(Press-News.org)
“This consideration could be the starting point to study whether Silibinin could contrast tumor progression, aging and inflammaging through molecular and cellular mechanisms [...].”
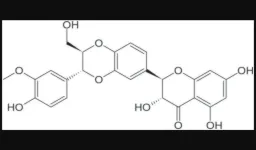
BUFFALO, NY- May 28, 2024 – A new review paper was published in Oncotarget's Volume 15 on May 23, 2024, entitled, “The importance of integrated therapies on cancer: Silibinin, an old and new molecule.”
In this new review, researchers Elisa Roca, Giuseppe Colloca, Fiorella Lombardo, Andrea Bellieni, Alessandra Cucinella, Giorgio Madonia, Licia Martinelli, Maria Elisa Damiani, Ilaria Zampieri, and Antonio Santo from Perderzoli Hospital and Fondazione Policlinico Universitario “A. Gemelli” begin their abstract by noting that the efficacy of coadjuvant molecules, in the landscape of cancer treatments, remains a focus of attention for clinical research with the aim of reducing toxicity and achieving better outcomes.
“Most of the pathogenetic processes causing tumour development, neoplastic progression, ageing, and increased toxicity involve inflammation.”
Inflammatory mechanisms can progress through a variety of molecular patterns. As is well known, the ageing process is determined by pathological pathways very similar and often parallel to those that cause cancer development. Among these complex mechanisms, inflammation is currently much studied and is often referred to in the geriatric field as ‘inflammaging’. In this context, treatments active in the management of inflammatory mechanisms could play a role as adjuvants to standard therapies.
Among these emerging molecules, Silibinin has demonstrated its anti-inflammatory properties in different neoplastic types, also in combination with chemotherapeutic agents. Moreover, this molecule could represent a breakthrough in the management of age-related processes. Thus, Silibinin could be a valuable adjuvant to reduce drug-related toxicity and increase therapeutic potential.
“For this reason, the main aim of this review is to collect and analyse data presented in the literature on the use of Silibinin, to better understand the mechanisms of the functioning of this molecule and its possible therapeutic role.”
Continue reading: DOI: https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.28587
Correspondence to: Elisa Roca
Email: elisaroca@gmail.com
Keywords: silibinin, anti-inflammatory, inflammation, toxicity, integrated therapy
Click here to sign up for free Altmetric alerts about this article.
About Oncotarget: Oncotarget (a primarily oncology-focused, peer-reviewed, open access journal) aims to maximize research impact through insightful peer-review; eliminate borders between specialties by linking different fields of oncology, cancer research and biomedical sciences; and foster application of basic and clinical science.
Oncotarget is indexed and archived by PubMed/Medline, PubMed Central, Scopus, EMBASE, META (Chan Zuckerberg Initiative) (2018-2022), and Dimensions (Digital Science).
To learn more about Oncotarget, visit Oncotarget.com and connect with us on social media:
X, formerly Twitter
Facebook
YouTube
Instagram
LinkedIn
Pinterest
Reddit
Spotify, and available wherever you listen to podcasts
Click here to subscribe to Oncotarget publication updates.
For media inquiries, please contact media@impactjournals.com.
Oncotarget Journal Office
6666 East Quaker Street., Suite 1A
Orchard Park, NY 14127
Phone: 1-800-922-0957 (option 2)
###
END
A pioneering study has used extensive global datasets and machine learning to map the activities of seafloor invertebrate animals, including worms, clams and shrimps, across the entire ocean, revealing for the first time critical factors that support and maintain the health of marine ecosystems.
The international team, led by Texas A&M University and including investigators from Yale University and the University of Southampton, specifically focused on the unsung yet vital role burrowing animals play as "ecosystem engineers" in shaping nutrient ...
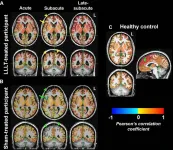
OAK BROOK, Ill. – Low-level light therapy appears to affect healing in the brains of people who suffered significant brain injuries, according to a study published today in Radiology, a journal of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
Lights of different wavelengths have been studied for years for their wound-healing properties. Researchers at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) conducted low-level light therapy on 38 patients who had suffered moderate traumatic brain injury, an injury to the head serious enough to alter cognition and/or be visible on a brain scan. Patients received ...
