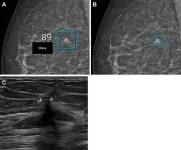
(Press-News.org) OAK BROOK, Ill. – Using artificial intelligence (AI), breast radiologists in Denmark have improved breast cancer screening performance and reduced the rate of false-positive findings. Results of the study were published today in Radiology, a journal of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
Mammography successfully reduces breast cancer mortality, but also carries the risk of false-positive findings. In recent years, researchers have studied the use of AI systems in screening.
“We believe AI has the potential to improve screening performance,” said Andreas D. Lauritzen, Ph.D., a post-doctoral student at the University of Copenhagen and researcher at Gentofte Hospital in Denmark.
When used to triage likely normal screening results or assist with decision support, AI also can substantially reduce radiologist workload.
“Population-based screening with mammography reduces breast cancer mortality, but it places a substantial workload on radiologists who must read a large number of mammograms, the majority of which don’t warrant a recall of the patient,” Dr. Lauritzen said. “The reading workload is further compounded when screening programs employ double reading to improve cancer detection and decrease false-positive recalls.”
Dr. Lauritzen and colleagues set out to compare workload and screening performance in two cohorts of women who underwent screening before and after AI implementation.
The retrospective study compared two groups of women between the ages of 50 and 69 who underwent biennial mammography screening in the Capital Region of Denmark.
In the first group, two radiologists read the mammograms of women screened between October 2020 and November 2021 before the implementation of AI. The screening mammograms of the second group of women performed between November 2021 and October 2022 were initially analyzed by AI. Mammograms deemed likely to be normal by AI were then read by one of 19 specialized full-time breast radiologists (called a single-read). The remaining mammograms were read by two radiologists (called a double-read) with AI-assisted decision support.
The commercially available AI system used for screening was trained by deep learning models to highlight and rate suspicious lesions and calcifications within mammograms. All women who underwent mammographic screening were followed for at least 180 days. Invasive cancers and ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) detected through screening were confirmed through needle biopsy or surgical specimens.
In total, 60,751 women were screened without AI, and 58,246 women were screened with the AI system. In the AI implementation group, 66.9% (38,977) of the screenings were single-read, and 33.1% (19,269) were double-read with AI assistance.
Compared to screening without AI, screening with the AI system detected significantly more breast cancers (0.82% versus 0.70%) and had a lower false-positive rate (1.63% versus 2.39%).
“In the AI-screened group, the recall rate decreased by 20.5 percent, and the radiologists’ reading workload was lowered by 33.4 percent,” Dr. Lauritzen said.
The positive predictive value of AI screening was also greater than that of screening without AI (33.5% versus 22.5%). In the AI group, a higher proportion of invasive cancers detected were 1 centimeter or less in size (44.93% vs. 36.60%).
“All screening performance indicators improved except for the node-negative rate which showed no evidence of change,” Dr. Lauritzen said.
Dr. Lauritzen said more research is needed to evaluate long-term outcomes and ensure overdiagnosis does not increase.
“Radiologists typically have access to the women’s previous screening mammograms, but the AI system does not,” he said. “That’s something we’d like to work on in the future.”
It is also important to note that not all countries follow the same breast cancer screening protocols and intervals. U.S. breast cancer screening protocols differ from protocols used in Denmark.
###
“Early Indicators of the Impact of Using AI in Mammography Screening for Breast Cancer.” Collaborating with Dr. Lauritzen were Martin Lillholm, Ph.D., Elsebeth Lynge, Ph.D., Mads Nielsen, Ph.D., Nico Karssemeijer, Ph.D., and Ilse Vejborg, M.D.
Radiology is edited by Linda Moy, M.D., New York University, New York, N.Y., and owned and published by the Radiological Society of North America, Inc. (https://pubs.rsna.org/journal/radiology)
RSNA is an association of radiologists, radiation oncologists, medical physicists and related scientists promoting excellence in patient care and health care delivery through education, research and technologic innovation. The Society is based in Oak Brook, Illinois. (RSNA.org)
For patient-friendly information on breast cancer screening, visit RadiologyInfo.org.
END
A new study by Carnegie Mellon University researchers found that when roboticists and people with disabilities collaborate on robot designs, interesting ideas emerge that could make existing robots more accessible and inspire new uses.
In their research, School of Computer Science faculty members Sarah Fox and Nikolas Martelaro highlight potential issues sidewalk robots encounter during deployment and propose solutions to mitigate them before the robots hit the streets. Their new study, led by Human-Computer Interaction Institute (HCII) Ph.D. student Howard Han, was presented last month at the ACM Conference on ...
