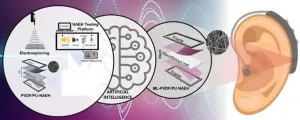
(Press-News.org) (LOS ANGELES) June 3, 2024 – Scientists at the Terasaki Institute for Biomedical Innovation (TIBI), have employed artificial intelligence techniques to improve the design and production of nanofibers used in wearable nanofiber acoustic energy harvesters (NAEH). These acoustic devices capture sound energy from the environment and convert it into electrical energy, which can then be applied in useful devices, such as hearing aids.
Many efforts have been made to capture naturally occurring and abundant energy sources from our surrounding environment. Relatively recent advances such as solar panels and wind turbines allow us to efficiently harvest energy from the sun and wind, convert it into electrical energy, and store it for various applications. Similarly, conversions of acoustic energy can be seen in amplifying devices such as microphones, as well as in wearable, flexible electronic devices for personalized healthcare.
Currently, there has been much interest in using piezoelectric nanogenerators - devices that convert mechanical vibrations, stress, or strain into electrical power – as acoustic energy harvesters. These nanogenerators can convert mechanical energy from sound waves to generate electricity; however, this conversion of sound waves is inefficient, as it occurs mainly in the high frequency sound range, and most environmental sound waves are in the low frequency range. Additionally, choosing optimal materials, structural design, and fabrication parameters make the production of piezoelectric nanogenerators challenging.
As described in their paper in Nano Research, the TIBI scientists’ approach to these challenges was two-fold: first, they chose their materials strategically and elected to fabricate nanofibers using polyvinylfluoride (PVDF), which are known for their ability to capture acoustic energy efficiently. When making the nanofiber mixture, polyurethane (PU) was added to the PVDF solution to impart flexibility, and electrospinning (a technique for generating ultrathin fibers) was used to produce the composite PVDF/PU nanofibers.
Secondly, the team applied artificial intelligence (AI) techniques to determine the best fabrication parameters involved in electrospinning the PVDF/polyurethane nanofibers; these parameters included the applied voltage, electrospinning time, and drum rotation speed. Employing these techniques allowed the team to tune the parameter values to obtain maximum power generation from their PVDF/PU nanofibers.
To make their nanoacoustic energy harvester, the TIBI scientists fashioned their PVDF/PU nanofibers into a nanofibrous mat and sandwiched it between aluminum mesh layers that functioned as electrodes. The entire assembly was then encased by two flexible frames.
In tests against conventionally fabricated NAEHs, the resultant AI-generated PVDF/PU NAEHs were found to have better overall performance, yielding a power density level more than 2.5 times higher and a significantly higher energy conversion efficiency (66% vs 42%). Furthermore, the AI-generated PVDF/PU NAEHs were able to obtain these results when tested with a wide range of low-frequency sound – well within the levels found in ambient background noise. This allows for excellent sound recognition and the ability to distinguish words with high resolution.
“Models using artificial intelligence optimization, such as the one described here, minimize time spent on trial and error and maximize the effectiveness of the finished product,” said Ali Khademhosseini, Ph.D., TIBI’s director and CEO. “This can have far-reaching effects on the fabrication of medical devices with significant practicability.”
Authors: Negar Hosseinzadeh Kouchehbaghi, Maryam Yousefzadeh, Aliakbar Gharehaghaji, Safoora Khosravi, Danial Khorsandi, Reihaneh Haghniaz, Ke Cao, Mehmet R. Dokmeci, Mohammad Rostami, Ali Khademhosseini & Yangzhi Zhu
###
About the Terasaki Institute for Biomedical Innovation
The Terasaki Institute for Biomedical Innovation is accelerating the pace of translational research by supporting the world’s leading scientists with an open, entrepreneurial environment for bioengineering new materials, biological models, and advanced technologies to address critical challenges to the health of the planet and its people. The Institute’s worldwide collaborations with academic, clinical, and entrepreneurial partners provide a rich foundation for translating innovations to the real world.
