(Press-News.org) Corvallis, OR — A study published today in the journal BioScience sheds light on the importance of gray wolves in western United States. Led by William Ripple, a scientist at Oregon State University and the Conservation Biology Institute, the research delves into the implications of large predator absence on plant and animal communities, and ecosystem functions. It calls attention to “shifting baselines” wherein increasingly degraded conditions are viewed as reflecting the historical state of a system.
"By the 1930s, wolves were largely absent from the American West, including its national parks. Most published ecological research from this region occurred after the extirpation of wolves," explains Ripple. "This situation underscores the potential impact of shifting baselines on our understanding of plant community succession, animal community dynamics, and ecosystem functions."
Age structure data for deciduous trees reveal substantial ecological impacts of elk and other ungulates following the removal of gray wolves from Yellowstone, Olympic, and Wind Cave National Parks. This has led to declines in long-term tree recruitment, influencing plant communities and ecological processes.
The study highlights the necessity of characterizing historical context and reference conditions when exploring areas where large predators, like wolves, are either absent, functionally extinct, or persist in reduced densities. The authors note that such areas likely occur in many regions of the world as a result of the widespread loss of large predators. Where applicable, the authors recommend that researchers include a discussion of how the presence or absence of large predators may have influenced their results and conclusions in future ecological studies in national parks.
"In addition to the loss or displacement of large predators, there may be other potential anthropogenic legacies within national parks that should be considered, including fire suppression, invasion by exotic plants and animals, and overgrazing by livestock," adds Dr. Robert Beschta, co-author of the study and emeritus professor at Oregon State University.
To address the effects of predator loss and other potential legacy factors, the study suggests that researchers investigate park archives to exploit historical data and information. National park archives can provide valuable insights into the history of predators and their prey, enabling scientists to discern among competing explanations for shifting ecological baselines.
"Studying altered ecosystems without recognizing how or why the system has changed over time since the absence of a large predator could have serious implications for wildlife management, biodiversity conservation, and ecosystem restoration," emphasizes Ripple.
The research underscores the importance of integrating historical context into ecological studies to provide a more comprehensive understanding of ecosystem dynamics. By acknowledging the historical presence of large predators and other anthropogenic legacies, as well as their potential ecosystem effects, researchers can contribute to more effective conservation and management strategies in national parks and beyond.
Recently, a coalition comprising nearly twelve conservation organizations initiated legal action against the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service and the U.S. Department of the Interior. Their aim is to reinstate safeguards for gray wolves in Montana and Idaho, contending that the states' forceful hunting strategies endanger these wolf populations.
The research has implications for the long-term conservation of wolves and other large predators, including current gray wolf management and litigation in the West. "We hope our study will be of use to both conservation organizations and government agencies in identifying ecosystem management goals," added Ripple.
END
New research illuminates the ecological importance of gray wolves in the American West
2024-06-19
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Forgotten predators: Ecological understanding is often marred by the exclusion of extirpated species
2024-06-19
New research published in the journal BioScience describes how the removal large predators is often unrecognized in ecological scholarship, creating an issue of "shifting baselines," with profound implications for restoration efforts.
A team led by researchers from Oregon State University, including co-lead authors William J. Ripple and Christopher Wolf, reviewed 96 published studies from 1955 to 2021 that were conducted in 11 national parks where gray wolves had been extirpated. Their analysis found that ...
Inclusive care: Strategies to support infant feeding for parents with disabilities through WIC
2024-06-19
Philadelphia, June 19, 2024 – Infant feeding, involving breastfeeding, formula feeding, and the introduction of solid foods, is crucial for parenting. Pregnant and postpartum individuals with intellectual and developmental disabilities face challenges in infant feeding compared to parents without intellectual and developmental disabilities, often due to ableism and inaccessible care. The Special Supplemental Nutrition Program for Women, Infants, and Children (WIC) program, a federal nutrition initiative, can address these disparities by offering inclusive and accessible support and counseling.
A recent research article in the Journal of Nutrition Education and Behavior, published ...
Computer modelling shows where Arizona’s winter precipitation originates
2024-06-19
The Sun Corridor in Arizona in the semi-arid Southwestern U.S. is a land of seeming unlimited growth that is constantly colliding with physical constraints. It is mountainous but also home to a large valley that includes one of the fastest growing metropolitan areas in the U.S.
