(Press-News.org) Including “tactile emoticons” into social media communications can enhance communication, according to a study published June 12, 2024 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Alkistis Saramandi and Yee Ki Au from University College London, United Kingdom, and colleagues.
Digital communications rely exclusively on visual and auditory cues (text, emoticons, videos, and music) to convey tone and emotion. Currently lacking from these platforms is touch, which can convey feelings of love and support, impact emotions, and influence behaviors. Technology companies are developing devices to incorporate touch into digital interactions, such as interactive kiss and hug transmission devices. These social touch devices can elicit feelings of closeness and positive emotions, but the effect of touch in social media communication is not well studied.
In this study, researchers incorporated tactile emoticons into social media interactions. Using a mock social media platform, participants were given posts to send that expressed either positive or negative emotions. They then received feedback via visual emoticons (e.g., a heart or thumbs up), tactile emoticons (a stroke on the forearm by either another person or a robotic device), or both.
Participants felt greater feelings of support and approval when they received the tactile emoticons compared to the visual-only feedback. This suggests that social touch, even by a stranger, can convey meaning without any other accompanying communication. Feedback consisting of both visual and tactile emoticons was preferred over either type of emoticon alone. The researchers noted that touch could offer additional context to visual emoticons, which can be misinterpreted. They also found that the type of touch matters. Touch delivered at a speed that activates the C-Tactile nervous system, which produces positive emotions associated with touching or embracing, was experienced more favorably than other types of touch.
According to the authors, this is the first study to explore the role of touch in communicating emotions via social media. They hope that the results can inform the development of devices to deliver touch during digital communications.
The authors add: “Touch has long been essential to human bonding and survival, yet in our digitized world we are more isolated and touch-deprived than ever. What if we could use 'digitalized touch' to bring us closer in communicating emotions in today's world?”
#####
In your coverage please use this URL to provide access to the freely available article in PLOS ONE: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0304417
Citation: Saramandi A, Au YK, Koukoutsakis A, Zheng CY, Godwin A, Bianchi-Berthouze N, et al. (2024) Tactile emoticons: Conveying social emotions and intentions with manual and robotic tactile feedback during social media communications. PLoS ONE 19(6): e0304417. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0304417
Author Countries: UK, Sweden, Australia
Funding: This work was undertaken with funding from the UCL Social Science+ award (to CJ, NB and AF; https://www.ucl.ac.uk/research/domains/collaborative-social-science/research/social-science-plus), and in part with funding from the European Research Council (ERC) Starting Grant ERC-2012-STG GA313755 (to AF; https://erc.europa.eu/apply-grant/starting-grant), and the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under grant agreement No. 818070, for the Consolidator Award METABODY (to AF; https://erc.europa.eu/apply-grant/consolidator-grant). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
END
Incorporating “touch” into social media interactions can increase feelings of support and approval
Responses to social media posts that included both visual and tactile feedback were most effective
2024-06-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
The gender gap in life expectancy: are eggs and sperm partly responsible?
2024-06-12
Osaka, Japan – Women live longer than men. This isn’t unique to humans, either; we see this trend in a wide range of other animals. Biologists have theorized that the discrepancy in life expectancy between sexes might be partly related to reproduction, but how?
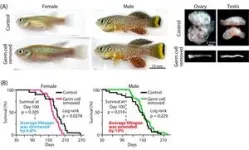
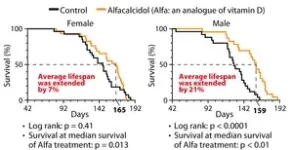
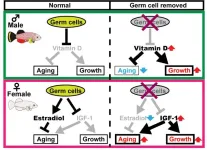
In a study published in Science Advances, researchers from Osaka University have discovered for the first time that germ cells, the cells that develop into eggs in females and sperm in males, drive sex-dependent lifespan differences in vertebrate animals.
The researchers ...
Swimming microrobots deliver cancer-fighting drugs to metastatic lung tumors in mice
2024-06-12
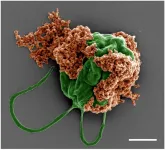
Engineers at the University of California San Diego have developed microscopic robots, known as microrobots, capable of swimming through the lungs to deliver cancer-fighting medication directly to metastatic tumors. This approach has shown promise in mice, where it inhibited the growth and spread of tumors that had metastasized to the lungs, thereby boosting survival rates compared to control treatments.
The findings are detailed in a paper published on June 12 in Science Advances.
The microrobots are an ingenious combination of biology ...
Ambivalence + polarized views can promote political violence
2024-06-12
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Feeling ambivalent about a political issue might seem to be a recipe for indecision and even inaction.
But a new study suggests, surprisingly, that ambivalence can actually lead some people –especially those with polarized views – to be more supportive of extreme actions, such as violence.
The reason? Researchers found that ambivalence creates discomfort in those with extreme views by making them feel weak or insecure about their beliefs – and that can lead them to compensate for that weakness by supporting extreme actions to signal strength.
“When people have ...
Unleashing the power of metamaterials to improve MRI imaging
2024-06-12
In recent years, the field of metamaterials has experienced substantial growth, revealing exciting potential, especially in advancing magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) technology. Three new studies led by Dr. Xin Zhang, a BU College of Engineering Distinguished Professor and a professor at the BU Photonics Center, highlight the promising opportunities within this field. These studies, in collaboration with Dr. Stephan Anderson, a BU Chobanian & Avedisian School of Medicine professor of radiology, published in Advanced Science, Advanced Materials, and Science Advances, showcase innovative approaches to enhance the MRI experience for all patients. ...
