(Press-News.org) A major earthquake 2,500 years ago caused one of the largest rivers on Earth to abruptly change course, according to a new study. The previously undocumented quake rerouted the main channel of the Ganges River in what is now densely populated Bangladesh, which remains vulnerable to big quakes. The study was just published in the journal Nature Communications.
Scientists have documented many river-course changes, called avulsions, including some in response to earthquakes. However, “I don’t think we have ever seen such a big one anywhere,” said study coauthor Michael Steckler, a geophysicist at Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory, which is part of the Columbia Climate School. It could have easily inundated anyone and anything in the wrong place at the wrong time, he said.
Lead author Liz Chamberlain, an assistant professor at the Netherlands’ Wageningen University, said, “It was not previously confirmed that earthquakes could drive avulsion in deltas, especially for an immense river like the Ganges.”
The Ganges rises in the Himalayas and flows for some 1,600 miles, eventually combining with other major rivers including the Brahmaputra and the Meghna to form a labyrinth of waterways that empty into a wide stretch of the Bay of Bengal spanning Bangladesh and India. Together, they form the world’s second-largest river system as measured by discharge. (The Amazon is first.)
Like other rivers that run through major deltas, the Ganges periodically undergoes minor or major course changes without any help from earthquakes. Sediments washed from upstream settle and build up in the channel, until eventually the river bed grows subtly higher than the surrounding flood plain. At some point, the water breaks through and begins constructing a new path for itself. But this does not generally happen all at once—it may take successive floods over years or decades. An earthquake-related avulsion, on the other hand, can occur more or less instantaneously, said Steckler.
In satellite imagery, the authors of the new study spotted what they say was probably the former main channel of the river, some 100 kilometers south of the Bangladeshi capital of Dhaka. This is a low-lying area about 1.5 kilometers wide that can be found intermittently for some 100 kilometers more or less parallel to the current river course. Filled with mud, it frequently floods, and is used mainly for rice cultivation.
Chamberlain and other researchers were exploring this area in 2018 when they came across a freshly dug excavation for a pond that had not yet been filled with water. On one flank, they spotted distinct vertical dikes of light-colored sand cutting up through horizontal layers of mud. This is a well-known feature created by earthquakes: In such watery areas, sustained shaking can pressurize buried layers of sand and inject them upward through overlying mud. The result: literal sand volcanoes, which can erupt at the surface. Called seismites, here, they were 30 or 40 centimeters wide, cutting up through 3 or 4 meters of mud.
Further investigation showed the seismites were oriented in a systematic pattern, suggesting they were all created at the same time. Chemical analyses of sand grains and particles of mud showed that the eruptions and the abandonment and infilling of the channel both took place about 2,500 years ago. Furthermore, there was a similar site some 85 kilometers downstream in the old channel that had filled in with mud at the same time. The authors’ conclusion: This was a big, sudden avulsion triggered by an earthquake, estimated to be magnitude 7 or 8.
The quake could have had one of two possible sources, they say. One is a subduction zone to the south and east, where a huge plate of oceanic crust is shoving itself under Bangladesh, Myanmar and northeastern India. Or it could have come from giant splay faults at the foot of the Himalayas to the north, which are slowly rising because the Indian subcontinent is slowly colliding with the rest of Asia. A 2016 study led by Steckler shows that these zones are now building stress, and could produce earthquakes comparable to the one 2,500 years ago. The last one of this size occurred in 1762, producing a deadly tsunami that traveled up the river to Dhaka. Another may have occurred around 1140 CE.
The 2016 study estimates that a modern recurrence of such a quake could affect 140 million people. “Large earthquakes impact large areas and can have long-lasting economic, social and political effects,” said Syed Humayun Akhter, vice-chancellor of Bangladesh Open University and a coauthor on both studies.
The Ganges is not the only river facing such hazards. Others cradled in tectonically active deltas include China’s Yellow River; Myanmar’s Irrawaddy; the Klamath, San Joaquin and Santa Clara rivers, which flow off the U.S. West Coast; and the Jordan, spanning the borders of Syria, Jordan, the Palestinian West Bank and Israel.
Other coauthors of the new study are at the University of Cologne, Germany; the University of Dhaka; Bangladesh University of Professionals; Noakhali Science and Technology University, Bangladesh; and the University of Salzburg, Austria. The research was funded by the U.S. National Science Foundation.
* * * * *
Scientist contacts:
Michael Steckler steckler@ldeo.columbia.edu
Liz Chamberlain liz.chamberlain@wur.nl
More information: Columbia Climate School senior editor, science news kevin Krajick kkrajick@climate.columbia.edu +1 917-361-7766
END
A pioneering study published today in the journal Nature Aging has unveiled significant heterogeneity in the risk factors affecting healthy aging in Latin America and emphasised the limitations of current models of brain health, which are primarily based on data from high-income countries. The research was conducted by researchers from Trinity College Dublin (Ireland), and by colleagues in Universidad Adolfo Ibanez (Chile) and Pontificia Universidad Javeriana (Colombia) among others.
