(Press-News.org) PITTSBURGH – If national guidelines are revised to incorporate a new risk equation, about 40% fewer people could meet criteria for cholesterol-lowering statins to prevent heart disease, according to a study by researchers at the University of Pittsburgh, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and University of Michigan. Published today in JAMA Internal Medicine, the study examines the potential impact of widespread adoption of the PREVENT equations, which were released by the American Heart Association in November 2023 to update physicians’ go-to calculators for assessing patients’ 10-year risk of heart attack or stroke.
At a population level, the number of adults recommended for statins could decrease from 45.4 million to 28.3 million. At the same time, the study showed that most people who would be recommended to take statins are not currently taking them.
“This is an opportunity to refocus our efforts and invest resources in the populations of patients at the highest risk,” said lead author Dr. Timothy Anderson, M.D., M.A.S., a primary care physician at UPMC and health services researcher and assistant professor of medicine at Pitt.
For their analysis, the team used nationally representative data from 3,785 adults, ages 40 to 75, who participated in the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey from January 2017 to March 2020. The researchers estimated 10-year risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) using the Predicting Risk of cardiovascular disease EVENTs (PREVENT) equations and compared the results to risk estimated using the previous tool, known as Pooled Cohort Equations (PCE). The PREVENT equations were developed by the American Heart Association to more accurately represent risk across the current U.S. population, as the PCE equations were based on patient data that were decades old and lacked diversity.
PREVENT also reflects more recent insights into the biology of ASCVD. Current statin use as well as metabolic and kidney diseases are incorporated into the new calculation, while race has been removed from it, reflecting a growing awareness that race is a social construct.
Using PREVENT, the team found that among the study’s entire cohort, 10-year risk of developing ASCVD was 4%, half as high as the risk calculated by the PCE (8%). The difference was even larger for Black adults (5.1% versus 10.9%) and for adults between the ages of 70 and 75 (10.2% versus 22.8%).
An estimated 4.1 million patients who are currently taking statins would no longer be recommended to take them based on PREVENT. For these patients and their physicians, clear and careful communication is key, said Anderson. “We don’t want people to think they were treated incorrectly in the past. They were treated with the best data we had when the PCE was introduced back in 2013. The data have changed.”
At the same time, it’s important to note that everyone’s risk will inevitably change over time, as well, he added. “For a patient who we now know is at lower risk than we previously thought, if we recommend they stop taking statins, they still could be back to a higher risk five years down the road, for the simple reason that everybody’s risk goes up as we get older.”
Other authors on the study were Linnea Wilson, M.P.H., of Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, and Jeremy B. Sussman, M.D., M.P.H., of University of Michigan, Ann Arbor.
This research was supported by the National Institute on Aging (#K76AG074878).
END
Statins for heart disease prevention could be recommended for far fewer Americans if new risk equation is adopted
2024-06-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Multicenter clinical study supports safety of deep general anesthesia
2024-06-10
General anesthesia makes it possible for millions of patients each year to undergo lifesaving surgeries while unconscious and free of pain. But the 176-year-old medical staple uses powerful drugs that have stoked fears of adverse effects on the brain — particularly if used in high doses.
New findings published June 10 in the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA), however, support an earlier study that indicates that anesthesia is no more hazardous for the brain at higher doses than at lower doses, ...
Cancer incidence trends in successive social generations in the US
2024-06-10
About The Study: In this model-based cohort analysis of incident invasive cancer in the general population, decreases in lung and cervical cancers in Generation X may be offset by gains at other sites. Generation X may be experiencing larger per-capita increases in the incidence of leading cancers than any prior generation born in 1908 through 1964. On current trajectories, cancer incidence could remain high for decades.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Philip S. Rosenberg, Ph.D., email rosenbep@mail.nih.gov.
To access the embargoed study: Visit ...
