(Press-News.org) Published today in the Alcheringa: An Australasian Journal of Palaeontology, evidence of an ‘Age of Monotremes’ has been unearthed by a team of Australian scientists at the Australian Museum (AM), Museums Victoria and Australian Opal Centre.
The findings were led by two renowned mammalogists, Honorary Associate of the Australian Museum, Professor Tim Flannery; and Professor Kris Helgen, Chief Scientist and Director of the Australian Museum Research Institute (AMRI).
Found in the Lightning Ridge opal fields, NSW, the opalised jaws date back to the Cenomanian Age of the Cretaceous Period, between 102 million to 96.6 million years ago.
Professor Flannery said the research reveals that 100 million years ago, Australia was home to a diversity of monotremes, of which the platypus and the echidna are the only surviving descendants.
“Today, Australia is known as a land of marsupials, but discovering these new fossils is the first indication that Australia was previously home to a diversity of monotremes. It’s like discovering a whole new civilisation,” Professor Flannery said.
Chief Scientist and Director of the Australian Museum Research Institute, Professor Kris Helgen, said the three new species demonstrate combinations of features not previously seen before in other living or fossil monotremes. One of the most striking of the new monotremes, Opalios splendens, retains characteristics of the earliest known monotremes, but also some that foreshadow adaptations in the living monotremes, the echidnas and platypus.
“Opalios splendens sits on a place in the evolutionary tree prior to the evolution of the common ancestor of the monotremes we have today. Its overall anatomy is probably quite like the platypus, but with features of the jaw and snout a bit more like an echidna – you might call it an ‘echidnapus’,” Professor Helgen said.
“The story of how our egg-laying mammals evolved is ‘toothy to toothless’ on the oldest monotreme, Teinolophos trusleri, which dates back to Victoria 130 million years ago. What we see at Lightning Ridge is that by 100 million years ago, some of the monotremes still have five molars but some of them are down to three,” Professor Helgen said.
Professor Flannery highlighted that today, echidnas have no teeth, and platypuses too are essentially toothless.
“Adult platypus have no teeth, though juveniles have rudimentary molars. Just when and why adult platypus lost their teeth after nearly 100 million years is a mystery we think we have solved. It may have been competition with the Australian water rat, which arrived in Australia within the last 2 million years, which caused platypus to seek out softer, slipperier food best processed with the leathery pads that adults use today,” Professor Flannery said.
“What is so unusual about this uniquely Australian story is that in one snapshot we see six different egg-laying mammals living together in Lightning Ridge over 100 million years ago. All of them are holding potential evolutionary destinies that can go off in different directions, and all of them are deep distant ancestors and relatives of the current living monotremes.”
Dr Matthew McCurry, Curator of Palaeontology, Australian Museum, said the discovery of three new genera of monotremes helps to piece together their remarkable evolutionary story.
“There are six species of monotremes, including the three newly described here, within the Cenomanian Lightning Ridge fauna of New South Wales making it the most diverse monotreme assemblage on record. Four species are known from a single specimen, suggesting that diversity remains underrepresented. This discovery adds more than 20 per cent to the previously known diversity of monotremes,” Dr McCurry said.
“We have very few monotreme fossils, and so finding new fossils can tell us more about where they lived, what they looked like and how changes in the environment influenced their evolution. Every significant monotreme fossil currently known fits into this evolutionary story, from Teinolophos, the tiny shrew-like creature in Antarctica 130 million years ago to the present day,” Dr McCurry said.
Co-authors from Museums Victoria Research Institute, Dr Thomas Rich, Senior Curator of Vertebrate Palaeontology, and Honorary Associate Professor Patricia Vickers-Rich AO said these curious, unique and ancient Australian animals still have the power to interest the scientific world.
“The platypus and echidna are iconic Australian species. The discovery of these several new species in one small area suggest that the family tree of the egg laying monotremes is far more complicated than the living platypus and echidna alone suggest,” Dr Thomas Rich said.
“As the fieldwork continues in the Mesozoic of Australia, we continue to increase our understanding of how life changed over time. This, to me, is what makes science so exciting,” Professor Patricia Vickers-Rich AO said.
The fossils were found by Elizabeth Smith and her daughter Clytie of the Australian Opal Centre in Lightning Ridge, who have spent decades working and searching over the opal fields.
“Opal fossils are rare, but opalised monotreme fossils are infinitely more rare, as there’s one monotreme fragment to a million other pieces. We don’t know when, or exactly where, they’ll turn up,” Elizabeth Smith said.
