(Press-News.org) About The Study: Higher adherence to the Mediterranean diet was associated with a 23% lower risk of all-cause mortality in this cohort study. This inverse association was partially explained by multiple cardiometabolic factors.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Shafqat Ahmad, Ph.D., email shafqat.ahmad@medsci.uu.se.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.14322)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time http://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.14322?utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_term=053124
About JAMA Network Open: JAMA Network Open is an online-only open access general medical journal from the JAMA Network. On weekdays, the journal publishes peer-reviewed clinical research and commentary in more than 40 medical and health subject areas. Every article is free online from the day of publication.
END
Mediterranean diet adherence and risk of all-cause mortality in women
JAMA Network Open
2024-05-31
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Traumatic brain injury strikes 1 in 8 older Americans
2024-05-31
Some 13% of older adults are diagnosed with traumatic brain injury (TBI), according to a study by UC San Francisco and the San Francisco VA Health Care System. These injuries are typically caused by falls from ground level.
Researchers followed about 9,200 Medicare enrollees, whose average age was 75 at the start of the study, and found that contrary to other studies of younger people, being female, white, healthier and wealthier was associated with higher risk of TBI.
The study publishes in JAMA Network Open on May 31, 2024.
The researchers, ...
Stem cells shed new light on how the human embryo forms
2024-05-31
A new study using stem cell-based models has shed new light on how the human embryo begins to develop, which could one day benefit the development of fertility treatment.
The study led by at the University of Exeter Living Systems Institute has revealed how early embryo cells decide between contributing to the foetus or to the supporting yolk sac.
Understanding this decision is important because the yolk sac is essential for later development in the womb. Producing the right number of yolk sac forming cells may be critical for infertility treatment using in vitro fertilised (IVF) embryos.
Only limited research ...
BU study finds policy makers’ use of in-hospital mortality as a sepsis quality metric may unfairly penalize safety-net hospitals
2024-05-31
EMBARGOED by JAMA Network Open until 11 a.m., ET May 31, 2024
Contact: Maria Ober, mpober@bu.edu
BU Study Finds Policy Makers’ Use of In-Hospital Mortality as a Sepsis Quality Metric May Unfairly Penalize Safety-net Hospitals
(Boston)—Sepsis is a leading cause of death and disability and a key target of state and federal quality measures for hospitals. In-hospital mortality of patients with sepsis is frequently measured for benchmarking, both by researchers and policymakers. For example, in New York, sepsis regulations mandate reporting of risk-adjusted in-hospital mortality, and hospitals with lower or higher than expected in-hospital ...
Mediterranean diet tied to one-fifth lower risk of death in women
2024-05-31
Investigators from Brigham and Women’s Hospital identified and assessed underlying mechanisms that may explain the Mediterranean diet’s 23 percent reduction in all-cause mortality risk for American women
The health benefits of the Mediterranean diet have been reported in multiple studies, but there is limited long-term data of its effects in U.S. women and little understanding about why the diet may reduce risk of death. In a new study that followed more than 25,000 initially healthy U.S. women for up ...
Relieving a fear of public speaking
2024-05-31
By Alistair Jones
SMU Office of Research - If you dread public speaking you are not alone. It is a leading social phobia, one that can cause a state of anxiety that reduces otherwise articulate people to nervous incoherence.
A strong fear of public speaking is known as glossophobia. Academic studies estimate it affects 20 per cent of the population, but depending on the sample and methodology, the figure could be as high as 40 per cent.
As American writer and humourist Mark Twain said, ...
Innovating learning with ChatGPT-based Prompt Tutor
2024-05-31
By Jovina Ang
SMU Office of Research – “Giving students immediate and frequent feedback makes online learning more effective,” Associate Professor Ouh Eng Lieh told the Office of Research.
However, based on how most online lessons are designed, questions could not be answered nor doubts clarified until students meet their instructor in the following face-to-face class.
The time delay of a few days to a few weeks can impede student learning as it might make it difficult for students to catch up and understand the subsequent topics in the course.
Learning also ...
Moving beyond cubicles: How an active workplace design can drive workers’ behaviors
2024-05-31
Ishikawa, Japan -- Physical inactivity and sitting for prolonged hours are highly prevalent among office-based workers, known to be resulting in various health risks and economic constraints. However, to reduce sedentary time and increase physical activity, health promotion interventions alone are insufficient. The design of workplaces should also be considered to promote interactive behavior among workers.
