(Press-News.org) Osaka, Japan – Part of what makes us human is our ability to think about people, places, or events that aren’t currently present—but we still don’t know exactly how our brains do this. Now, researchers from Osaka University have identified a specific kind of brain activity linked with these kinds of thoughts, such as when we daydream or let our minds wander.
When we think about things that aren’t actually happening, like when we daydream, the brain is essentially making up information rather than receiving and processing it—for this reason, researchers classify it as a “self-generated” brain state. In a recent study published in Nature Communications, researchers from Japan have identified that these self-generated states are associated with a specific pattern of brain activity known as “sharp-wave ripples.” These ripples start in the hippocampus, a brain region that is essential for making and retrieving memories.
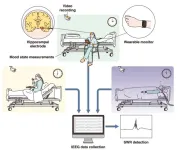
To study the relationship between these sharp-wave ripples and different kinds of thoughts, the research team made use of the information that’s collected when patients with drug-resistant epilepsy are about to undergo surgery (to remove the starting point of the epileptic activity in the brain). Intracranial electrodes are implanted in the hippocampus in these patients and the activity in the brain is continuously tracked, so that the surgeons can identify the epileptic region and be sure that they aren’t removing a part of the brain that will have unexpected consequences.
“We asked patients undergoing this electroencephalographic brain monitoring for 10 days to complete an hourly questionnaire relating to their thoughts and emotions,” says lead author of the study Takamitsu Iwata. “We mainly wanted to see if we could identify any links between the recorded brain activity and how the patients were feeling and thinking at the time.”
In general, the sharp-wave ripples from the hippocampus were generated in patients at night (presumably during sleep). Furthermore, the research team noticed a link between increased sharp-wave activity and thoughts that were more vivid or imaginative and less desirable or task-related, i.e. when their minds wandered.
“Notably, although our study was conducted entirely on people with epilepsy, we did our best to remove epilepsy-related data so that the results are applicable to healthy populations,” explains Takufumi Yanagisawa, senior author of the study. “The similarities between many of our results and those of previous studies, using other species or methods, indicate that our approach worked well.”
There is increasing evidence that self-generated brain states, including mind wandering and intrusive thoughts, have complex links with intelligence, autism, attention deficit disorder, and happiness/well-being. A better understanding of the brain regions and activity that cause these states may therefore help people with a range of different conditions.
###
The article, “Hippocampal sharp-wave ripples correlate with periods of naturally occurring self-generated thoughts in humans,” was published in Nature Communications at DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-48367-1
About Osaka University
Osaka University was founded in 1931 as one of the seven imperial universities of Japan and is now one of Japan's leading comprehensive universities with a broad disciplinary spectrum. This strength is coupled with a singular drive for innovation that extends throughout the scientific process, from fundamental research to the creation of applied technology with positive economic impacts. Its commitment to innovation has been recognized in Japan and around the world, being named Japan's most innovative university in 2015 (Reuters 2015 Top 100) and one of the most innovative institutions in the world in 2017 (Innovative Universities and the Nature Index Innovation 2017). Now, Osaka University is leveraging its role as a Designated National University Corporation selected by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to contribute to innovation for human welfare, sustainable development of society, and social transformation.
Website: https://resou.osaka-u.ac.jp/en
END
From ripples to daydreams: the brain activity behind mind wandering
Researchers from Osaka University find that mind wandering, especially when associated with less pleasurable and more vivid and imaginative self-generated thoughts, is associated with a specific pattern of brain activity linked to memory and sleep
2024-05-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Ancient viral DNA in the human genome linked to major psychiatric disorders.
2024-05-22
New research led by King’s College London has found that thousands of DNA sequences originating from ancient viral infections are expressed in the brain, with some contributing to susceptibility for psychiatric disorders such as schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and depression.
Published in Nature Communications, the study was part-funded by the National Institute for Health and Care Research (NIHR) Maudsley Biomedical Research Centre and the US National Institutes of Health (NIH).
About eight percent of our genome is comprised of sequences called Human Endogenous Retroviruses (HERVs), which are products of ancient viral infections ...
Excavation reveals ‘major’ ancient migration to Timor Island
2024-05-22
The discovery of thousands of stone artefacts and animal bones in a deep cave in Timor Island has led archaeologists to reassess the route that early humans took to reach Australia.
Researchers from The Australian National University (ANU), Flinders University, University College London (UCL) and the ARC Centre of Excellence for Australian Biodiversity and Heritage dated and analysed the artefacts and sediment at the Laili rock shelter in central-north Timor-Leste, north of Australia, to pinpoint the arrival ...
Gene cluster expression index and potential indications for targeted therapy and immunotherapy for lung cancers
2024-05-22
Background and objectives
About 30% of lung cancer patients are accessible to targeted therapy or immunotherapy based on the current criteria. In this study, a novel gene cluster expression analysis was introduced with a goal to potentially expand the treatments to more patients based on the proposed criteria.
Methods
Selected gene expression omnibus data sets were downloaded, normalized, and analyzed. A univariate recurrence prediction model was built based on the receiver operating characteristic, for which an optimal cutoff was determined to set abnormality status, called ...
FRONTIERS Residency program awards grants to seven European journalists
2024-05-22
Javier Pérez Barbuzano, Aisling Irwin, Ruairi Mackenzie, Jacopo Pasotti, Samuel Schlaefli, Vedrana Simičević, and Zuzana Vitková are the chosen candidates for the inaugural round of the FRONTIERS Residency Program. This ERC-supported initiative will finance journalists to spend 3 to 5 months at a European research institution.
Originating from Spain, Slovakia, the United Kingdom, Ireland, Italy, Switzerland, and Croatia, the selected journalists will develop their journalistic projects, during their residencies in scientific institutions. The initiative will award a monthly ...
