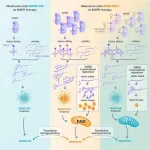
(Press-News.org) An international research team led by scientists from the University of Liège has discovered an interesting new therapeutic target for the treatment of melanoma resistant to targeted therapies. Inhibition of the VARS enzyme could prevent this therapeutic resistance by resensitising tumours resistant to these targeted therapies.
Melanoma is one of the most serious and aggressive forms of skin cancer. When diagnosed early, melanoma is surgically removed. However, once metastases (i.e. secondary distant tumours) have developed, melanoma becomes difficult to treat, limiting patients' chances of recovery . Every year in Belgium, around 3,000 people are diagnosed with melanoma. Doctors use targeted therapies* to treat skin melanoma patients with a mutation in the BRAF gene - the gene responsible for producing B-Raf, the protein that promotes the development of cancer. This mutation is found in over 50% of patients," explains Pierre Close, researcher at the University of Liège. While targeted therapies are highly effective in shrinking tumours, almost all patients who use them will develop acquired or secondary resistance to these therapies, which limits the long-term therapeutic response". It is therefore crucial to understand the mechanisms involved in resistance to targeted therapies in order to develop new therapeutic strategies for melanoma patients.
ARNt and VARS
The team from the Cancer Signalling Laboratory (ULiège) has just made a very interesting discovery in this field. Thanks to the analysis of the data collected, we were able to observe that the adaptation of melanoma cells to targeted therapy was associated with a reprogramming of protein synthesis," explains Najla El Hachem, a researcher from the Belgian Foundation against Cancer. "We combined a number of protein and RNA sequencing approaches and discovered that therapy-resistant cells developed a dependence on certain essential players in protein synthesis, regulating transfer RNAs (tRNAs)." These players include the enzyme VARS (Valyl tRNA synthetase), which regulates aminoacylation - the process by which an amino acid attaches to tRNA - of transfer RNAs and promotes resistance in melanoma cells. Genetic inhibition of VARS therefore prevents therapeutic resistance and resensitises tumours resistant to targeted therapies.
New hope for patients
The promising results of this research pave the way for new treatment combinations for malignant melanoma. This discovery shows that the regulation of transfer RNAs plays an important role in therapeutic resistance," enthuses Pierre Close. In addition, inhibition of VARS could enhance the efficacy of targeted therapies and limit the development of resistance to treatment. These results could lead to the development of new therapeutic strategies and offer a new ray of hope for patients suffering from resistant melanoma. The researchers will be continuing their work to transform this discovery into a concrete and effective therapeutic option.
* Targeted therapies are new forms of cancer treatment that exploit the biological differences between cancer cells and healthy cells in the body.
END
Transfer RNAs at the heart of therapeutic resistance
Researchers discover a new therapeutic target for the treatment of melanoma resistant to targeted therapies
2024-06-07
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Brain circuits underlying learning from negative experiences
2024-06-07
‘I’m not gonna do this again’, we often say when faced with negative feedback, adverse effects, or disappointing outcomes. Thus, we attempt to learn from such negative experiences. This principle is also a cornerstone of our education system: failing an exam ought to encourage students to do better next time.
How does the brain achieve this type of learning? Positive and negative reinforcement appear as two sides of the same coin in parts of the brain’s valuation system. Notably, some neurons that release the neuromodulator ‘dopamine’ represent outcomes better vs. worse ...
What’s going on in our brains when we plan?
2024-06-07
In pausing to think before making an important decision, we may imagine the potential outcomes of different choices we could make. While this “mental simulation” is central to how we plan and make decisions in everyday life, how the brain works to accomplish this is not well understood.
An international team of scientists has now uncovered neural mechanisms used in planning. Its results, published in the journal Nature Neuroscience, suggest that an interplay between the brain’s prefrontal cortex and hippocampus allows us to imagine future outcomes in order to guide our decisions.
“The prefrontal cortex acts as a ‘simulator,’ ...
Robotic device restores wavelike muscular function involved in processes like digestion, aiding patients with compromised organs
2024-06-07
A team of Vanderbilt researchers has developed a wirelessly activated device that mimics the wavelike muscular function in the esophagus and small intestine responsible for transporting food and viscous fluids for digestion.
The soft-robotic prototype, which is driven by strong magnets controlled by a wearable external actuator, can aid patients suffering from blockages caused by tumors or those requiring stents. For example, traditional esophageal stents are metal tubes used in patients with esophageal cancer, mostly in an aging population. These patients risk food being blocked from entering the stomach, potentially ...
DOE announces new decadal fusion energy strategy
2024-06-07
WASHINGTON, D.C.—The U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) today marked the two-year anniversary of the Biden-Harris Administration's launch of the U.S. Bold Decadal Vision for Commercial Fusion Energy with the release of the DOE Fusion Energy Strategy 2024 and an event at the White House co-hosted by the White House Office of Science and Technology Policy.
At the inaugural event where the Bold Decadal Vision was unveiled, DOE launched a Department-wide initiative to develop a strategy for accelerating the viability of commercial fusion energy in partnership with the private sector. The newly released DOE Fusion Energy ...
