Patients seen by female gastroenterologists have significantly less health care utilization than patients seen by male providers
Study investigates whether provider’s gender impacts patient care in gastroenterology
2024-05-18
(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON, DC (May 18, 2024) — Patients seen by a female gastroenterologist for an initial consultation are less likely to use medical care in the emergency department, hospital or primary care office for two years after their visit when compared to patients initially seen by male gastroenterologists, according to a study to be presented at Digestive Disease Week® (DDW) 2024.
“If there really is something different about the way female and male gastroenterologists provide care that impacts patient outcomes, it will be important to share these learnings broadly among health care providers to improve the standard of care for all patients,” said lead author Laura Targownik, MD, clinician-investigator at Mount Sinai Hospital in Toronto and departmental division director, gastroenterology and hepatology, at the University of Toronto.
Researchers examined data from more than 2.7 million gastroenterology consultations between 2002 and 2020 from the Ontario Health IC/ES population-wide database, of which 15% of consultations were performed by female gastroenterologists and female patients comprised 55%.
Overall, female patients had a higher rate of emergency department visits and primary care visits than male patients; however, when female gastroenterologists provided the initial consultation, subsequent use of all health care services by all patients, regardless of gender, was lower when compared with patients initially seen by male gastroenterologists. The lower health care utilization after seeing a female gastroenterologist was more pronounced among female patients than males.
“We need more research to understand what is causing this difference in patient outcomes,” said Grace Wang, gastroenterology resident, University of Toronto. “The next step is to take a closer look at the patient data – including preexisting conditions, the health care utilization patterns prior to an initial GI consultation, and the diagnoses that occur during that consultation – in order to investigate whether there are other factors driving patients’ health care-seeking behavior.”
DDW Presentation Details
Dr. Targownik will present data from the study, “The impact of physician gender on health care utilization among men and women following initial GI consultation,” abstract Sa1002, on Saturday, May 18, at 12:30 p.m. EDT. For more information about featured studies, as well as a schedule of availability for featured researchers, please visit www.ddw.org/press.
###
Digestive Disease Week® (DDW) is the largest international gathering of physicians, researchers and academics in the fields of gastroenterology, hepatology, endoscopy and gastrointestinal surgery. Jointly sponsored by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases (AASLD), the American Gastroenterological Association (AGA), the American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ASGE) and the Society for Surgery of the Alimentary Tract (SSAT), DDW is an in-person and online meeting from May 18-21, 2024. The meeting showcases more than 5,600 abstracts and hundreds of lectures on the latest advances in GI research, medicine and technology. More information can be found at www.ddw.org
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-05-17
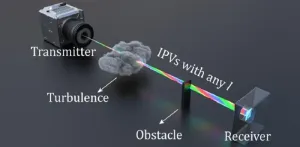
The future of optical communications just got brighter. In a groundbreaking development reported in Advanced Photonics, researchers from Nanjing University have introduced iso-propagation vortices (IPVs), a novel concept that offers a solution to a long-standing challenge faced by scientists and engineers: how to increase information processing capacity while overcoming the limitations of traditional vortex beams.
Challenge: divergence and beam size
Multiplexing of optical degrees of freedom, such as polarization and wavelength, has been a staple in enhancing communication capacity. ...
2024-05-17
On a cold winter night in 2016, Ukrainians experienced the first-ever known blackout caused by malicious code (malware) designed to autonomously attack the power grid. One-fifth of Kyiv’s citizens were plunged into darkness as attackers used malware to target the capital city’s power grid. Six years later, in the early months of the ongoing Russia-Ukraine war, a second attack attempted to combine kinetic and cyber attacks to take down Ukraine’s power grid.
Malware attacks against physical ...
2024-05-17
“Practice makes perfect” is no mere cliché, according to a new study from researchers at The Rockefeller University and UCLA. Instead, it’s the recipe for mastering a task, because repeating an activity over and over solidifies neural pathways in your brain.