“These specimens are a revelation. They show the world that long before Australia became the land of pouched mammals, marsupials, this was a land of furry egg-layers – monotremes. It seems that 100 million years ago, there were more monotremes at Lightning Ridge than anywhere else on earth, past or present,” Elizabeth said.
END
Echidnapus identified from an ‘Age of Monotremes’
Australian researchers have found evidence of the oldest known platypus and a new species, dubbed ‘echidnapus’, which has a platypus-like anatomy alongside features that more closely resemble an echidna
2024-05-26
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Semaglutide may protect kidney function in individuals with overweight or obesity and cardiovascular disease
2024-05-25
The SELECT Trial has revealed the potential of semaglutide, a glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist, in combating kidney function decline among individuals with overweight or obesity and established cardiovascular disease but without diabetes.1
Unveiling the results today at the 61st ERA Congress, researchers presented the impressive secondary analysis from the SELECT (Semaglutide Effects on Heart Disease and Stroke in Patients with Overweight or Obesity) trial, a randomised trial comprising a participant pool of 17,604 individuals.
Experts believe the study’s results offer hope for those affected by obesity, a condition known ...
New technique detects novel biomarkers for kidney diseases with nephrotic syndrome
2024-05-25
A groundbreaking study, presented today at the 61st ERA Congress, has uncovered a significant breakthrough in the diagnosis and monitoring of kidney diseases associated with nephrotic syndrome.1
Using a hybrid technique, researchers identified anti-nephrin autoantibodies as a reliable biomarker for tracking disease progression, opening new avenues for personalised treatment approaches.
Nephrotic syndrome, characterised by elevated protein levels in the urine, is linked to kidney diseases such as minimal change disease (MCD), primary focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS), and membranous nephropathy (MN). The primary cause behind nephrotic syndrome is damage to podocytes, the ...
Political elites take advantage of anti-partisan protests to disrupt politics
2024-05-24
Protest movements that reject political parties have an unintended consequence, according to new research from the University of Notre Dame: They empower savvy politicians who channel them to shake up the status quo.
The findings provide a framework for understanding recent global political realignments and offer lessons for activists who want to make a meaningful impact. They are particularly relevant in an era when mass protests have become an increasingly common tool to voice dissent with powerful institutions and draw attention to overlooked issues ranging from climate and conflict ...
Tiny target discovered on RNA to short-circuit inflammation, UC Santa Cruz researchers find
2024-05-24
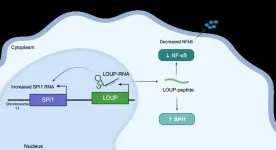
UC Santa Cruz researchers have discovered a peptide in human RNA that regulates inflammation and may provide a new path for treating diseases such as arthritis and lupus. The team used a screening process based on the powerful gene-editing tool CRISPR to shed light on one of the biggest mysteries about our RNA–the molecule responsible for carrying out genetic information contained in our DNA.
This peptide originates from within a long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) called LOUP. According to the researchers, ...
Charge your laptop in a minute? Supercapacitors can help; new research offers clues
2024-05-24
Imagine if your dead laptop or phone could charge in a minute or if an electric car could be fully powered in 10 minutes.
While not possible yet, new research by a team of CU Boulder scientists could potentially lead to such advances.
Published today in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, researchers in Ankur Gupta’s lab discovered how tiny charged particles, called ions, move within a complex network of minuscule pores. The breakthrough could lead to the development of more efficient energy storage devices, such as supercapacitors, said Gupta, an assistant professor of chemical and biological engineering.
“Given the critical role ...
Scientists discover CO2 and CO ices in outskirts of solar system
2024-05-24
ORLANDO, May 24, 2024 – For the first time, carbon dioxide and carbon monoxide ices have been observed in the far reaches of our solar system on trans-Neptunian objects (TNOs).
A research team, led by planetary scientists Mário Nascimento De Prá and Noemí Pinilla-Alonso from the University of Central Florida’s Florida Space Institute (FSI), made the findings by using the infrared spectral capabilities of the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) to analyze the chemical composition of 59 trans-Neptunian objects and Centaurs.
The pioneering study, published ...
Theory and experiment combine to shine a new light on proton spin
2024-05-24
NEWPORT NEWS, VA – Nuclear physicists have long been working to reveal how the proton gets its spin. Now, a new method that combines experimental data with state-of-the-art calculations has revealed a more detailed picture of spin contributions from the very glue that holds protons together. It also paves the way toward imaging the proton’s 3D structure.
