ...
The case for sharing carbon storage risk
2024-05-15
Even the most optimistic projections for the rapid build-out of solar, wind, and other low-carbon resources acknowledge that coal, natural gas, and other fossil fuels will dominate the world’s energy mix for decades to come. If the vast greenhouse gas emissions from burning these fossil fuels continue to enter the planet’s atmosphere, global warming will not be limited to sustainable levels. The capture and geologic sequestration of carbon emissions (CCS) offer a promising solution to the world’s carbon conundrum.
Even with growing technological maturity ...
Genetics provide key to fight crown-of-thorns starfish
2024-05-15
Scientists are one step closer to combatting coral-destroying crown-of-thorns starfish, following a University of Queensland study into the pest’s genetics.
In a world first study, University of Queensland PhD candidates Marie Morin and Mathias Jönsson analysed the genetics of the toxic coral-eating invertebrates found on the Great Barrier Reef.
“By understanding how crown-of-thorns (COTS) starfish genes work, we can unlock the mechanisms behind their key behaviours and find ways to stop them breeding,” Ms Morin said.
“In this study we looked at ...
Tiger beetles fight off bat attacks with ultrasonic mimicry
2024-05-15
Bats, as the main predator of night-flying insects, create a selective pressure that has led many of their prey to evolve an early warning system of sorts: ears uniquely tuned to high-frequency bat echolocation. To date, scientists have found at least six orders of insects – including moths, beetles, crickets and grasshoppers – that have evolved ears capable of detecting ultrasound.
But tiger beetles take things a step further. When they hear a bat nearby, they respond with their own ultrasonic signal, and for the past 30 years, no one has known why.
“It’s ...
Focus on diagnosing dyslexia is failing struggling readers, experts warn
2024-05-15
UNDER STRICT EMBARGO UNTIL 19:01 EDT TUESDAY 14 MAY 2024
An undue focus on diagnosing dyslexia is leaving many children without the help they urgently need, according to two leading educational and clinical psychologists.
The experts are calling for educators, psychologists and policy makers to rethink approaches to assessment and support for children who are struggling to learn to read.
In a new book, Professors Julian Elliott (Durham University, UK) and Elena Grigorenko (University of Houston, USA) argue that the clinical diagnosis of dyslexia is not only scientifically questionable, but current procedures are failing to serve the needs of many struggling readers, particularly ...
Most dangerous areas for whale shark-shipping vessel collisions revealed
2024-05-15
Researchers have found that heavily used shipping lanes pass through crucial whale shark feeding grounds, posing a threat to this endangered species.
Research published today (Wednesday 15 May) in Science of the Total Environment has revealed areas where the sharks are at the highest risk of colliding with large shipping vessels by mapping the locations of whale shark aggregations and overlaying them with information on shipping traffic.
“The almost ubiquitous overlap of at least some large shipping vessel traffic with whale shark aggregations underlines the magnitude of the threat the shipping industry ...
Petroleum, chlorine mix could yield harmful byproducts in new UH study
2024-05-15
A new study from the University of Hawaiʻi at Mānoa shows that chlorine mixed with petroleum in water can potentially produce inadvertent byproducts harmful to human health.
Small amounts of chlorine, within safe industry standards, are added to disinfect Oʻahu’s drinking water by the Honolulu Board of Water Supply (BWS) and military installations, according to BWS. In late November 2021, a petroleum release from the Red Hill Bulk Fuel Storage Facility contaminated the Red Hill ...