(Press-News.org) PLYMOUTH MEETING, PA [May 16, 2024] — Daniel M. Geynisman, MD, is being announced as the new Editor-in-Chief for JNCCN—Journal of the National Comprehensive Cancer Network. Dr. Geynisman has a long history of working with NCCN in a variety of roles and served as medical oncology section editor for Urologic Oncology: Seminars and Original Investigations since 2018 and authored more than 130 peer-reviewed publications. He is an Associate Professor in the Department of Hematology/Medical Oncology and Chief of the Division of Genitourinary Medical Oncology at Fox Chase Cancer Center.
“We are thrilled to welcome Dr. Geynisman into this crucial position for JNCCN,” said Crystal S. Denlinger, MD, Chief Executive Officer for NCCN. “Our journal fills many important roles when it comes to oncology knowledge sharing. In addition to publishing exclusive insights and updates for the NCCN Guidelines, JNCCN publishes rigorous health services research, original investigations, and reviews addressing all aspects of cancer care delivery. Its impact factor grows every year—currently calculated at 13.4, placing it in the top 10 percent of cancer-related publications. We look forward to seeing what new heights we can reach under Dan’s leadership.”
JNCCN is dedicated to improving the quality of cancer care locally, nationally, and globally. The journal is focused on the highest quality original research in the areas of health services, outcomes, quality improvement, and policy. It is also a trusted resource for information on the NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines®).
“It is an honor to be named Editor-in-Chief for JNCCN,” said Dr. Geynisman. “Fox Chase Cancer Center was a founding Member Institution for NCCN, and the opportunity to lead JNCCN is an enormous privilege. I am excited to expand upon the legacy of practice setting guidelines and outstanding research contributions published and look forward to working with the editorial board and journal staff to continue to build and grow JNCCN as a premier destination for oncology research.”
Dr. Geynisman has a long history of advancing cancer care with NCCN, including serving as a Member on the NCCN Guidelines Panels for both Testicular Cancer and Wilms Tumor. He has reviewed abstracts for presentation at the NCCN Annual Conference, served on various NCCN grant selection committees, and was himself a past recipient of NCCN research grants through NCCN’s Oncology Research Program (ORP). He also serves as an ad hoc reviewer for multiple other journals, including New England Journal of Medicine, European Urology, Journal of Clinical Oncology, and Cancer.
Dr. Geynisman is succeeding longtime JNCCN Editor-in-Chief Margaret Tempero, MD, UCSF Helen Diller Family Comprehensive Cancer Center, who now leads the Cancer Early Detection Initiative (CEDI) at UCSF Helen Diller Family Comprehensive Cancer Center. Under her tenure, the journal emphasized molecular medicine, health services research, and principles in cancer care. It has undergone several redesigns both digitally and in print, including an ongoing shift towards increased online content with a more streamlined, modern look. Learn more about her legacy and achievements in the March issue of JNCCN.
Dr. Geynisman’s first issue as Editor-in-Chief will be published in June 2024.Visit JNCCN.org to view the newly published May issue, including an official welcome from the journal’s editorial board and staff.
# # #
About JNCCN—Journal of the National Comprehensive Cancer Network
More than 25,000 oncologists and other cancer care professionals across the United States read JNCCN—Journal of the National Comprehensive Cancer Network. This peer-reviewed, indexed medical journal provides the latest information about innovation in translational medicine, and scientific studies related to oncology health services research, including quality care and value, bioethics, comparative and cost effectiveness, public policy, and interventional research on supportive care and survivorship. JNCCN features updates on the NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines®), review articles elaborating on guidelines recommendations, health services research, and case reports highlighting molecular insights in patient care. JNCCN is published by Harborside/BroadcastMed. Visit JNCCN.org. To inquire if you are eligible for a FREE subscription to JNCCN, visit NCCN.org/jnccn/subscribe. Follow JNCCN at x.com/JNCCN.
About the National Comprehensive Cancer Network
The National Comprehensive Cancer Network® (NCCN®) is a not-for-profit alliance of leading cancer centers devoted to patient care, research, and education. NCCN is dedicated to improving and facilitating quality, effective, equitable, and accessible cancer care so all patients can live better lives. The NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines®) provide transparent, evidence-based, expert consensus recommendations for cancer treatment, prevention, and supportive services; they are the recognized standard for clinical direction and policy in cancer management and the most thorough and frequently-updated clinical practice guidelines available in any area of medicine. The NCCN Guidelines for Patients® provide expert cancer treatment information to inform and empower patients and caregivers, through support from the NCCN Foundation®. NCCN also advances continuing education, global initiatives, policy, and research collaboration and publication in oncology. Visit NCCN.org for more information.
