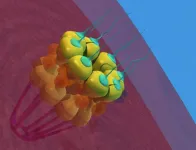
(Press-News.org) Nuclear pore complexes (NPCs) are channels composed of multiple proteins that ferry molecules in and out of the nucleus, regulating many critical cellular functions, such as gene expression, chromatin organization and RNA processes that influence cell survival, proliferation, and differentiation.
In recent years, new studies, including work by Maximiliano D’Angelo, Ph.D., associate professor in the Cancer Metabolism and Microenvironment Program at Sanford Burnham Prebys, have noted that NPCs in cancer cells are different, but how these alterations contribute to malignancy and tumor development—or even how NPCs function in normal cells—is poorly understood.
In a new paper, published June 5, 2024 in Science Advances, D’Angelo with first author Valeria Guglielmi, Ph.D., and co-author Davina Lam, uncover Nup358, one of roughly 30 proteins that form the NPCs, as an early player in the development of myeloid cells, blood cells that if not formed or working properly leads to myeloid disorders such as leukemias.
The researchers found that when they eliminated Nup358 in a mouse model, the animals experienced a severe loss of mature myeloid cells, a group of critical immune cells responsible for fighting pathogens that are also responsible for several human diseases including cancer. Notably, Nup358 deficient mice showed an abnormal accumulation of early progenitors of myeloid cells referred as myeloid-primed multipotent progenitors (MPPs).
“MPPs are one of the earliest precursors of blood cells,” said D’Angelo. “They are produced in the bone marrow from hematopoietic stem cells, and they differentiate to generate the different types of blood cells.
“There are different populations of MPPs that are responsible for producing specific blood cells and we found that in the absence of Nup358, the MPPs that generate myeloid cells, which include red blood cells and key components of the immune system, get stuck in the differentiation process.”
Fundamentally, said Gugliemi, Nup358 has a critical function in the early stages of myelopoiesis (the production of myeloid cells). “This is a very important finding because it provides insights into how blood cells develop, and can help to establish how alterations in Nup358 contribute to blood malignancies.”
The findings fit into D’Angelo’s ongoing research to elucidate the critical responsibilities of NPCs in healthy cells and how alterations to them contribute to immune dysfunction and the development and progression of cancer.
“Our long-term goal is to develop novel therapies targeting transport machinery like NPCs,” said D’Angelo, who recently received a two-year, $300,000 Discovery Grant from the American Cancer Society to advance his work.
This research was supported in part by a Research Scholar Grant from the American Cancer Society (RSG-17-148-01), the Department of Defense (grant W81XWH-20-1-0212) and the National Institutes of Health (AI148668).
The study’s DOI is 10.1126/sciadv.adn8963.
END
How a protein component of nuclear pore complexes regulates development of blood cells and may contribute to myeloid disorders
2024-06-06
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Drug used to treat eczema may provide relief for patients with intensely itchy skin diseases
2024-06-06
A drug approved to treat eczema provided significant improvement in the symptoms of patients with severe itching diseases that currently have no targeted treatments, according to a new study published in JAMA Dermatology. The drug, abrocitinib, was found to cause minimal side effects during a small 12-week study led by University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM) researchers. It was beneficial for those with an itching disease called prurigo nodularis as well as for those with chronic pruritus of unknown origin, a condition that causes chronic unexplainable itching symptoms.
“Very ...
The problem with prison abolition? Misunderstanding it
2024-06-06
“Approximately one in seventy working people in the United States are employed by either the police or departments of corrections.” In recent years, and in particular, in the aftermath of the Black Lives Matter protests of 2020, activists have focused renewed attention on the role of prisons in the United States. Thinkers like Angela Davis have articulated the ways in which the prison-industrial complex serves the interest of an oppressive state by reinforcing race and class hierarchies and extracting value from its incarcerated population. But despite this surge of interest ...
The Lancet Psychiatry: One in six people who stop antidepressants will experience discontinuation symptoms as a direct result, finds most comprehensive study to date
2024-06-06
Peer-reviewed / Systematic review & meta-analysis / People
Embargoed access to the paper and linked comment and contact details for authors are available in Notes to Editors at the end of the release.