Background and Goal: Team-based care is considered the gold standard in delivery models. It uses integrated clinical teams with diverse skills and perspectives to provide efficient, high-quality health care services. Within these teams, individuals from minoritized racial-ethnic groups, often referred to as persons of color (POC), typically occupy roles with less authority (e.g., medical assistants), while white individuals more frequently hold positions of greater power (e.g., physicians). Few studies have explored the viewpoints of staff members in lower-power roles, who are disproportionately POC and constitute the majority of a health care team. This study aims to ...
NRG Oncology (NRG), a National Cancer Institute (NCI) National Clinical Trials Network (NCTN) group focused on improving outcomes for adults with cancer through multi-center clinical research, recently announced two new Vice-Chairs to co-lead the NRG Patient Advocate Committee (PAC) alongside the current PAC Committee Chair, Dorothy Erlanger.
Marlyn Molero, was appointed as Vice-Chair of the NRG PAC. Marlyn is a clinical researcher in the oncology area with Commonspirit Research Institute as well as a Spanish interpreter at Vituity. Marlyn brings a unique perspective to the NRG PAC leadership ...
The toe tapping behavior of various amphibians has long attracted attention from researchers and pet owners. Despite being widely documented, the underlying functional role is poorly understood. In a new paper, researchers demonstrate that Dyeing poison frogs modulate their taps based on specific stimuli.
Dyeing poison frogs, Dendrobates tinctorius, have been shown to tap their posterior toes in response to a range of prey sizes, from small fruit flies to large crickets. In the present study, ...
Irvine, Calif., May 28, 2024 — A multidisciplinary research team at the University of California, Irvine has revealed that the circadian clock – the biological pacemaker that governs daily rhythms in physiological processes, including immune functions – can be leveraged to enhance the efficacy of checkpoint inhibitor cancer therapy. Checkpoint inhibitors block different proteins from binding to tumor cells, allowing the immune system’s T cells to kill the tumor.
The study, published online ...
(MEMPHIS, Tenn. – May 27, 2024) As gene sequencing technologies become more powerful, our understanding of cellular diversity has grown in parallel. This led scientists at St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital to create a tool to improve the ease and accuracy with which investigators can study specific subpopulations of cells. The tool, named Conditional Viral Expression by Ribozyme Guided Degradation (ConVERGD), allows researchers to specifically access these subgroups of cells and precisely manipulate ...
Researchers at the University of California, Davis, have updated their guidelines on when to neuter 40 popular dog varieties by breed and sex. Their recent paper in Frontiers in Veterinary Science adds five breeds to a line of research that began in 2013 with a study that suggested that early neutering of golden retrievers puts them at increased risk of joint diseases and certain cancers.
That initial study set off a flurry of debate about the best age to neuter other popular breeds. Professors Lynette and Benjamin Hart of the School of Veterinary Medicine, the study’s lead authors, set out to add more breed studies by examining more than a decade ...
Music and speech are among the most frequent types of sounds we hear. But how do we identify what we think are differences between the two?
An international team of researchers mapped out this process through a series of experiments—yielding insights that offer a potential means to optimize therapeutic programs that use music to regain the ability to speak in addressing aphasia. This language disorder afflicts more than 1 in 300 Americans each year, including Wendy Williams and Bruce Willis.
“Although music and speech are different in many ways, ranging from pitch to timbre to sound texture, ...
An inexpensive, accurate test that detects infections with the parasite Toxoplasma gondii can provide results within 30 minutes from a finger-prick in a doctor’s office or within an hour from a small blood sample tested in a local medical laboratory. The new test can also identify false positives in other types of commercial diagnostic tests for toxoplasmosis, providing swift reassurance to uninfected pregnant women and their doctors and facilitating timely interventions to protect a fetus against toxoplasmosis in acutely infected pregnant mothers.
These findings appear in a study, led by toxoplasmosis specialist Rima McLeod, MD, ...