(Press-News.org) Research led by the University of Hawaiʻi at Mānoa Hawaiʻi Institute of Marine Biology (HIMB) has led to a new tool for forecasting coral disease that could help conservationists step in at the right times with key interventions. Ecological forecasts are critical tools for conserving and managing marine ecosystems, but few forecasting systems can account for the wide range of ecological complexities in near-real-time.
Using ecological and marine environmental conditions, the Multi-Factor Coral Disease Risk product predicts the risk of two diseases across reefs in the central and western Pacific and along the east coast of Australia. An article introducing the new tool was published in Ecological Applications.
The tool can be accessed through the U.S. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) Coral Reef Watch program, and can help end users detect early changes in the environment and better protect coral reef ecosystems.
“Partnering with NOAA Coral Reef Watch, our team developed ecological forecasts to predict the times and conditions when coral disease outbreaks are most likely to occur,” said NASA-funded Principal Investigator and HIMB Interim Director Megan Donahue.
“We are really excited about this new tool,” said lead author, Jamie Caldwell, of High Meadows Environmental Institute at Princeton University. “Users can employ this tool to make decisions about how to manage coral health, similar to how we use weather forecasts to decide how to pack for an upcoming trip.”
More than half a billion people depend on Earth’s coral reefs, and ensuring their resilience in the face of many threats is an ongoing challenge for managers. Tools like this help ensure these vital ecosystems survive.
Understanding localized risks
Insights gleaned from the tool can help managers better understand localized risks of coral disease and develop timely strategies for intervention.
“A key project element was the consultation with and input from coral reef managers from across the Pacific, including here in Australia,” said Professor Scott Heron, a collaborator from James Cook University. “We’ve also provided several training sessions in the various aspects of how the tool is used so that stakeholders in the varying locations have the best opportunity to inform effective reef management.”
Coral reefs are the most biologically diverse, species-rich marine ecosystem on Earth. They are culturally significant to Indigenous people throughout the world, and they provide food, jobs, recreation, medicine and coastline protection from storms and erosion. While disease is a natural part of marine ecosystems, increased runoff, global climate change and a slough of human impacts stress corals and cause disease.
The Multi-Factor Coral Disease Risk Product was developed by HIMB, in close collaboration with NOAA Coral Reef Watch, James Cook University, University of Newcastle and University of New South Wales.
END
New coral disease forecasting system led by University of Hawai'i team
2024-05-31
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Tobacco funded research still appearing in top medical journals
2024-05-31
Tobacco-funded research is still appearing in highly-cited medical journals - despite attempts by some to cut ties altogether, finds an investigation by The Investigative Desk and The BMJ today.
Although the tobacco industry has a long history of subverting science, most leading medical journals don’t have policies which ban research wholly or partly funded by the industry.
And even when publishers, authors and universities are willing to restrict tobacco industry ties, they struggle ...
Trout in mine-polluted rivers are genetically ‘isolated’
2024-05-31
Trout living in rivers polluted by metal from old mines across the British Isles are genetically “isolated” from other trout, new research shows.
Researchers analysed brown trout at 71 sites in Britain and Ireland, where many rivers contain metal washed out from disused mines.
While trout in metal-polluted rivers appear healthy, they are genetically distinct – and a lack of diversity in these populations makes them vulnerable to future threats.
By comparing the DNA of trout in rivers with and without metal pollution, the researchers found that metal-tolerant trout ...
How researchers are protecting AI of the future
2024-05-31
Trust is vital to the widespread acceptance of AI across industries, especially when safety is a concern. For example, people may be hesitant to ride in a self-driving car knowing that the AI running it can be hacked. One barrier to increasing trust is that the algorithms powering AI are vulnerable to such attacks.
Dr. Samson Zhou, assistant professor in the Department of Computer Science and Engineering at Texas A&M University, and Dr. David P. Woodruff, professor in the Computer Science Department at Carnegie Mellon University, hope to strengthen algorithms used by big data AI models against attacks. Big data AI models are ...