Global prevalence of overweight and obesity in children and adolescents
2024-06-10
About The Study: This study’s findings indicated 1 of 5 children or adolescents experienced excess weight and that rates of excess weight varied by regional income and Human Development Index. Excess weight among children and adolescents was associated with a mix of inherent, behavioral, environmental, and sociocultural influences that need the attention and committed intervention of primary care professionals, clinicians, health authorities, and the general public.
Corresponding Author: To ...
Severe pediatric neurological manifestations with SARS-CoV-2 or MIS-C hospitalization and new morbidity
2024-06-10
About The Study: The results of this study suggest that children and adolescents with acute SARS-CoV-2 or multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C) and severe neurological manifestations may be at high risk for long-term impairment and may benefit from screening and early intervention to assist recovery.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Ericka L. Fink, M.D., M.S., email finkel@ccm.upmc.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.14122)
Editor’s ...
Elephants have names for each other like people do, new study shows
2024-06-10
Colorado State University scientists have called elephants by their names, and the elephants called back.
Wild African elephants address each other with name-like calls, a rare ability among nonhuman animals, according to a new study published in Nature Ecology and Evolution.
Researchers from CSU, Save the Elephants and ElephantVoices used machine learning to confirm that elephant calls contained a name-like component identifying the intended recipient, a behavior they suspected based on observation. When the researchers played back recorded calls, elephants responded affirmatively ...
In a significant first, researchers detect water frost on solar system’s tallest volcanoes
2024-06-10
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — An international team of planetary scientists has detected patches of water frost sitting atop the Tharsis volcanoes on Mars, which are not only the tallest volcanic mountains on the Red Planet but in the entire solar system.
The discovery marks the first time frost has been spotted near the planet’s equator, challenging existing perceptions of the planet’s climate dynamics, according to the team’s new study in Nature Geoscience.
“We thought it was improbable for frost to form around Mars’ equator, as the mix ...
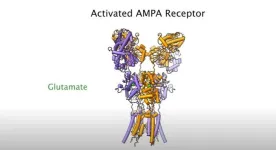
Super-chilled brain cell molecules reveal how epilepsy drug works
2024-06-10
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
By super cooling a molecule on the surface of brain cells down to about minus 180 degrees Celsius — nearly twice as cold as the coldest places in Antarctica — scientists at Johns Hopkins Medicine say they have determined how a widely-used epilepsy drug works to dampen the excitability of brain cells and help to control, although not cure, seizures.
The research, published June 4 in Nature Structural & Molecular Biology, identifies critical connections between activity of the epilepsy drug ...
Benefits of failure are overrated
2024-06-10
The platitude that failure leads to success may be both inaccurate and damaging to society, according to research published by the American Psychological Association.
Researchers conducted 11 experiments with more than 1,800 participants across many domains and compared national statistics to the participants’ responses. In one experiment, participants vastly overestimated the percentage of prospective nurses, lawyers and teachers who pass licensing exams after previously failing them.
“People expect success to follow failure much more often than it actually does,” said lead researcher Lauren Eskreis-Winkler, PhD, an assistant ...
NUTRITION 2024 showcases groundbreaking research on what we eat and why it matters
2024-06-10
Don’t miss your chance to be among the first to hear breaking news in food and nutrition science at NUTRITION 2024. The annual flagship meeting of the American Society for Nutrition will be held June 29–July 2 at McCormick Place in Chicago.
Reporters and bloggers are invited to explore the meeting schedule and register for a complimentary press pass to attend.
The meeting will feature stimulating discussions, exciting research announcements and updates from groups shaping the nutrition and health policies that affect us all. Highlights include:
Diet and exercise performance – As the ...
Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai awarded $21 million NIH grant to advance understanding of aging-related hormone
2024-06-10
New York, NY [June 10, 2024]—Researchers at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai have been awarded a $21 million grant from the National Institute on Aging (NIA) of the National Institutes of Health (NIH), to further advance understanding of an aging-related hormone known as follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), including its potential role in obesity, osteoporosis, and Alzheimer’s disease. The work could lead to the development of new treatments for these and other conditions involving aging.
This is a collaborative ...