Contact:
Stewart Han
President
Terasaki Institute for Biomedical Innovation
shan@terasaki.org
END
Enhancing nanofibrous acoustic energy harvesters with artificial intelligence
Maximizes production and performance of wearable sound amplifiers
2024-06-03
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Research pioneer and paradigm-shifting thought leader for breast cancer precision medicine to receive the 2024 Szent-Györgyi Prize for Progress in Cancer Research
2024-06-03
June 3, 2024 (Rockville, MD)
The National Foundation for Cancer Research (NFCR) is announcing that the blue-ribbon selection committee, composed of world-renowned research leaders and visionaries, has awarded the 2024 Szent-Györgyi Prize for Progress in Cancer Research to Dennis J. Slamon, M.D., Ph. D. from UCLA Health for his groundbreaking research discoveries that helped to shape the field of precision medicine for breast cancer patients.
The cancer research community will celebrate Dr. ...
Assessing the environmental and downstream human health impacts of decentralizing cancer care
2024-06-03
About The Study: This cohort study found that using decentralization through telemedicine and local care may substantially reduce cancer care’s greenhouse gas emissions; this corresponds to small reductions in human mortality.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Gregory A. Abel, M.D., M.P.H., email gregory_abel@dfci.harvard.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamaoncol.2024.2744)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, ...
Telehealth can significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions associated with cancer care, study finds
2024-06-03
BOSTON – Telemedicine visits for cancer care may not only be more convenient and easier to schedule than in-person appointments, they're also better for the planet, new research by Dana-Farber Cancer Institute scientists shows.
Based on an analysis of data from a regional cancer center, the researchers calculate that, nationwide, cancer care that utilizes telehealth and local care would generate 33.1% less greenhouse gas emissions than the traditional model of in-person care, primarily because of reduced travel to medical appointments. ...
Brain waves shape the words we hear
2024-06-03
The timing of our brain waves shapes how we perceive our environment. We are more likely to perceive events when their timing coincides with the timing of relevant brain waves. Lead scientist Sanne ten Oever and her co-authors set out to determine whether neural timing also shapes speech perception. Is the probability of speech sounds or words encoded in our brain waves and is this information used to recognise words?
The team first created ambiguous stimuli for both sounds and words. For instance, the initial sounds in da and ga differ in probability: ‘d’ is more common than ‘g’. The Dutch words dat “that” and gat “hole” ...
Geographic distribution of clinical trials for advanced-stage cancer
2024-06-03
About The Study: This quality improvement analysis of clinical trials for metastatic breast, lung, colon, pancreatic, and prostate cancers found that a large proportion of the U.S. population lived within 30 miles of a clinical trial site. This finding suggests that while many clinical trials are available, they are not evenly distributed across the country and may not be accessible to all individuals, particularly racial and ethnic minority individuals. This disparity in access to clinical trials raises important questions about equity and fairness in the distribution of health care resources and opportunities ...
PSU secures $1 million grant for high-performance computing cluster across Oregon
2024-06-03
Portland State will power up a new high-performance computing cluster that will give researchers at universities and colleges across Oregon the ability to advance computing-intensive research projects by processing large datasets and performing complex computations in a fraction of the time — thanks to a nearly $1 million grant from the National Science Foundation’s Campus Cyberinfrastructure program.
The Oregon Regional Computing Accelerator (Orca) aims to provide free-of-cost computing resources and cyberinfrastructure ...
New $12.5 million National Science Foundation grant awarded to study phenomenon affecting agriculture, cancer, biodiversity and more
2024-06-03
It’s in your heart and liver, in the vegetables you eat, in the rogue cells that cause cancer. Those who live in temperate regions are surrounded by more of it than people who live in the tropics, and without it, humans wouldn’t exist.
It’s called polyploidy, and only within the last few years have biologists begun to recognize its significance across the tree of life.