The study developed a metanalytical approach with 146,000 participants and findings emphasise how current models of brain health may not apply ...
A new thesis at Uppsala University questions the traditional view of stress-induced exhaustion disorder. A new model is proposed in its place that puts more focus on meaningfulness rather than recovery.
“There are no established evidence-based models for the psychological treatment of stress-induced exhaustion disorder. The concepts of ‘recovery’ and ‘stress’ are so widely accepted in our current era that it is difficult to examine them critically. It’s easy to think that patients with stress-related exhaustion should prioritise rest and relaxation, but an overly one-sided focus on recovery ...
ANN ARBOR, Mich. – Many bedtime battles stem from children’s after dark worries, suggests a new national poll.
And while most families have bedtime rituals to help their little ones ease into nighttime, many rely on strategies that may increase sleep challenges long term, according to the University of Michigan Health C.S. Mott Children’s Hospital National Poll on Children’s Health.
Overall, one in four parents describe getting their young child to bed as difficult – and these parents are less likely to have a bedtime routine, more likely to leave on a video or TV show, and more likely to stay with their child until they’re ...
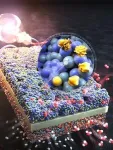
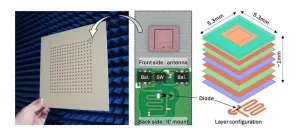
A novel 256-element wirelessly powered transceiver array for non-line-of-sight 5G communication, featuring efficient wireless power transmission and high-power conversion efficiency, has been designed by scientists at Tokyo Tech. The innovative design can enhance the 5G network coverage even to places with link blockage, improving flexibility and coverage area, and potentially making high-speed, low-latency communication more accessible.
Millimeter wave 5G communication, which uses extremely high-frequency radio signals (24 to 100 GHz), is a promising technology for next-generation wireless ...
Newfound evidence reveals that the upsurge of the exotic Nile perch in Lake Victoria had long-lasting effects on the genetic diversity of various local cichlid species, report scientists from Tokyo Tech. Through large-scale comparative genomic analyses, the researchers found concrete proof in the collective genome of multiple species that this artificially introduced perch decimated many local fish populations, causing a 'bottleneck effect.'
The careless introduction of exotic species by humans into ecosystems can lead to truly catastrophic results, as has been ...
With wildfires becoming more frequent and extensive in Canada, it’s important for people to understand the health risks of wildfire smoke. An article in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) https://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.240135 aims to provide information for clinicians and people in Canada as wildfire season is upon us.
"As climate change causes more frequent and severe wildfires, wildfire smoke becomes a larger health problem,” says Dr. Mehdi Aloosh, assistant professor, Health Research Methods, Evidence, and Impact, McMaster University, Hamilton, and medical officer of health of Windsor–Essex County, Ontario. “Communities need ...
Children across the United States who identify as LGBTQ+ say the sexual health education curricula they receive is leaving them without essential information to make informed decisions about their sexual health – which could force them to seek potentially dangerous advice elsewhere.
The results of a new, national, peer-reviewed survey, show that these young people — aged 13 to 17 — believe crucial topics surrounding sexual orientation and gender identity are being omitted from sexual health education programs.
Experts who led the study – published today in The Journal of Sex Research, as people around the ...
WASHINGTON – A rigorous, comprehensive synthesis of evidence from 62 studies related to the use of oral nicotine pouches by Georgetown University’s Lombardi Comprehensive Cancer Center scientists and colleagues provides a much-needed assessment of how these products could lead to potential harmful consequences if used by young people.
Oral nicotine pouches were first introduced in the U.S. in the past decade and are pre-portioned white granular packets containing nicotine placed between the gums and lips, marketed as tobacco-free, and are sold in various flavors and nicotine strengths.
The findings appeared ...
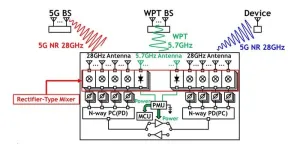
A recently developed wirelessly powered 5G relay could accelerate the development of smart factories, report scientists from Tokyo Tech. By adopting a lower operating frequency for wireless power transfer, the proposed relay design solves many of the current limitations, including range and efficiency. In turn, this allows for a more versatile and widespread arrangement of sensors and transceivers in industrial settings.
One of the hallmarks of the Information Age is the transformation of industries towards a greater flow of ...
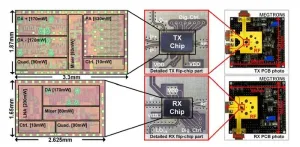
A new D-band CMOS transceiver chipset with 56 GHz signal-chain bandwidth achieves the highest transmission speed of 640 Gbps for a wireless device realized with integrated circuits, as reported by researchers from Tokyo Tech and National Institute of Information and Communications Technology. The proposed chipset is highly promising for the next generation of wireless systems.
To achieve faster speeds and handle increasing data traffic, wireless systems are operating in higher millimeter-wave frequency bands. Current high-band 5G systems offer speeds as high as 10 Gbps and operate in frequency bands between 24–47 GHz. The next generation ...