The work was led by Joseph Karpie, a postdoctoral associate in the Center for Theoretical and Computational Physics (Theory Center) at the U.S. Department of Energy's Thomas Jefferson National Accelerator Facility.
He said that this decades-old mystery began with measurements of the sources of the proton’s spin in ...
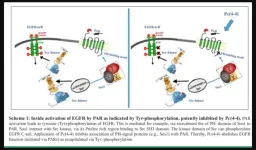
PKMYT1, a potential ‘Achilles heel’ of treatment resistant ER+ breast cancers with the poorest prognosis
2024-05-24
Up to 80% of breast cancer deaths occur in patients with tumors that express estrogen receptor-alpha. Although these estrogen receptor-positive (ER+) breast cancers often initially respond to standard treatment that combines endocrine therapies with CDK4/6 inhibitors, drug resistance often develops leading to lethal metastatic disease that spreads from the breast and does not respond to available treatments.
Looking to identify new vulnerabilities in this type of cancer that could lead to improved therapies, ...
PH-binding motifs as a platform for drug design: Lessons from protease-activated receptors (PARs)
2024-05-24
“We have identified binding motifs within the C-tails of PAR1,2&4, indispensable for cancer growth and development.”
BUFFALO, NY- May 24, 2024 – A new editorial paper was published in Oncoscience (Volume 11) on April 25, 2024, entitled, “PH-binding motifs as a platform for drug design: Lessons from protease-activated receptors; PARs.”
While targeted cancer therapy is greatly dependent on specific oncogenic pathways or conferred by genetic alterations, it remains yet challenging and somewhat disappointing. The high level of failure relies ...
Virginia Tech researcher creates new tool to move tiny bioparticles
2024-05-24
Undergoing surgery is seldom a pleasant experience, and it can sometimes be highly invasive. Surgical procedures have evolved steadily over the centuries, growing with the knowledge of anatomy and biology.
Innovative methods have also been bolstered with new tools, and a growth in the use of robotics since the 1980s has moved health care forward significantly. Assistant Professor Zhenhua Tian has pressed forward another step in the march of progress using robotics and noninvasive acoustics, and his team’s work has been published in Science Advances.
Robot-assisted surgery
Surgery using robots has been invasive since its invention because ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
How boron helps to produce key proteins for new cancer therapies
Writing the catalog of plasma membrane repair proteins
A comprehensive review charts how psychiatry could finally diagnose what it actually treats
Thousands of genetic variants shape epilepsy risk, and most remain hidden
First comprehensive sex-specific atlas of GLP-1 in the mouse brain reveals why blockbuster weight-loss drugs may work differently in females and males
When rats run, their gut bacteria rewrite the chemical conversation with the brain
Movies reconstructed from mouse brain activity
Subglacial weathering may have slowed Earth's escape from snowball Earth
Simple test could transform time to endometriosis diagnosis
Why ‘being squeezed’ helps breast cancer cells to thrive
Mpox immune test validated during Rwandan outbreak
Scientists pinpoint protein shapes that track Alzheimer’s progression
Researchers achieve efficient bicarbonate-mediated integrated capture and electrolysis of carbon dioxide
Study reveals ancient needles and awls served many purposes
Key protein SYFO2 enables 'self-fertilization’ of leguminous plants
AI tool streamlines drug synthesis
Turning orchard waste into climate solutions: A simple method boosts biochar carbon storage
New ACP papers say health care must be more accessible and inclusive for patients and physicians with disabilities
Moisture powered materials could make cleaning CO₂ from air more efficient
Scientists identify the gatekeeper of retinal progenitor cell identity
American Indian and Alaska native peoples experience higher rates of fatal police violence in and around reservations
Research alert: Long-read genome sequencing uncovers new autism gene variants
Genetic mapping of Baltic Sea herring important for sustainable fishing
In the ocean’s marine ‘snow,’ a scientist seeks clues to future climate
Understanding how “marine snow” acts as a carbon sink
In search of the room temperature superconductor: international team formulates research agenda
Index provides flu risk for each state
Altered brain networks in newborns with congenital heart disease
Can people distinguish between AI-generated and human speech?
New robotic microfluidic platform brings ai to lipid nanoparticle design
[Press-News.org] Echidnapus identified from an ‘Age of Monotremes’Australian researchers have found evidence of the oldest known platypus and a new species, dubbed ‘echidnapus’, which has a platypus-like anatomy alongside features that more closely resemble an echidna