(Press-News.org) [BOSTON, MAY 21, 2024] – Stuart Orkin, MD, a researcher at the Dana-Farber/Boston Children's Cancer and Blood Disorders Center and David G. Nathan Distinguished Professor of Pediatrics at Harvard Medical School, has been honored with The Shaw Prize in Life Science & Medicine for his pioneering work discovering the genetic and molecular mechanisms underlying the switch from fetal to adult hemoglobin. Dr. Orkin shares the prize with Swee Lay Thein, PhD, Senior Investigator and Chief of the Sickle Cell Branch of National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute at the National Institutes of Health (NIH).
The Shaw Prize, often referred to as the "Nobel of the East," honors individuals “who have made outstanding contributions in academic and scientific research or applications”. Established in 2002 by Mr. Run Run Shaw, a philanthropist, The Shaw Prize recognizes excellence and innovation in scientific research on a global scale.
Dr. Orkin’s discoveries made possible the world’s first FDA-approved therapy using CRISPR/Cas9 – Casgevy. The therapy is intended to treat patients with sickle cell anemia and β thalassemia, debilitating blood disorders affecting millions worldwide. It works by knocking down a gene called BCL11A, a mechanism discovered by Dr. Orkin’s team in 2008 that enables fetal hemoglobin production to restart and represses sickled hemoglobin.
"Receiving The Shaw Prize is an honor and a testament to the dedication of countless researchers who have contributed to our understanding of hemoglobin regulation over the years. This recognition underscores the potential of our findings to revolutionize the treatment landscape for sickle cell anemia and β thalassemia, offering new hope to patients worldwide," says Dr. Orkin.
###
About Boston Children’s Hospital
Boston Children’s Hospital, a pediatric teaching affiliate of Harvard Medical School, is ranked among the best children’s hospitals in the nation, as well as top-ranked in every specialty by U.S. News & World Report. Home to the world’s largest research enterprise based at a pediatric medical center, its discoveries have benefited children and adults since 1869. Today, 3,000 researchers and scientific staff, including 11 members of the National Academy of Sciences, 28 members of the National Academy of Medicine, and nine Howard Hughes Medical Investigators, comprise Boston Children’s research community. Boston Children’s is a 485-bed comprehensive center for pediatric and adolescent health care. For more, visit our Answers blog and follow us on social media on Instagram, Facebook, LinkedIn, and YouTube.
END
Stuart Orkin awarded the Shaw Prize in Life Science & Medicine 2024 for groundbreaking hemoglobin research
2024-05-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Drug-like inhibitor shows promise in preventing flu
2024-05-21
LA JOLLA, CA—Currently available flu medications only target the virus after it has already established an infection, but what if a drug could prevent infection in the first place? Now, scientists at Scripps Research and the Albert Einstein College of Medicine have designed drug-like molecules to do just that, by thwarting the first stage of influenza infection.
The drug-like inhibitors block the virus from entering the body’s respiratory cells—specifically, they target hemagglutinin, a protein on the surface of type A influenza viruses. The findings, published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences ...
Study finds widespread ‘cell cannibalism,’ related phenomena across tree of life
2024-05-21
In a new review paper, Carlo Maley and Arizona State University colleagues describe cell-in-cell phenomena in which one cell engulfs and sometimes consumes another. The study shows that cases of this behavior, including cell cannibalism, are widespread across the tree of life.
The findings challenge the common perception that cell-in-cell events are largely restricted to cancer cells. Rather, these events appear to be common across diverse organisms, from single-celled amoebas to complex multicellular animals.
The widespread occurrence of such interactions in non-cancer cells suggests that these events are not inherently "selfish" or "cancerous" ...
Germicidal lamps using UV-C radiation may pose health safety issues
2024-05-21
“Despite the potential advantages of utilizing UV-C radiation for deactivating pathogens such as SARS-CoV-2, the prevailing conclusion remains that UV-C radiation poses concurrent risks to human health.”
BUFFALO, NY- May 21, 2024 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 16, Issue 9, entitled, “Germicidal lamps using UV-C radiation may pose health safety issues: a biomolecular analysis of their effects on apoptosis and senescence.”
The battle against the COVID-19 pandemic has spurred a heightened state of vigilance in global healthcare, ...