25-year longitudinal study shows mothers’ empathy for teens may predict teens’ empathy for friends and future parenting
2024-05-22
A new Child Development study from researchers at the University of Virginia provides the first long-term, longitudinal evidence for the transmission of empathic care across three generations: from mother to teen to child.
The findings suggest that interactions with close friends in adolescence may provide a “training ground” in which teens can practice providing care in their peer relationships and pay forward the empathy they experience from their mothers, which may help strengthen their future parenting skills.
For families and service providers, ...
One in two children with ADHD experience emotional problems, study finds
2024-05-22
Cambridge scientists have shown that problems regulating emotions – which can manifest as depression, anxiety and explosive outbursts – may be a core symptom of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD).
In research published in Nature Mental Health, the team found that as many as one in two children with ADHD show signs of emotional dysregulation, and that Ritalin – the commonly-prescribed drug to help the condition – appears to be less effective at treating this symptom.
ADHD affects around ...
Dermatologists find ultraviolet irradiation increases appetite but prevents body weight gain
2024-05-22
Philadelphia, May 22, 2024 – Obesity and metabolic disorders are increasingly significant global public health issues. In a novel study, a team of dermatologists evaluated the effect of ultraviolet (UV) exposure on appetite and weight regulation. They found that UV exposure raises norepinephrine levels, decreases leptin levels, and induces the browning of subcutaneous fat, thereby increasing energy expenditure. These results potentially pave the way for new approaches to prevent and treat obesity and metabolic disorders. Their findings appear in the Journal of Investigative Dermatology, published by Elsevier.
UV ...
Babies in the womb exposed to two languages hear speech differently when born
2024-05-22
It’s well established that babies in the womb hear and learn about speech, at least in the third trimester. For example, newborns have been shown to already prefer the voice of their mother, recognize a story that had been repeatedly told to them while in the womb, and tell apart their mother’s native language.
What wasn’t known until now was how developing fetuses learn about speech when their mother speaks to them in a mix of languages. Yet this is common: there are 3.3 billion bilingual people (43% of the population) worldwide, and in many countries, bilingualism or multilingualism is the norm.
“Here we show that exposure to monolingual or a bilingual speech ...
Study analyses the impact of summer heat on hospital admissions in Spain
2024-05-22
A team from the Barcelona Institute for Global Health, a centre supported by the "la Caixa" Foundation, and the French National Institute of Health and Medical Research (Inserm), has carried out an analysis of hospital admissions related to high summer temperatures in Spain over more than a decade. The study concludes that the causes of hospitalisation in which the heat has the most notable impact are:
Metabolic disorders and obesity
Renal failure
Urinary tract infection
Sepsis
Urolithiasis
Poisoning by drugs and other non-medicinal substances
The research, published in Environmental Health Perspectives, included ...
Ohio State survey finds half of Americans feel unprepared to help in a life-threatening emergency
2024-05-22
COLUMBUS, Ohio – If someone collapsed after going into cardiac arrest, would you be prepared to help? For nearly half of Americans, the answer is no.
A new survey from The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center finds many Americans are ill-prepared to help in emergency situations.
The national poll of 1,005 people found only 51% of Americans feel they would be able to perform hands-only CPR in an emergency. When it comes to serious bleeding, 49% said they could step in to help. And 56% of survey ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Researchers determine structural motifs of water undecamer cluster
Researchers enhance photocatalytic hydrogen evolution performance of covalent organic frameworks by constitutional isomer strategy
Molecular target drives immunogenicity in cancer immunotherapy
Plant cell structure could hold key to cancer therapies and improved crops
Sustainable hydrogen peroxide production: Breakthroughs in electrocatalyst design for on-site synthesis
Cash rewards for behavior change: A review of financial incentives science in one health contexts and implications
One Health antimicrobial resistance modelling: from science to policy
Artificial feeding platform transforms study of ticks and their diseases
Researchers uncover microscopic mechanism of alkali species dissolution in water clusters
Methionine restriction for cancer therapy: A comprehensive review of mechanisms and clinical applications
White House autism briefing linked to swift shifts in prescribing patterns, study finds
Specialist palliative care can save the NHS up to £8,000 per person and improves quality of life
New research warns charities against ‘AI shortcut’ to empathy
Cannabis compounds show promise in fighting fatty liver disease
Study in mice reveals the brain circuits behind why we help others
Online forum to explore how organic carbon amendments can improve soil health while storing carbon
Turning agricultural plastic waste into valuable chemicals with biochar catalysts
Hidden viral networks in soil microplastics may shape the future of sustainable agriculture
Americans don’t just fear driverless cars will crash — they fear mass job losses
Mayo Clinic researchers find combination therapy reduces effects of ‘zombie cells’ in diabetic kidney disease
Preventing breast cancer resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors using genomic findings
Carbon nanotube fiber ‘textile’ heaters could help industry electrify high-temperature gas heating
Improving your biological age gap is associated with better brain health
Learning makes brain cells work together, not apart
Engineers improve infrared devices using century-old materials
Physicists mathematically create the first ‘ideal glass’
Microbe exposure may not protect against developing allergic disease
Forest damage in Europe to rise by around 20% by 2100 even if warming is limited to 2°C
Rapid population growth helped koala’s recovery from severe genetic bottleneck
CAR-expressing astrocytes target and clear amyloid-β in mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease
[Press-News.org] From ripples to daydreams: the brain activity behind mind wanderingResearchers from Osaka University find that mind wandering, especially when associated with less pleasurable and more vivid and imaginative self-generated thoughts, is associated with a specific pattern of brain activity linked to memory and sleep