“It’s one of the most important biological processes that hardly anybody knows about,” said Doug Soltis, a distinguished professor at the Florida Museum of Natural History.
Soltis is one of 18 scientists who have received a combined ...
SwRI-led team to bolster earthquake readiness for U.S. Federal Highway Administration
2024-06-03
SAN ANTONIO — June 3, 2024 — Southwest Research Institute will enhance models to strengthen the earthquake resilience of America’s transportation infrastructure and improve public safety in earthquake-prone areas. As part of a contract with the U.S. Federal Highway Administration (FHWA), an SwRI-led team will update and improve liquefaction models. Liquefaction occurs during an earthquake when intense shaking causes soil to temporarily act more like a fluid, losing its capacity to support roads and structures.
“For highways specifically, sometimes state and ...
Updating the way the Lab computes
2024-06-03
Unraveling the behavior of plasma increasingly requires intensive computing resources. That’s why plasma demands a calculated approach to computation.
As the new head of computational sciences at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory (PPPL), Shantenu Jha is excited to be at the helm of the Lab’s computing efforts, fusing computer science expertise with PPPL’s pioneering research into the fourth state of matter.
“I want to continue to grow the excellence that already exists in computing for fusion energy at PPPL, which ...
New study finds popular diabetes and weight-loss drugs associated with reduction in incidence and recurrence of alcohol-use disorder by at least half
2024-06-03
CLEVELAND—A new study by researchers at the Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine reveals that the popular diabetes and weight-loss drugs Wegovy and Ozempic are linked to reduced incidence and recurrence of alcohol abuse or dependence.
The team’s findings, recently published in the journal Nature Communications, may suggest a possible new treatment for excessive alcohol use—including alcohol-use disorder (AUD), a health condition that causes about 178,000 deaths in the United States each year, according to the Centers for Disease Control.
To date, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved only three medications to treat AUD.
The active ingredient ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Simple test could transform time to endometriosis diagnosis
Why ‘being squeezed’ helps breast cancer cells to thrive
Mpox immune test validated during Rwandan outbreak
Scientists pinpoint protein shapes that track Alzheimer’s progression
Researchers achieve efficient bicarbonate-mediated integrated capture and electrolysis of carbon dioxide
Study reveals ancient needles and awls served many purposes
Key protein SYFO2 enables 'self-fertilization’ of leguminous plants
AI tool streamlines drug synthesis
Turning orchard waste into climate solutions: A simple method boosts biochar carbon storage
New ACP papers say health care must be more accessible and inclusive for patients and physicians with disabilities
Moisture powered materials could make cleaning CO₂ from air more efficient
Scientists identify the gatekeeper of retinal progenitor cell identity
American Indian and Alaska native peoples experience higher rates of fatal police violence in and around reservations
Research alert: Long-read genome sequencing uncovers new autism gene variants
Genetic mapping of Baltic Sea herring important for sustainable fishing
In the ocean’s marine ‘snow,’ a scientist seeks clues to future climate
Understanding how “marine snow” acts as a carbon sink
In search of the room temperature superconductor: international team formulates research agenda
Index provides flu risk for each state
Altered brain networks in newborns with congenital heart disease
Can people distinguish between AI-generated and human speech?
New robotic microfluidic platform brings ai to lipid nanoparticle design
COSMOS trial results show daily multivitamin use may slow biological aging
Immune cells play key role in regulating eye pressure linked to glaucoma
National policy to remedy harms of race-based kidney function estimation associated with increased transplants for Black patients
Study finds teens spend nearly one-third of the school day on smartphones, with frequent checking linked to poorer attention
Team simulates a living cell that grows and divides
Study illuminates the experiences of people needing to seek abortion care out of state
Digital media use and child health and development
Seeking abortion care across state lines after the Dobbs decision
[Press-News.org] Enhancing nanofibrous acoustic energy harvesters with artificial intelligenceMaximizes production and performance of wearable sound amplifiers