END
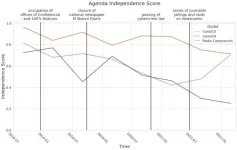
Worldwide news media are facing increasing pressure from autocrats to report favourably about their leaders and party politics. Political scientists launch a new computational method that can detect such media censorship by states while it is happening. This method provides valuable insights for communicating regime-driven media capture to the public. It is now described in detail in the scientific journal ‘Democratization’.
One of the first steps of would-be autocrats is to control the ...
Spinal muscular atrophy or “SMA” for short is a terrible disease in which a genetic mutation causes certain nerves responsible for sending signals to muscles to degenerate. This leads to muscles wasting away, and many patients have died a painful death due to this rare condition. Genetic treatments have only been available for a few years. Now, a team led by Emmanuel Nedoschill, Ferdinand Knieling and Adrian Regensburger from the “Translational Pediatrics” working group at the Department of Pediatrics and Adolescent Medicine at Uniklinikum Erlangen have devised ...
OTTAWA, Ontario, May 16, 2024 – The best microphone in the world might have an unexpected source: spider silk. Spiders weave webs to trap their insect snacks, but the sticky strands also help spiders hear. Unlike human eardrums and conventional microphones that detect sound pressure waves, spider silk responds to changes in the velocities of air particles as they are thrust about by a sound field. This sound velocity detection method remains largely underexplored compared to pressure sensing, but it holds great potential for high-sensitivity, long-distance sound detection.
Researchers ...
INDIANAPOLIS – An Expert Insight, published in the journal Transplantation, highlights health equity, disparity and inequality in organ transplantation along the continuum of care and across organ types. The authors provide a guide to transplant centers for the use of disparity-sensitive measures to monitor and address health disparities in transplantation and to redress long-standing inequities and inequalities in this vital arena.
“Our goal is to ensure that all patients who need a transplant have ...
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Disc-related back pain may one day meet its therapeutic match: gene therapy delivered by naturally derived nanocarriers that, a new study shows, repairs damaged discs in the spine and lowers pain symptoms in mice.
Scientists engineered nanocarriers using mouse connective-tissue cells called fibroblasts as a model of skin cells and loaded them with genetic material for a protein key to tissue development. The team injected a solution containing the carriers into damaged discs in mice at the same time the back injury ...
OTTAWA, Ontario, May 16, 2024 – As a hockey player, Andrew Bray was familiar with the slang thrown around the “barn” (hockey arena). As a linguist, he wanted to understand how sport-specific jargon evolved and permeated across teams, regions, and countries. In pursuit of the sociolinguistic “biscuit” (puck), he faced an unexpected question.
“It was while conducting this initial study that I was asked a question that has since shaped the direction of my subsequent research,” said Bray. “‘Are you trying to figure out why the Americans sound like fake Canadians?’”
Canadian ...
If you tend to do other things or get distracted while eating dinner, you may be running the risk of over-consuming everyday pleasures later, possibly because the distraction caused you to enjoy yourself less, according to research published by the American Psychological Association.
The study looked at how distraction affects “hedonic consumption,” or buying and using products and experiences because they make us feel good and not necessarily because we need them.
“On any given day, a person may take great pleasure from one or more of these activities, yet people often consume more hedonic ...
WASHINGTON—The Endocrine Society is delighted to announce that Lily Ng, PhD, and Douglas Forrest, Ph.D., have won the Society's 2024 Endocrine Images Art Competition for their image of the astrocyte cell that expresses type 2 deiodinase.
Now in its third year, the Art Competition celebrates the beauty of endocrine science as seen through the lens of a microscope. This year’s 19 entries were judged by a panel of Society members who based their assessments on aesthetic value of the images and their significance ...
DALLAS, May 16, 2024 — Pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S. have risen 140% over the past three decades and cardiovascular disease is the leading cause.[1] Despite existing medical guidance on pregnancy and cardiovascular health, current trends in health outcomes suggest a significant opportunity for an improved system of care, particularly in the postpartum period.
The American Heart Association, the world’s leading voluntary organization focused on heart and brain health and this year ...
When a patient is experiencing heart failure, a leading cause of death worldwide, they begin to lose healthy and functioning cardiac cells. Heart failure causes these once-flexible cells to develop into fibrotic cells that are no longer able to contract and relax. This stiffening of the cardiac cells compromises their ability to carry blood efficiently to the rest of the organs in the human system. Because humans cannot regenerate these cardiac cells, the patient faces a long road to recovery marked by preventative or symptomatic treatments.
However, some ...