Study identifies potential pathway to reducing breast cancer brain metastases
2024-06-07
A study led by researchers from the University of Arizona Cancer Center at UArizona Health Sciences identified a biological mechanism that could lead to more effective treatments for breast cancer that has metastasized to the brain.
By studying the metabolic differences between primary breast cancer cells and those that metastasize to the brain, they determined that autophagy was significantly upregulated in brain metastases. Autophagy is a cellular recycling process that cancer cells can use to stay alive when faced with stressful conditions such as those triggered by anticancer drugs.
“The prognosis for individuals with ...
How does oxygen depletion disrupt memory formation in the brain?
2024-06-07
When we learn something new, our brain cells (neurons) communicate with each other through electrical and chemical signals. If the same group of neurons communicate together often, the connections between them get stronger. This process helps our brains learn and remember things and is known as long-term potentiation or LTP.
Another type of LTP occurs when the brain is deprived of oxygen temporarily – anoxia-induced long-term potentiationor aLTP. aLTP blocks the former process, thereby impairing learning and ...
Study investigates relationship between phthalate exposure and high blood pressure, related complications during pregnancy
2024-06-07
Higher exposure to certain chemicals called phthalates is linked to an increased risk of pregnancy complications, including preeclampsia and eclampsia (PE/E) and other hypertensive or high blood pressure disorders, according to a study funded by the NIH Environmental influences on Child Health Outcomes program. Here are the key findings:
Doubling the levels of a specific molecule linked to exposure to phthalates found in PVC plastics and insect repellents—mono (3-carboxypropyl) phthalate (MCPP)—increased ...
YALE NEWS: Study finds no association between COVID-19 vaccines and stillbirths
2024-06-07
New Haven, Conn. — In a new study funded by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, researchers from Yale and 11 other institutions found “no association between COVID-19 vaccination and stillbirth.”
In a case-control study led by Yale School of Medicine’s Dr. Anna Denoble, researchers compared 276 stillbirths with 822 live births during a one-year period from February 2021 to February 2022. Their results, published June 6 in the journal Obstetrics & Gynecology, found no linkage between pregnant individuals ...
University of South Florida using AI to help combat malaria in Africa
2024-06-06
Media Contact:
John Dudley
(814) 490-3290 (cell)
jjdudley@usf.edu
TAMPA, Fla. (June 6, 2024) – University of South Florida researchers are using artificial intelligence to revolutionize mosquito surveillance to help combat malaria in Africa. Ryan Carney, professor of integrative biology, and Sriram Chellappan, professor in the department of computer science and engineering, will collaborate with an interdisciplinary team of researchers to advance malaria research and explore innovative solutions ...
Webb finds plethora of carbon molecules around young star
2024-06-06
An international team of astronomers has used NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope to study the disk of gas and dust around a young, very low-mass star. The results reveal the largest number of carbon-containing molecules seen to date in such a disk. These findings have implications for the potential composition of any planets that might form around this star.
Rocky planets are more likely than gas giants to form around low-mass stars, making them the most common planets around the most common stars in our galaxy. Little is known about the chemistry of such worlds, which may be similar to or very different from Earth. By studying the disks from which such planets form, astronomers hope ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Concrete sensor manufacturer Wavelogix receives $500,000 grant from National Science Foundation
California communities’ recovery time between wildfire smoke events is shrinking
Augmented reality job coaching boosts performance by 79% for people with disabilities
Medical debt associated with deferring dental, medical, and mental health care
AAI appoints Anand Balasubramani as Chief Scientific Programs Officer
Prior authorization may hinder access to lifesaving heart failure medications
Scholars propose transparency, credit and accountability as key principles in scientific authorship guidelines
Jeonbuk National University researchers develop DDINet for accurate and scalable drug-drug interaction prediction
IEEE researchers achieve 20x signal boost in cerebral blood flow monitoring with next-generation interferometric diffusing wave spectroscopy
IEEE researchers achieve low-power ultrashort mid-IR pulse compression
Deep-sea natural compound targets cancer cells through a dual mechanism
Antibiotics can affect the gut microbiome for several years
Study: Electrical stimulation can restore ability to move limbs, receive sensory feedback after spinal cord injury
Rice scientists unveil new tool to watch quantum behavior in action
Gene-based therapies poised for major upgrade thanks to Oregon State University research
Extreme heat has extreme effects r—but some like it hot
Blood marker for Alzheimer’s may also be useful in heart and kidney diseases
Climate extremes hinder early development in young birds
Climate policies: The swing voters that determine their fate
Building protection against infectious diseases with nanostructured vaccines
Oval orbit casts new light on black hole - neutron star mergers
Does online sports gambling affect substance use behaviors?
How do rapid socio-environmental transitions reshape cancer risk?
Do abortion bans affect birth rates and food-assistance costs?
Can artificial intelligence help reduce the carbon footprint of weather forecasting models?
Mangrove forests are short of breath
Low testosterone, high fructose: A recipe for liver disaster
SKKU research team unravels the origin of stochasticity, a key to next-generation data security and computing
Flexible polymer‑based electronics for human health monitoring: A safety‑level‑oriented review of materials and applications
Could ultrasound help save hedgehogs?
[Press-News.org] Transfer RNAs at the heart of therapeutic resistanceResearchers discover a new therapeutic target for the treatment of melanoma resistant to targeted therapies