Low-sodium alternatives can lead to major health gains in Indonesia
Excess sodium intake and a lack of potassium are major contributing factors towards high blood pressure in Indonesia, prompting calls for low-sodium potassium-rich salt substitutes (LSSS) to be readily available to improve health and curb health costs.
2024-06-14
(Press-News.org)
Excess sodium intake and a lack of potassium are major contributing factors towards high blood pressure in Indonesia, prompting calls for low-sodium potassium-rich salt substitutes (LSSS) to be readily available to improve health and curb health costs.
New Griffith University research has looked at the impact of switching out current table salt (100 per cent sodium chloride) with a low-sodium alternative in Indonesia.
Lead author Dr Leopold Aminde from the School of Medicine and Dentistry said the World Health Organisation has recommended a population-wide reduction in sodium consumption to tackle the burden of high blood pressure and non-communicable diseases.
“LSSS look similar to table salt and research shows they have a similar taste with some consumers unable to differentiate between the two options,” Dr Aminde said.
“The research shows that making LSSS available would have a positive impact on the Indonesian health system by reducing blood pressure, and preventing heart attacks, strokes, and kidney disease.
“Ultimately it would reduce health expenditure by up to US$2 billion [IDR 27.7 trillion] over 10 years, providing a much-needed cost-saving measure.”
Dr. Wahyu Nugraheni, co-author and Head of the Research Centre for Public Health and Nutrition at the National Research and Innovation Agency in Jakarta said: “Indonesians consume more sodium than is physiologically required.”
“LSSS are an excellent option to help people effortlessly reduce the sodium in their diet,” Dr Nugraheni said.
Over the first 10 years of implementation, LSSS could prevent up to 1.5 million non-fatal cardiovascular disease events and more than 640,000 new cases of chronic kidney disease.
“The greatest health benefits will likely be seen in the low-income bracket of the population,” Dr Aminde said.
The research team is hoping the findings will prompt the government in Indonesia, and other countries globally, to consider reformulation of regular salt to LSSS alternatives, or facilitate supply chains to expand their availability and affordability.
The research findings will inform the upcoming WHO guidelines on the evidence gaps related to implementation costs, cost-effectiveness, and the possible impacts on health inequalities.
The paper ‘Cost-effectiveness analysis of low-sodium potassium-rich salt substitutes in Indonesia: an equity modelling study’ has been published in The Lancet Regional Health – Southeast Asia.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-06-14
Background
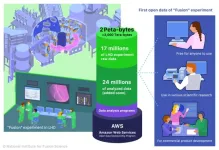
High-temperature fusion plasma experiments conducted in the Large Helical Device (LHD) of the National Institute for Fusion Science (NIFS), have renewed the world record for an acquired data amount, 0.92 terabytes (TB) per experiment, in February 2022, by using a full range of state-of-the-art plasma diagnostic devices*1. The International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor (ITER), which is currently under construction in France through the international collaboration of seven parties, is expected to generate ...
2024-06-14
EMBARGOED for release until 1pm U.S. Central Time (2pm Eastern) on June 13, 2024
HOUSTON – (June 13, 2024) – Solar power is not only the fastest growing energy technology in recent history but also one of the cheapest energy sources and the most impactful in terms of reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
A Rice University study featured on the cover of today’s issue of Science describes a way to synthesize formamidinium lead iodide (FAPbI3) ⎯ the type of crystal currently used to make the highest-efficiency perovskite solar cells ⎯ into ultrastable, high-quality photovoltaic films. The overall efficiency of the resulting ...
2024-06-14
A group of researchers from the University of Tartu and international scientists discovered new mechanisms of how stroke occurs by studying changes in mouse and human cells. The study lays the foundation for new, more precise treatment methods and better diagnostics, which could improve cardiovascular health in the future.
One of the authors of the study, a PhD student of Faculty of Medicine of University of Tartu Katyayani Sukhavasi said that affecting people of all ages, every fifth minute, someone suffers a stroke resulting in brain bleeding or ischemia. „Consequently, many people die ...
2024-06-14
Long term thinking and stable, consistent policies are key to improving our nation’s financial prosperity and wellbeing, say experts on The BMJ Commission on the Future of the NHS as they set out their manifesto for a healthier UK.
The BMJ Commission brings together leading experts from medicine and healthcare to identify the key challenges and priorities and make recommendations aimed at ensuring that the vision of the NHS is realised.
Their key pledges of what they would do if they were in government are:
Reaffirming ...
2024-06-14
RIVERSIDE, Calif. -- An international team led by researchers at the University of California, Riverside, has made a significant breakthrough in how to enable and exploit ultra-fast spin behavior in ferromagnets. The research, published in Physical Review Letters and highlighted as an editors’ suggestion, paves the way for ultra-high frequency applications.
Today’s smartphones and computers operate at gigahertz frequencies, a measure of how fast they operate, with scientists working to make them even faster. The new research has found a way to achieve terahertz frequencies using conventional ferromagnets, which ...
2024-06-14
A new report offers lessons for post-pandemic transit policy and planning. Notably, it calls for planners to downplay the role of offices in transit station areas and increase the opportunity for people to live in them. Researchers Arthur C. Nelson and Robert Hibberd published "Transit Station Area Development and Demographic Outcomes (PDF)," updating their longitudinal analysis of the impacts of development near transit stations.
The new report includes a foreword by U.S. Congressman Earl Blumenauer. An excerpt reads:
"In this report, Arthur ...
2024-06-13
New York, NY [June 13, 2024]—Deploying and evaluating a machine learning intervention to improve clinical care and patient outcomes is a key step in moving clinical deterioration models from byte to bedside, according to a June 13 editorial in Critical Care Medicine that comments on a Mount Sinai study published in the same issue. The main study found that hospitalized patients were 43 percent more likely to have their care escalated and significantly less likely to die if their care team received AI-generated alerts signaling adverse changes in their health. ...
2024-06-13
COLLEGE PARK, Md. – The University of Maryland School of Public Health, together with Bowie State University, is expanding its study abroad options for marginalized faculty and students and for students who are Pell Grant recipients, in part due to a grant announced June 13 from the U.S. State Department. The schools were among a select 37 institutions nationwide to receive this 2024 grant.
The award will connect underrepresented faculty and students from both universities with opportunities to study global public health in Rwanda, focusing on countering violent extremism, prevention of emerging tropical infectious diseases, ...
2024-06-13
Corn is one of the planet’s most important crops. It not only provides sweet kernels to flavor many dishes, but it’s also used in oils, as a sweetener syrup, and as a feed crop for livestock. Corn has been bred to maximize its yield on farms around the world.
But what will happen under climate change? Research led by the University of Washington combined climate projections with plant models to determine what combination of traits might be best adapted to future climates. The study used projections of weather and climate across ...
2024-06-13
By Ann Kellett, Texas A&M University School of Public Health
Health practitioners and fitness buffs have long known that regular physical activity offers numerous health benefits, including the prevention of chronic conditions such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes, some cancers and osteoporosis.
In addition, exercise enhances immune function and pain control, reduces fall risk and extends life expectancy. Mental health benefits include improved mood, reduced anxiety and decreased ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Low-sodium alternatives can lead to major health gains in Indonesia
Excess sodium intake and a lack of potassium are major contributing factors towards high blood pressure in Indonesia, prompting calls for low-sodium potassium-rich salt substitutes (LSSS) to be readily available to improve health and curb health costs.