The first meta-analysis on the incidence of antidepressant discontinuation symptoms includes data from over 20,000 patients gathered from 79 randomised controlled trials and observational studies.
Overall, approximately one in three patients reported a discontinuation ...
Antidepressants: new data on prevalence of discontinuation symptoms
2024-06-06
Joint press release from Charité & University Hospital Cologne
How hard is it to stop taking antidepressants? If countless Internet posts and a number of scientific studies are to be believed, discontinuing these medications is highly problematic, and doctors often underestimate the difficulties involved. But it is unclear how common discontinuation symptoms actually are. Researchers from Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin and University Hospital Cologne have now conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis. In their article in The Lancet ...
Scientists question effectiveness of nature-based CO2 removal using the ocean
2024-06-06
Limited understanding of basic ocean processes is hindering progress in marine carbon dioxide removal, with the on-going commercialisation of some approaches “premature and misguided”.
In a new paper, scientists from the University of East Anglia (UEA), the University of Tasmania’s Institute for Marine and Antarctic Studies, Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique, and the Institute for Sustainable Development and International Relations, review the climatic effectiveness of four 'nature-based' techniques using marine biological processes.
These involve shellfish cultivation, seaweed ...
Minimum pricing for alcohol helped curb demand during COVID lockdown
2024-06-06
Minimum pricing can be very effective in reducing demand for cheap high-strength alcohol amid concerns about affordability fuelling problematic drinking - according to a study on the impact of the measure during the COVID lockdown.
The research, led by the University of East Anglia (UEA), examined the efficacy of minimum unit pricing (MUP) to help curb excessive consumption following the outbreak of the pandemic in 2020.
As a flat-rate form of minimum prices applying to all alcohol products based on their ...
New home-administered treatment for binge eating disorder shows promising results
2024-06-06
Researchers from the Institute of Psychiatry, Psychology & Neuroscience (IoPPN) at King’s College London have investigated the feasibility of a new home-administered treatment for binge eating disorder. The new treatment combines a gentle brain stimulation technique called transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) with a training programme that targets unhelpful patterns of attention around food.
The findings, published in BJPsychOpen, indicate that this might be a welcome new avenue for treatment.
Binge eating disorder (BED) is a serious mental illness that can affect anyone of any age, gender, ethnicity or background. People ...
Nuclear medicine highlighted in documentary series
2024-06-06
Reston, VA—The field of nuclear medicine is in the spotlight this season on the TV documentary Jobs of Tomorrow. The series, hosted by Kristin Marand, explores how technology and innovation drive the changing job market and impact the workforce.
Six episodes of this season of Jobs of Tomorrow highlight the many facets of nuclear medicine and the Society for Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging (SNMMI) members currently working in the profession.
Nuclear medicine is a multidisciplinary field that encompasses physicians, chemists, physicists, pharmacists, and technologists—all ...
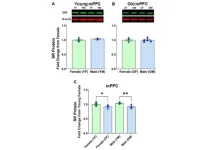
Serine racemase expression in the brain during aging in male and female rats
2024-06-05
“The findings of the present study reveal that aging is linked to a decline in serine racemase protein levels across various brain regions [...]”
BUFFALO, NY- June 5, 2024 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 16, Issue 10, entitled, “Serine racemase expression profile in the prefrontal cortex and hippocampal subregions during aging in male and female rats.”
Aging is associated with a decrease in N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor ...
Virginia Tech researcher helps reach nutrition security goals
2024-06-05
Food is many things.
It nourishes our bodies, delights our senses, and gives us something to gather around. Food is also a powerful cultural symbol, reflecting traditions, values, and histories of communities around the world.
But for a researcher in the College of Agriculture and Life Sciences, food is also medicine.
Bailey Houghtaling Ph.D. ’19, a registered dietician, is working to promote overall wellness among low-income individuals experiencing food insecurity, aiming to prevent or treat diet-related diseases.
“Access to enough nutritious food is essential for individual well-being,” ...