Many models, such as the socio-ecological model, show how multiple factors interact to influence workers' active and sedentary behaviors. These models specifically magnify the impact of workplace environments in shaping these behaviors. Several studies ...
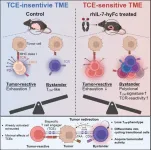
Breakthrough in using bispecific antibodies for solid tumors
2024-05-31
Professor Seung-Woo Lee and PhD candidate Kun-Joo Lee from the Department of Life Sciences at Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH), in collaboration with NeoImmuneTech Director Donghoon Choi and Professors Dae Hee Kim and Sun Shim Choi from Kangwon National University, have revealed a groundbreaking method to significantly enhance the efficacy of bispecific antibody therapies in treating solid tumors. Their findings were published on May 13 in “Cell Reports Medicine”, an international journal of healthcare research.
Bispecific antibodies, which can simultaneously bind to two different ...
Fjords are effective carbon traps regardless of oxygen levels
2024-05-31
The fjords on Sweden’s west coast act as effective carbon traps regardless of whether the bottom water is oxygen-rich or not. This is the conclusion of a new study with researchers from the University of Gothenburg.
Large quantities of plant parts sink to the bottom of fjords on the Swedish west coast where they form sediment. This buries organic carbon, which would otherwise contribute to ocean acidification and the greenhouse effect. When the plant parts are exposed to oxygen and other substances, the organic carbon begins to decompose into inorganic carbon, which can be dissolved into carbonic acid in the water. Research ...
Korea University College of Medicine’s team predict hearing conditions in vestibular schwannoma patients using radiomics
2024-05-31
Korea University College of Medicine’s Team Predict Hearing Conditions in Vestibular Schwannoma Patients Using Radiomics
A recent study demonstrates that radiomics imaging analysis can effectively forecast the hearing status of patients with vestibular schwannoma patients. Since treatment methods, such as surgery or active surveillance, vary for these patients based on tumor size and hearing condition, predicting hearing status is crucial in planning and determining the appropriate treatment.
The research team led by Professor June Choi from the Department ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Scientists pinpoint protein shapes that track Alzheimer’s progression
Researchers achieve efficient bicarbonate-mediated integrated capture and electrolysis of carbon dioxide
Study reveals ancient needles and awls served many purposes
Key protein SYFO2 enables 'self-fertilization’ of leguminous plants
AI tool streamlines drug synthesis
Turning orchard waste into climate solutions: A simple method boosts biochar carbon storage
New ACP papers say health care must be more accessible and inclusive for patients and physicians with disabilities
Moisture powered materials could make cleaning CO₂ from air more efficient
Scientists identify the gatekeeper of retinal progenitor cell identity
American Indian and Alaska native peoples experience higher rates of fatal police violence in and around reservations
Research alert: Long-read genome sequencing uncovers new autism gene variants
Genetic mapping of Baltic Sea herring important for sustainable fishing
In the ocean’s marine ‘snow,’ a scientist seeks clues to future climate
Understanding how “marine snow” acts as a carbon sink
In search of the room temperature superconductor: international team formulates research agenda
Index provides flu risk for each state
Altered brain networks in newborns with congenital heart disease
Can people distinguish between AI-generated and human speech?
New robotic microfluidic platform brings ai to lipid nanoparticle design
COSMOS trial results show daily multivitamin use may slow biological aging
Immune cells play key role in regulating eye pressure linked to glaucoma
National policy to remedy harms of race-based kidney function estimation associated with increased transplants for Black patients
Study finds teens spend nearly one-third of the school day on smartphones, with frequent checking linked to poorer attention
Team simulates a living cell that grows and divides
Study illuminates the experiences of people needing to seek abortion care out of state
Digital media use and child health and development
Seeking abortion care across state lines after the Dobbs decision
Smartphone use during school hours and association with cognitive control in youths ages 11 to 18
Maternal acetaminophen use and child neurodevelopment
Digital microsteps as scalable adjuncts for adults using GLP-1 receptor agonists
[Press-News.org] Mediterranean diet adherence and risk of all-cause mortality in womenJAMA Network Open