While experiencing explosive growth, the Phoenix metropolitan area faces an uncertain future due to prolonged drought and fluctuating seasonal water availability. Planning for the future, especially in terms of water, ...
STUDY: Sourcing genomically diverse seedlings to create climate-change resilient forests brings optimism for partnerships between science and practice
2024-06-19
The roots of the project formed during a CASRI conference in 2018 when experts from various organizations learned about red spruce genetic research being conducted by Keller’s lab and collaborators at University of Maryland with funding by the National Science Foundation. The group saw an opportunity to join forces to take an on-the-ground approach to utilizing the genetic data for red spruce restoration. In 2019, funding from the Wildlife Conservation Society’s Climate Adaptation Fund enabled this group to pursue science-informed restoration at scale.
“Science-informed ...
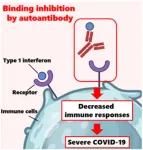
Could auto-antibodies be linked to severe COVID-19?
2024-06-19
Even though COVID-19 manifests as a mild and short-lived disease in most people, some suffer extremely severe symptoms; in the worst cases, these patients die due to complications such as respiratory failure or thromboembolism. It is well-known that factors such as age and underlying medical conditions like diabetes or immunodeficiencies increase vulnerability to severe COVID-19. However, some patients still experience severe COVID-19 without any apparent reason.
One possible explanation may lie in auto-antibodies, which are antibodies that erroneously target specific proteins produced by one’s own body. In normal circumstances, type I interferons ...
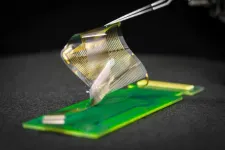
Breakthrough UC San Diego brain recording device receives FDA approval for a clinical trial
2024-06-19
Video: https://youtu.be/-7ggs6e2UXI?si=lnFqEscjJh-91n64
B-roll: https://youtu.be/pvNBa733ICw?si=DotUuQkxVgMQ0jY7
The Federal Drug Administration approved a clinical trial to test the effectiveness of an electronic grid that records brain activity during surgery, developed by engineers at the University of California San Diego.
The device with nanoscale sensors records electrical signals directly from the surface of the human brain in record-breaking detail. The grid’s breakthrough resolution could provide better guidance for planning and performing surgeries to remove brain tumors and treat drug-resistant epilepsy.
The grid’s higher resolution ...
A study led by ISGlobal and IDIAPJGol recommends strengthening immunity against COVID-19 in people with cancer
2024-06-19
Researchers from the Institut d’Investigació en Atenció Primària Jordi Gol (IDIAPJGol) and the Barcelona Institute for Global Health (ISGlobal), a center promoted by “la Caixa” Foundation, have led a study on the effectiveness of vaccines against COVID-19 among cancer patients in Catalonia. The research, published in the journal Nature Communications, recommends administering additional doses of the vaccine among this risk population.
Cancer patients are at increased risk of death from COVID-19, especially ...
A railroad of cells
2024-06-19
Looking under the microscope, a group of cells slowly moves forward in a line, like a train on the tracks. The cells navigate through complex environments. A new approach by researchers involving the Institute of Science and Technology Austria (ISTA) now shows how they do this and how they interact with each other. The experimental observations and the following mathematical concept are published in Nature Physics.
The majority of the cells in the human body cannot move. Some specific ones, however, can go to different places. For example, in wound healing, cells move through the body to repair damaged tissue. They sometimes ...
Much of the Nord Stream gas remained in the sea
2024-06-19
Much of the methane released into the southern Baltic Sea from the Nord Stream gas pipeline has remained in the water. This is shown by measurements taken by researchers from the University of Gothenburg.
At the end of September 2022, the Nord Stream gas pipeline on the bottom of the Baltic Sea exploded east of Bornholm and one of the largest unnatural methane gas emissions ever was a fact. The methane gas from the pipeline created large bubbles at the water surface and measurements showed elevated levels of methane in the atmosphere.
Expedition ...
Dwindling arousal levels during brain scans have been distorting fMRI results, study shows
2024-06-19
In a new study, investigators from McLean Hospital (a member of Mass General Brigham), Harvard Medical School and the National Institute on Drug Abuse – Intramural Research Program (NIDA-IRP) discovered that the tendency of people’s arousal to wane over the course of brain scans has been distorting the brain connection maps produced by functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI). The team found that as people’s arousal levels dwindle during an fMRI, such as if they become more relaxed and sleepy, changes in breathing and heart rates alter blood oxygen levels in the ...