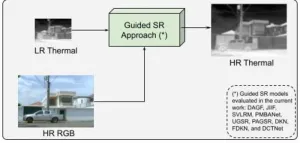
Enhancement of guided thermal image super-resolution approaches
2024-05-31
Researchers of CIDIS at ESPOL Polytechnic University have developed a new method to enhance thermal image super-resolution by employing synthetic imagery. This novel approach utilizes high-resolution images from the visible spectrum to guide the super-resolution of low-resolution thermal images, significantly improving the detail and utility of thermal imaging across various applications.
When visualizing thermal images, one typically imagines the blurry, less-detailed outputs common with standard thermal ...
Virginia Tech scientists develop visual tool to help people group foods based on their levels of processing
2024-05-31
Fralin Biomedical Research Institute at VTC scientists studying ultra-processed foods have created a new tool for assessing the rewarding and reinforcing properties of foods that make up 58 percent of calories consumed in the United States. The foods have been linked to a wide range of negative health outcomes.
The research, which was published in April in the journal Appetite, provides a collection of carefully curated images of minimally processed and ultra-processed foods matched on 26 characteristics, including macronutrients, sodium, dietary fiber, calories, price, and visual characteristics such as a color and portion size.
The work was based on the NOVA classification system ...
Glimpses of a volcanic world: New telescope images of Jupiter's moon Io rival those from spacecraft
2024-05-31
New images of Jupiter's volcano-studded moon Io, taken by the Large Binocular Telescope on Mount Graham in Arizona, offer the highest resolution of Io ever achieved with an Earth-based instrument. The observations were made possible by a new high-contrast optical imaging instrument, dubbed SHARK-VIS, and the telescope's adaptive optics system, which compensates for the blurring induced by atmospheric turbulence.
The images, to be published in the journal Geophysical Research Letters, reveal surface features as small as 50 miles across, ...
Wake Forest University School of Medicine awarded $1.5 million from NIH to use advanced imaging to assess bone loss after bariatric surgery
2024-05-30
WINSTON-SALEM, N.C. – May 30, 2024 – Researchers at Wake Forest University of School of Medicine have received a five-year, $1.5 million grant from the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases, part of the National Institutes of Health (NIH), to study bone microarchitecture in patients following bariatric surgery.
With the funding support, researchers at Wake Forest University School of Medicine will partner with Virginia Tech to add a virtual biopsy that uses an innovative technique called high-resolution peripheral quantitative ...
Researchers identify factors that heighten risk for catheter-associated urinary tract infections and sepsis
2024-05-30
Urinary catheters are required for nearly every surgical procedure. However, a major challenge for the health care industry is predicting who may develop catheter-associated urinary tract infections (CAUTIs) and when these infections may lead to death.
Now, a study from the University of Notre Dame has identified a population that is more susceptible to developing a CAUTI.
Researchers showed that models with fibrinolytic deficiencies, or conditions that cause overactivation of the protein fibrin, had increased risk for developing severe and persistent CAUTIs. ...
How community stress affects Black Americans’ mental health and wellbeing
2024-05-30
URBANA, Illinois – Residential segregation is an example of the long history of structural racism in the United States. Black Americans are more likely to live in low-quality neighborhoods, which contributes to disparities in health outcomes. A new study from the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign looks at how community stress affects the mental and emotional health of Black men and women in the U.S.
“Community stress refers to the effects of living in disadvantaged areas. This includes objective aspects, such as buildings ...
Every drop counts: New algorithm tracks Texas daily reservoir evaporation rates
2024-05-30
Summer can be an extra challenging time for Texas’ 189 major water supply reservoirs. With temperatures consistently reaching 100 degrees or higher, reservoir evaporation rates see high increases.
Accurate evaporation rate estimates are crucial for water resource managers, as reservoirs play an essential role in our social and economic systems by supplying water for agricultural, municipal, and industrial consumption. Reservoirs are also critical for mitigating impacts from droughts and floods.
A recent study published ...