A new study by Florida Atlantic University’s Schmidt College of Medicine has uncovered a disturbing trend in drug-related infant deaths in the United States from 2018 to 2022.
Infant deaths are those that occur between the time a child is born and age 1. Drug-involved deaths are those in which drugs are either the primary cause of death or a contributing factor and may occur due to maternal drug use, inadvertent or accidental intake of specific prescriptions, illicit or non-medical use of drugs and other incidents where drugs were linked to death.
Results of the study, published in the Journal of Perinatal Medicine, show that in the U.S. from 2018 to 2022, drug-involved ...
Scientists at Duke-NUS Medical School have identified how the first domino falls after a person encounters an allergen, such as peanuts, shellfish, pollen or dust mites. Their discovery, published in the April issue of Nature Immunology, could herald the development of drugs to prevent these severe reactions.
It is well established that when mast cells, a type of immune cell, mistake a harmless substance, such as peanuts or dust mites, as a threat, they release an immediate first wave of bioactive chemicals against the perceived threat. When mast cells, which reside under the skin, around blood vessels and in the linings of the airways and the gastrointestinal tract, simultaneously release ...
As sad as it is, child maltreatment continues to be a prevalent global social issue. Recent studies have revealed that up to one billion children aged two to 17 experience some form of abuse or neglect every year. While it is possible that some children may eventually overcome these experiences, abundant evidence indicates that child abuse can continue to have a lasting negative impact on brain and mental development, even as these children age. Therefore, prioritizing the prevention of this menacing behavior is crucial.
One way to pursue this goal is to focus on the underlying causes that lead to the perpetuation of abuse, ...
SAN FRANCISCO—June 4, 2024—In recent years, technologies that allow scientists to study a person’s DNA at single-molecule resolution have vastly expanded our knowledge of the human genome, the microbiome, and the genetic basis of disease. With such a detailed view of DNA, it’s possible to see genetic variants and structural details that were simply undetectable with earlier sequencing technologies.
However, today’s gold-standard methods for single-molecule analysis typically require at least 150,000 human cells—containing millions of individual DNA molecules. That means researchers can’t apply these tools when just ...
DALLAS, June 4, 2024 — Significant barriers prevent or slow treatment for many patients with stroke, including long travel times to stroke center hospitals and the lack of availability of stroke specialists who can evaluate the patient and determine if they are a candidate for treatment.[1] Telehealth stroke care, also known as telestroke, can expand access to rural areas and other communities that face barriers to stroke care.
A new American Heart Association certification for health care professionals is designed to help standardize training and increase skills and competencies for health care providers ...
By Jake Siegel
Seattle, WASH.—June 4, 2024—The Allen Institute for Cell Science unveiled a set of tools to accelerate research into hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM), the most common genetic heart condition in the world: six new cell line collections, each carrying a different mutation associated with HCM.
HCM is primarily caused by mutations that thicken heart muscle and, in rare cases, lead to heart failure and cardiac arrest. The new cell line collections will help scientists investigate ...
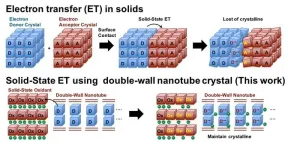
Electron transfer (ET) is a process in which an electron is transferred from one atom or molecule to another. ET is fundamental to electrochemical reactions with applications in many fields. Nanoscale ET, which involves the transfer of electrons in the range of 1–100 nanometers in solids is fundamental to the design of multifunctional materials. However, this process is not yet clearly understood.
Nanotubes, nanomaterials with unique cylindrical nanostructures, offer a variety of ET properties that can be realized through electron and hole (vacant spaces left by electrons) injections into the nanotubes, making them a suitable candidate for studying nanoscale ET. Although ...
While mentally stimulating activities and life experiences can improve cognition in memory clinic patients, stress undermines this beneficial relationship. This is according to a new study from Karolinska Institutet published in Alzheimer’s & Dementia: The Journal of the Alzheimer’s Association.
Researchers in the late 1980s found that some individuals who showed no apparent symptoms of dementia during their lifetime had brain changes consistent with an advanced stage of Alzheimer’s disease. It has since been postulated that so-called ...
OAKLAND, CA – New research finds that even people with an average sense of smell could be living with a natural gas leak and not know it. The peer-reviewed study, published in Environmental Research Letters, finds that small gas leaks can impact indoor air quality by introducing a number of hazardous air pollutants, including the carcinogen benzene, which researchers found in 97% of natural gas samples across North America.
“While these smaller leaks are not large enough to cause gas explosions, hard-to-smell leaks are common,” ...