USC EdTech Accelerator collaborates with Intel
2024-06-12
USC Rossier Education Technology Accelerator (USC EdTech Accelerator) announced a unique collaboration with Intel Corporation focused on supporting the use of technology for learning with a particular emphasis on supporting marginalized communities and AI.
The Partnership
The USC EdTech collaboration with Intel will provide free educational and technical assistance to learning-focused start-ups to increase the likelihood that they design viable, efficacious and scalable AI-enhanced solutions for learners. “We believe ...
What is the neural mechanism behind helping someone at your own cost?
2024-06-12
Using a unique setup, researchers from the Social Brain Lab at the Netherlands Institute for Neuroscience have researched the neural mechanism behind a universal dilemma: deciding whether to help someone else even when it involves a personal sacrifice.
We often have opportunities to give up something we care about to help others. What brain mechanisms help us make those decisions, and why do some people help more than others?
Over the years, philosophers and scientists have suggested that the extent to which a person empathizes with the distress of others influences their willingness to help.
To explore this hypothesis experimentally, Kalliopi ...
Can we withdraw treatment in post-menopausal osteoporosis?
2024-06-12
Osteoporosis is characterised by low bone mineral density and bone fragility.5 During menopause, falling oestrogen levels impair normal bone turnover, with an average reduction in bone mineral density of 10%.5 This is compounded by the age-related bone loss that occurs in both men and women. With an ageing population, post-menopausal osteoporosis represents a growing health problem.
These new data are from a case-control cohort study of over 128,000 women included in the French national claim database. The main aim was to estimate the incidence of long-term discontinuation of bisphosphonates – ...
Vexas: towards molecular and phenotypic characterization
2024-06-12
VEXAS is characterised by predominantly rheumatic and haematologic systemic involvement, and caused by somatic mutation in UBA1 – a gene encoding ubiquitin-activating enzyme 1,1,2 which is necessary for a post-translation modification that affects protein functions ranging from degradation to subcellular localisation and kinase activation.3 The syndrome was first described in 2020, but diagnosis can be challenging as the symptoms overlap with many other inflammatory conditions.1 Hot on the heels of this recent discovery, research is underway to better understand pathogenesis, clinical features, and potential treatment options.1
To support this, ...
Location, location, location – does it matter in psoriatic arthritis?
2024-06-12
Arthritis affects various joints differently, despite systemic inflammatory cues.2 In people with rheumatoid arthritis, transcriptomic variances identified in synovial fibroblasts from various joint sites have been shown to translate into joint-specific phenotypes with distinct characteristics and responsiveness to cytokines.2,3 These findings suggest that different joints may potentially respond variably to specific immunosuppressive treatments. To expand on this, Ciurea and colleagues set out to investigate whether joints at different anatomical locations in people with PsA might respond differently to treatment with a tumour necrosis ...
Stopping the march
2024-06-12
The estimated prevalence of psoriatic arthritis (PsA) in people with psoriasis ranges widely –between 6% and 42% – but in most cases, skin symptoms precede PsA, thus making skin psoriasis a model for pre-PsA.2 Assuming that there are shared pathways in the pathogenesis, it is possible that stringent treatment of moderate-to-severe psoriasis could reduce progression to clinically overt PsA.3,4 Biologic treatments are effective at controlling psoriasis, but there are no conclusive data that these treatments help prevent people from developing PsA. Several risk factors for transition have previously been identified by a EULAR taskforce.5 ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Researchers determine structural motifs of water undecamer cluster
Researchers enhance photocatalytic hydrogen evolution performance of covalent organic frameworks by constitutional isomer strategy
Molecular target drives immunogenicity in cancer immunotherapy
Plant cell structure could hold key to cancer therapies and improved crops
Sustainable hydrogen peroxide production: Breakthroughs in electrocatalyst design for on-site synthesis
Cash rewards for behavior change: A review of financial incentives science in one health contexts and implications
One Health antimicrobial resistance modelling: from science to policy
Artificial feeding platform transforms study of ticks and their diseases
Researchers uncover microscopic mechanism of alkali species dissolution in water clusters
Methionine restriction for cancer therapy: A comprehensive review of mechanisms and clinical applications
White House autism briefing linked to swift shifts in prescribing patterns, study finds
Specialist palliative care can save the NHS up to £8,000 per person and improves quality of life
New research warns charities against ‘AI shortcut’ to empathy
Cannabis compounds show promise in fighting fatty liver disease
Study in mice reveals the brain circuits behind why we help others
Online forum to explore how organic carbon amendments can improve soil health while storing carbon
Turning agricultural plastic waste into valuable chemicals with biochar catalysts
Hidden viral networks in soil microplastics may shape the future of sustainable agriculture
Americans don’t just fear driverless cars will crash — they fear mass job losses
Mayo Clinic researchers find combination therapy reduces effects of ‘zombie cells’ in diabetic kidney disease
Preventing breast cancer resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors using genomic findings
Carbon nanotube fiber ‘textile’ heaters could help industry electrify high-temperature gas heating
Improving your biological age gap is associated with better brain health
Learning makes brain cells work together, not apart
Engineers improve infrared devices using century-old materials
Physicists mathematically create the first ‘ideal glass’
Microbe exposure may not protect against developing allergic disease
Forest damage in Europe to rise by around 20% by 2100 even if warming is limited to 2°C
Rapid population growth helped koala’s recovery from severe genetic bottleneck
CAR-expressing astrocytes target and clear amyloid-β in mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease
[Press-News.org] Incorporating “touch” into social media interactions can increase feelings of support and approvalResponses to social media posts that included both visual and tactile feedback were most effective