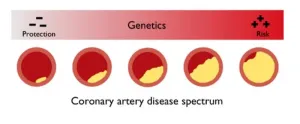
The discoveries, detailed in the June 11 online issue of Nature Genetics [DOI: 10.1038/s41588-024-01791-x], reveal genetic factors impacting heart disease that open new avenues for targeted treatments and personalized approaches to cardiovascular care.
The investigators used an in silico, or computer-derived, score for coronary artery disease (ISCAD) that holistically represents CAD, as described in a previous paper by the team in The Lancet. The ISCAD score incorporates hundreds of different clinical features from the electronic health record, including vital signs, laboratory test results, medications, symptoms, and diagnoses. To build the score, they trained machine learning models on the electronic health records of 604,914 individuals across the UK Biobank, All of Us Research Program, and BioMe Biobank in this comprehensive meta-analysis.
The score was then tested for association with rare and ultra-rare coding variants found in the exome sequences of these individuals. In addition, the research team conducted further investigation into the discovered genes to study their roles in causal CAD risk factors, clinical manifestations of CAD, and their connections with CAD status in traditional large-scale genome-wide association studies, among other factors.
“Our findings help us understand how these 17 genes are involved in coronary artery disease. Some of these genes are already known to influence heart disease development, while others have never been linked to it before,” says Ron Do, PhD, senior study author and the Charles Bronfman Professor in Personalized Medicine at Icahn Mount Sinai. “Our study shows how machine learning tools can uncover genetic insights that traditional methods might miss when comparing cases and controls. This could lead to new ways to identify biological mechanisms of heart disease or gene targets for treatment.”
Because they occur in only a small percentage of individuals, rare coding variants may have a significant impact on disease risk or susceptibility when present. Therefore, studying these variants is essential to understanding the genetic basis of diseases and can inform therapeutic targets.
The study was driven by the challenges faced, over the last decade, in identifying rare coding variants associated with CAD using traditional methods relying on diagnosed cases and controls. Diagnostic codes' limitations in capturing the complexity of CAD prompted the researchers to explore new avenues of investigation.
"Our previous Lancet paper showed that a machine learning model trained with electronic health records can generate an in silico score for coronary artery disease, capturing disease across its spectrum," says lead author Ben Omega Petrazzini, BS, Associate Bioinformatician in Dr. Do's lab at Icahn Mount Sinai. "Based on these findings, we hypothesized that the in-silico score for CAD could reveal novel rare coding variants related to CAD by offering a more holistic view of the disease.”
Next, the investigators plan to further investigate the role of the identified genes in CAD biology and explore potential applications of machine learning in the genetic study of other complex diseases, as part of their ongoing efforts to advance understanding of disease mechanisms, discover new treatments, and improve patient outcomes.
The paper is titled “Exome sequence analysis identifies rare coding variants associated with a machine learning-based marker for coronary artery disease.”
The remaining authors of the paper, all with Icahn Mount Sinai except where indicated, are:
Iain S. Forrest, PhD (MD candidate); Ghislain Rocheleau, PhD; Ha My T. Vy, PhD; Carla Márquez-Luna, PhD; Áine Duffy, MS (PhD candidate); Robert Chen, MS (MD/PhD candidate); Joshua K. Park, BS (MD/PhD candidate); Kyle Gibson, BA (MD candidate); Sascha N. Goonewardena, MD (University of Michigan); Waqas A. Malick, MD; Robert S. Rosenson, MD; and Daniel M. Jordan, PhD.
Please see [DOI: 10.1038/s41588-024-01791-x] to view more details on the paper and competing interests.
The study was made possible by funding from the National Institutes of Health: National Institute of General Medical Sciences (R35-GM124836); National Institute of Aging (R01 AG061186-0); the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (R01HL157439, R01-HL139865, R01-HL155915); and by VA MERIT grant 1I01CX002560.
-####-
About the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai
The Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai is internationally renowned for its outstanding research, educational, and clinical care programs. It is the sole academic partner for the eight- member hospitals* of the Mount Sinai Health System, one of the largest academic health systems in the United States, providing care to a large and diverse patient population.
Ranked 13th nationwide in National Institutes of Health (NIH) funding and among the 99th percentile in research dollars per investigator according to the Association of American Medical Colleges, Icahn Mount Sinai has a talented, productive, and successful faculty. More than 3,000 full-time scientists, educators, and clinicians work within and across 44 academic departments and 36 multidisciplinary institutes, a structure that facilitates tremendous collaboration and synergy. Our emphasis on translational research and therapeutics is evident in such diverse areas as genomics/big data, virology, neuroscience, cardiology, geriatrics, as well as gastrointestinal and liver diseases.
Icahn Mount Sinai offers highly competitive MD, PhD, and Master’s degree programs, with current enrollment of approximately 1,300 students. It has the largest graduate medical education program in the country, with more than 2,000 clinical residents and fellows training throughout the Health System. In addition, more than 550 postdoctoral research fellows are in training within the Health System.
A culture of innovation and discovery permeates every Icahn Mount Sinai program. Mount Sinai’s technology transfer office, one of the largest in the country, partners with faculty and trainees to pursue optimal commercialization of intellectual property to ensure that Mount Sinai discoveries and innovations translate into healthcare products and services that benefit the public.
Icahn Mount Sinai’s commitment to breakthrough science and clinical care is enhanced by academic affiliations that supplement and complement the School’s programs.
Through the Mount Sinai Innovation Partners (MSIP), the Health System facilitates the real-world application and commercialization of medical breakthroughs made at Mount Sinai. Additionally, MSIP develops research partnerships with industry leaders such as Merck & Co., AstraZeneca, Novo Nordisk, and others.
The Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai is located in New York City on the border between the Upper East Side and East Harlem, and classroom teaching takes place on a campus facing Central Park. Icahn Mount Sinai’s location offers many opportunities to interact with and care for diverse communities. Learning extends well beyond the borders of our physical campus, to the eight hospitals of the Mount Sinai Health System, our academic affiliates, and globally.
-------------------------------------------------------
* Mount Sinai Health System member hospitals: The Mount Sinai Hospital; Mount Sinai Beth Israel; Mount Sinai Brooklyn; Mount Sinai Morningside; Mount Sinai Queens; Mount Sinai South Nassau; Mount Sinai West; and New York Eye and Ear Infirmary of Mount Sinai.
END