As they describe in Nature, the scientists used a cutting-edge technology developed by Rockefeller’s Alipasha Vaziri to simultaneously observe 73,000 cortical neurons in mice as the animals learned and repeated a given task over two weeks. The study revealed that memory representations transform from unstable to solid in ...
2024-05-17
New initiative, launched on World NF Awareness Day, focuses on developing improved models to understand neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) with the goal of rapidly testing new treatments.
18 grants will be provided to leading medical research institutions in the United States and Europe.
The Next-Generation NF1 Models Initiative is the Foundation’s fourth research initiative focused on accelerating a cure for neurofibromatosis.
DETROIT, May 17, 2024 – Gilbert Family Foundation, a private foundation established by Dan and Jennifer Gilbert to accelerate a cure for ...
2024-05-17
About The Study: This study found that BRCA1-associated protein (BAP1) tumor predisposition syndrome was associated with a high rate of nail abnormalities consistent with onychopapillomas (a benign tumor of the nail) in adult carriers of the disease. Findings suggest that this novel cutaneous sign may facilitate detection of the syndrome in family members who are at risk and patients with cancers associated with BAP1 given that multiple onychopapillomas are uncommon in the general population and may be a distinct clue to the presence of a pathogenic germline variant in the BAP1 gene.
Corresponding Authors: To contact the corresponding authors, ...
2024-05-17
The silver chub isn’t considered sensitive to climate change on a national scale, but context matters. For example, if climate change sensitivity is evaluated in only one region of the United States, the freshwater fish appears quite a bit more susceptible.
“Relative to other species we looked at in the gulf region of the U.S., the silver chub occupied a pretty small geographic area,” said Samuel Silknetter, a Ph.D. student in biological sciences. “If we didn’t look at the climate sensitivity across multiple ...
2024-05-17
PHILADELPHIA (May 16, 2024) – The rich research portfolio of the Monell Chemical Senses Center on sweet taste goes way back: Monell scientists were one of four teams in 2001 that found and described the mammalian sweet taste receptor – TAS1R2-TAS1R3. Twenty years later in 2021, a pair of papers published in Mammalian Genome by Monell researchers covered the genetics of sugar-loving mice.
The sweet taste receptor, expressed in taste bud cells, conveys sweetness from the mouth when it is activated. Earlier this month, a study in PLOS One, led by another Monell researcher, delved into how the sweet-taste receptor might be the first stop ...
2024-05-17
The Science
Scientists have the first direct evidence that the powerful magnetic fields created in off-center collisions of atomic nuclei induce an electric current in “deconfined” nuclear matter. This is a plasma “soup” of quarks and gluons that have been set free, or “deconfined,” from nuclear matter—protons and neutrons—in the particle collisions. The magnetic fields in deconfined nuclear matter are a billion times stronger than a typical refrigerator magnet, but their effects can be hard to detect. This new study’s evidence is from measuring the way ...
2024-05-17
In recognition of her exceptional work in advancing health equity, the Society of General Internal Medicine (SGIM) bestowed its 2024 Herbert W. Nickens Award to Rita Lee, MD, a University of Colorado Department of Medicine faculty member, at a May 17 meeting in Boston.
“The committee has chosen to honor you as an exemplary SGIM member who has made prioritizing minority health and diversity the primary focus of your career,” Alana Biggers, MD, MPH, the chair of the award selection committee, said in a congratulatory letter to Lee.
The ...
2024-05-17
A lack of detailed record-keeping in clinics and emergency departments may be getting in the way of reducing the inappropriate use of antibiotics, a pair of new studies by a pair of University of Michigan physicians and their colleagues suggests.
In one of the studies, about 10% of children and 35% of adults who got an antibiotic prescription during an office visit had no specific reason for the antibiotic in their record.
The rate of this type of prescribing is especially high in adults treated seen in emergency departments and in adults seen in clinics who have Medicaid coverage or no insurance, the ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Patients seen by female gastroenterologists have significantly less health care utilization than patients seen by male providers
Study investigates whether provider’s gender impacts patient care in gastroenterology