Inhibitory effect of miR-377 on prostate cancer cells
2024-05-21
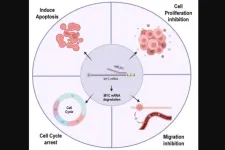
“Our research findings suggest that miR-377 could potentially serve as a valuable therapeutic strategy for the treatment of prostate cancer (PCa).”
BUFFALO, NY- May 21, 2024 – A new research paper was published in Genes & Cancer on May 16, 2024, entitled, “Inhibitory effect of miR-377 on the proliferative and invasive behaviors of prostate cancer cells through the modulation of MYC mRNA via its interaction with BCL-2/Bax, PTEN, and CDK4.”
The MYC gene is a regulatory and proto-oncogenic gene that is overexpressed in the majority of prostate cancers (PCa). Numerous studies have indicated that aberrant expression of microRNAs is involved in the ...
Innovative imaging technique may revolutionize ureteral thermal injury detection
2024-05-21
In a groundbreaking study, scientists have explored a novel approach to detect electrothermal ureteral injuries, a common complication during pelvic surgery. The ureters, delicate tubes that transport urine from the kidneys to the bladder, are particularly vulnerable due to their proximity to other anatomical structures. Unfortunately, current detection methods often fall short in promptly identifying subtle thermal injuries, which can take days or even weeks to manifest.
Enter optical coherence tomography ...
Conservation of nature’s strongholds needed to halt biodiversity loss
2024-05-21
To achieve global biodiversity targets, conservationists and governments must prioritize the establishment and effective management of large, interconnected protected areas with high ecological integrity, John G. Robinson from the Wildlife Conservation Society, US, and colleagues argue in an essay publishing May 21st in the open-access journal PLOS Biology.
The Kunming–Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework (GBF), signed at the 2022 Conference of Parties to the UN Convention on Biological Diversity in Montreal, recognized the importance of protecting large areas of natural habitat to maintain the resilience and integrity of ecosystems. To halt biodiversity ...
Body lice may be bigger plague spreaders than previously thought
2024-05-21
A new laboratory study suggests that human body lice are more efficient at transmitting Yersinia pestis, the bacterium that causes plague, than previously thought, supporting the possibility that they may have contributed to past pandemics. David Bland and colleagues at the United States’ National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS Biology on May 21st.
Y. pestis has been the culprit behind numerous pandemics, including the Black Death of the Middle Ages that ...
Gun violence touches nearly 60 percent of Black Americans – and predicts disability
2024-05-21
Roughly 60 percent of all Black Americans are exposed to some form of gun violence, and such exposures predict elevated rates of disability, according to Rutgers Health research.
Survey data from 3,015 Black Americans linked specific disabilities ranging from trouble concentrating to difficulty dressing or bathing with exposure to various types of gun violence: being shot, being threatened with a firearm, knowing a shooting victim, and witnessing a shooting or hearing of one nearby.
“Traditionally, the majority of efforts related to gun violence have focused on reducing homicides, but this study indicates that we need ...
A rise in sea urchins and related damage to kelp forests impacts Oregon’s gray whales and their food
2024-05-21
NEWPORT, Ore. – A recent boom in the purple sea urchin population off the southern Oregon Coast appears to have had an indirect and negative impact on the gray whales that usually forage in the region, a new study shows.
When urchin numbers rise, the spiky marine invertebrates can devour kelp forests that are a critical habitat for zooplankton, the tiny aquatic organisms that are the primary prey of many marine animals. Damaged kelp forests lead to reductions in zooplankton, and with fewer zooplankton to feed on, gray whales spend less time foraging there, researchers with Oregon State University’s Marine Mammal Institute found.
“This study shows the cascading ...
Detroit researchers find connection between PFAS exposure in men and the health of their offspring
2024-05-21
DETROIT – Wayne State University researchers are reporting new findings that demonstrate a link between exposure to per- and polyfluorinated alkyl substances (PFAS) in males and health issues in their offspring.
The study, “Mixtures of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) alter sperm methylation and long-term reprogramming of offspring liver and fat transcriptome,” published recently in Environment International, assessed the effect of PFAS mixtures on the sperm methylome and transcriptional changes in offspring metabolic tissues such as in the ...